Contents
Not all pregnancies are normal. Sometimes, at the very beginning, the expectant mother finds out that the next few months will mean lying down for her and taking special care of herself and her baby. Sometimes during one of the first ultrasound examinations, the doctor diagnoses abnormalities in the child’s development and orders additional tests. One of them is amniocentesis. What is it and how much does it cost?
Amniocentesis – what is this test?
Amniocentesis is one of the invasive prenatal tests. It is performed after the 15th week of pregnancy. Amniocentesis is a procedure that involves taking a small sample of amniotic fluid for examination. It is the fluid that surrounds the fetus in a pregnant woman. Amniotic fluid is a clear, pale yellow fluid that:
- protects the fetus against injuries,
- protects the fetus against infection,
- allows the child to properly move and develop,
- helps to control the temperature of the fetus.
Along with various enzymes, proteins, hormones, and other substances, the amniotic fluid contains the cells exfoliated by the fetus. These cells possess genetic information that can be used to diagnose genetic disorders and neural tube defects such as spina bifida. Amniocentesis can also be performed to check for inherited gene defects and metabolic disorders based on family history.
The amniotic fluid also contains other substances that provide information about the fetus. This procedure can be performed in late pregnancy to check the condition of the fetus and diagnose fetal health problems such as infection. If the baby is suspected to be born early, amniocentesis may be performed to check the maturity of the fetal lungs.
This test also allows you to determine the sex of the child with 100% certainty, and also allows you to perform a paternity test.
Read also: Diseases detected in the womb – clefts, hydrocephalus, heart defects. Diagnostics and prenatal tests indicated
Amniocentesis – course
Amniocentesis is the most common invasive prenatal test. The examination can diagnose or rule out genetic birth defects in a child. The exact date of the examination is determined by the doctor. However, it should be remembered that the earlier the examination is performed, the greater the risk of complications.
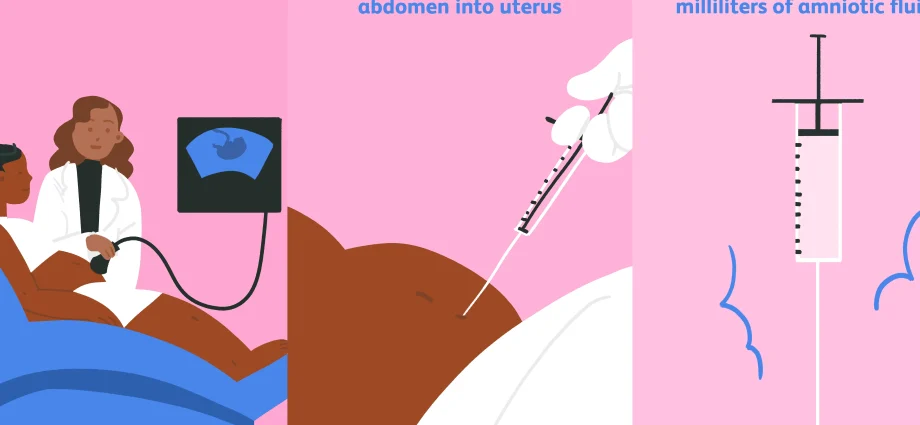
During amniocentesis, sterile conditions are maintained, and the examination itself is performed under ultrasound supervision. Thanks to this, the examination is safe for the developing baby, as the doctor chooses the place furthest from the location of the fetus.
The first step is to administer local anesthesia to the mother’s abdomen. Then the injection site is disinfected. During amniocentesis, the doctor takes approx. 15 ml of amniotic fluid with a sterile needle. A dressing is placed over the puncture site. The entire test takes a few minutes.
The fluid sample taken contains fetal cells which are used to grow more of them. It contains cells from the baby’s skin, digestive and urogenital systems. When the cells multiply, they will be used to determine the so-called karyotype, i.e. the set of baby’s chromosomes. The results are available after approx. 2-3 weeks.
Amniocentesis – indications
It should be remembered that amniocentesis is not a standard prophylactic examination performed in every pregnancy. As it carries a certain risk of complications, it should be performed only in justified cases. The most common indication for amniocentesis is incorrect results from one of the previously performed tests Pregnancy ultrasound.
If, during the ultrasound, the doctor notices abnormalities in the child’s development, such as abnormal dimensions of the limbs or nuchal translucency, the absence of the nasal bone or other organs of the child, he will certainly recommend amniocentesis. Other indications include:
- mother’s age over 35;
- the presence of genetic diseases in the family of the child’s mother or father;
- the occurrence of genetic diseases in previously born children;
- the occurrence of metabolic diseases or defects of the central nervous system in previously born children;
- abnormal triple test result.
It is worth knowing that amniocentesis is also performed when for some reason it is necessary to establish paternity before the child is born.
Read: Prenatal examination – indications, course, price. What is the purpose of prenatal testing?
Amniocentesis – what diseases does it detect?
Amniocentesis can identify several hundred genetic disorders, including some of the most common:
- almost all chromosomal disorders, including Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome
- other genetic disorders such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, Tay-Sachs disease, and Huntington’s disease
- neural tube defects such as spina bifida and anencephaly. More than 95 percent of the women who are at high risk who undergo amniocentesis test negative.
See: Scientists have discovered a cure for Huntington’s disease
Amniocentesis – complications
In 4 percent women who underwent amniocentesis develop complications. The most common are damage to the placenta or umbilical cord, bleeding from the mother’s genital tract or the bleeding of the child, puncture of the child’s body, rupture of the fetal bladder, intrauterine infection or drainage of amniotic fluid.
At worst, amniocentesis could result in a miscarriage. However, this situation occurs in 0,5-1 percent. cases. In order to protect yourself from any complications and complications after amniocentesis, it is worth choosing an experienced doctor for the examination.
Check what diseases are most often responsible for a miscarriage
Amniocentesis – reimbursement
If the patient belongs to the risk group of giving birth to a sick child, i.e. she is at least 35 years old, has previously given birth to a sick child, there was a genetic disease in her or the child’s father’s family, or if the results of the tests performed so far have raised the doctor’s concern, the amniocentesis will be reimbursed by the National Health Fund. Otherwise, if the expectant mother wants to perform the test but does not belong to the risk group, she will have to pay PLN 1,3 thousand for the test. up to 2 zloty.
Amniocentesis – is it worth it?
The benefits of amniocentesis apply to both the baby and the mother and father. The statistics clearly show that in most cases the risk of genetic defects in children is quite low and the examination only excludes the occurrence of genetic defects. Therefore, amniocentesis provides a sense of security and peace, which also affects the developing baby.
Conversely, if the amniocentesis confirms the child’s illness, parents have time to get used to what will happen after the baby is born. They can get used to the thought of the baby’s illness and reorganize themselves during the treatment and care of the newborn.
It is also worth noting that some defects can be treated while still in the womb. Doctors can also plan and prepare for your birth properly so that they can give your baby specialist help right after birth.