Contents
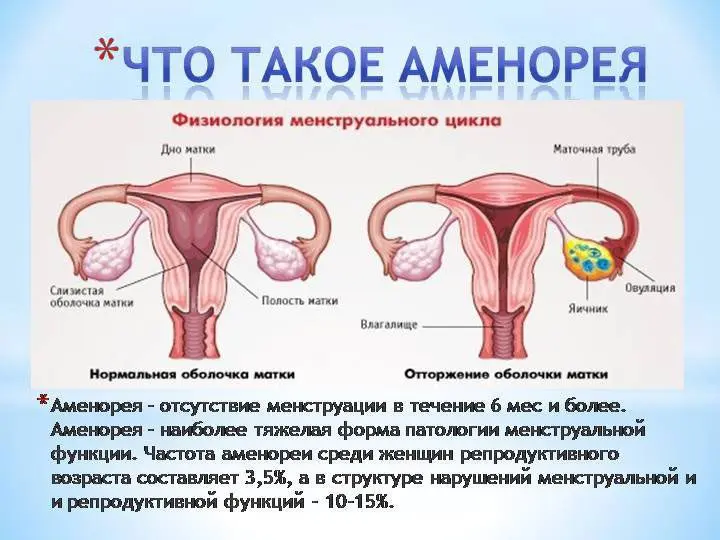
Amenorrhea is the absence of menstruation in a woman of childbearing age. Normally, menstruation should come on certain dates, without delays and failures. They begin at the age of 12-16 and persist until the end of menopause. Of course, menstruation somewhat worsens the quality of life of a woman. She does not have the opportunity to engage in active sports or go to the pool. At the same time, the absence of menstruation for no apparent reason may indicate a serious violation in the body. Amenorrhea is a common problem affecting about 3,5% of women.
When is amenorrhea normal?

Menstruation begins at the age of 12-16 years, until this moment its absence is normal. The female reproductive system is at rest.
During menopause, the absence of menstruation is also a variant of the norm. Menopause occurs in the period of 49-52 years. These are average values. You should focus on the age at which menopause occurred in women in the family.
Breastfeeding and amenorrhea are two normal phenomena that should be combined with each other. When a woman breastfeeds her baby, she produces hormones that prevent the maturation of the egg. A similar situation occurs during pregnancy. The main purpose of the egg fulfilled – the woman conceived a child. Until the moment of his birth, other eggs will not be needed, so they are at rest, which means that the woman does not have her period.
Degrees of amenorrhea
There are 3 degrees of amenorrhea:
Mild amenorrhea. Menstruation is absent during the year. During this period, it will not be difficult to find the right treatment.
The average degree of amenorrhea. Menstruation does not occur within 1-3 years.
Severe amenorrhea. No menses for more than 3 years.
Amenorrhea can be primary or secondary. It is very important to determine what kind of violation develops in the patient, since the features of treatment depend on it.
Primary amenorrhea
If a woman or girl has never had a period before, and it does not occur on time, then they speak of primary amenorrhea. Normally, menstruation should begin before the age of 16. Their absence before this age should alert parents.
Primary amenorrhea with delayed puberty
Primary amenorrhea with delayed puberty can occur for the following reasons:
Malformations of the organs of the reproductive system. Genetic disorders. Gonadal dysgenesis is a chromosomal abnormality that a child has from birth. They lead to the fact that the genitals of the girl develop defectively. Normally, in a female child, the set of chromosomes is represented as “46 XX”. However, sometimes mutations occur, for example, “46 XO” and others. This is due to improper division of chromosomes during fetal development.
Such pathologies are manifested by the absence of menstruation, disturbances in the structure and functioning of internal organs, and external developmental anomalies. The girls are small (less than 150 cm), their neck is short, covered with folds, the bite is often disturbed, strabismus, deformity of the elbow and knee joints occur. Ultrasound examination allows visualization of small ovaries in which there is no glandular tissue. They do not contain eggs, their structure is represented by compounds resembling scar tissue. The uterus in such patients is underdeveloped, often the organ does not have a cavity.
In women with such disorders, menstruation is absent, they cannot become pregnant. An anomaly occurs in 1 girl out of 12 thousand newborns.
To accurately establish the diagnosis, you will need to consult a geneticist. In the future, the woman will need lifelong treatment with taking drugs that replace her own hormones. Most often, patients are prescribed Femoston. Since prolonged hormone therapy can cause damage to liver cells, patients are prescribed hepatoprotectors (Heptor, Heptral, Essentiale) every 6 months.
STF This is testicular feminization syndrome. The disorder is characterized by a failure in the metabolism and production of testosterone during fetal development. The girl who was born has all the female characteristics. However, there is no area of pigmentation around the nipples, no hair grows under the armpits and on the pubis.
An examination of the internal genital organs reveals a short vagina that ends blindly. The patient has no uterus, cervix and ovaries. Instead, a woman grows testes (male reproductive organs), but they do not produce sex hormones. The absence of female genital organs leads to the fact that menstruation, and hence pregnancy, is impossible. There is such a malformation in 1 out of 15 newborn girls.
Therapy is reduced to the removal of the testes by surgery. This must be done for the reason that these organs often become the basis for the development of a cancerous tumor. The operation is carried out after the girl reaches the age of 16, when her breasts and body have formed. After that, the patient is prescribed femosterone for the rest of her life. Vaginoplasty allows a woman to have a normal sex life.
Violations in the work of the GGS. The hypothalamic-pituitary system is responsible for the production of hormones and other substances that are needed to start menstruation and the normal course of metabolic processes in general.
Disruptions in the work of these systems can occur due to poor-quality nutrition that the child receives, with chronic infectious and non-infectious diseases, against the background of prolonged intoxication of the body. Low hemoglobin levels also often cause girls to miss periods during puberty.
If a teenager begins to eat right, gain the missing body weight, or lose weight, then menstruation will stabilize on its own, without any therapy.
In some cases, delayed sexual development occurs due to the peculiarities of the constitution of the girl. Often a similar situation is observed among the people of Karelia, the Nenets Autonomous Okrug, among the inhabitants of Chukotka. In this case, the absence of menstruation up to 16 years of age and older is a variant of the norm, but provided that other causes of amenorrhea have been excluded. Girls with such a problem are shown the passage of an ultrasound of the genital organs, as well as an x-ray of the bones of the hand, forearm and wrist. If the growth zones in them are normal, then there is no cause for concern, and menstruation will begin soon.
Diseases of the hypothalamic-pituitary system with its organic damage. Amenorrhea and other malfunctions in the functioning of the reproductive system occur due to congenital tumors that are located in the pituitary gland. It is not difficult to detect them during an x-ray or MRI. After the operation to remove the neoplasm, the menstrual function stabilizes.
Primary amenorrhea without delayed puberty

If a girl does not have menstruation, but secondary sexual characteristics develop as expected, then the cause of this is most often gynatresia or uterine aplasia. These pathologies originate even while the fetus is in the womb. With gynathresia, a girl will have part of the vagina closed, or the hymen will be completely closed. Treatment is operative. In most cases, it is successful. If the operation is not carried out before the onset of menstruation, then the menstrual blood will have nowhere to pour out. Therefore, it will not be possible to do without surgical intervention.
Aplasia of the uterus is its absence. Often the girl has an underdevelopment of the vagina, defects of the kidneys and organs of the urinary system. The ovaries function as expected, the level of hormones remains normal. In this case, the uterus will be represented by a stripless neoplasm, which is often not detected at all. Such women cannot become a mother, menstruation is impossible for them. However, the operation allows them to have a normal sex life.
Such disorders, caused by malformations of intrauterine development, are often found only during the puberty of a girl. Medical assistance allows girls with identified pathologies to adapt as much as possible to the natural needs of a growing organism and live fully. However, it is often not possible to completely cope with congenital developmental anomalies.
Secondary amenorrhea
Intrauterine pathologies

Many surgeries performed on the uterus have a negative impact on the health of a woman. Dangerous in this regard are intrauterine abortions, curettage, hysteroscopy, removal of polyps.
Such manipulations can lead to a significant thinning of the uterine wall, which affects the functioning of the organ. During the natural cycle, the endometrium cannot fully grow, so when the time comes for the next menstruation, there is simply nothing to reject. Such a violation does not develop by itself. Menstruation becomes less abundant over time, after which they stop going at all. If a woman has inflammation of the internal genital organs in parallel, then the pathology acquires a severe course.
Sometimes after the operation there is an infection of the cervical canal. You can cope with the pathology in an operative way.
Adhesions may be the result of an abortion or other traumatic procedure. They grow in the uterus, filling it from the inside.
All these complications lead to the fact that it will be difficult for a woman to get pregnant, and sometimes impossible.
Treatment is reduced to hysteroscopy, cutting adhesions, the introduction of special drugs that prevent their re-growth. To cope with the violation, hyaluronic acid preparations can be used.
Violations in the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary system

Amenorrhea associated with low body weight. This amenorrhea most often occurs in adolescent girls. Many of them, in pursuit of imaginary beauty, begin to lose weight a lot. This leads to the fact that the fat layer completely disappears. The body perceives menstruation as a loss of blood and energy, so it stops producing hormones so that the follicles continue to mature.
To cope with the problem, you need to start eating right and gain weight. Be sure to prescribe vitamins to the girl.
Amenorrhea of psychogenic genesis. If a girl is experiencing a strong emotional shock, then her periods may stop. So, during the war, women who sent their husbands and sons to the front often lacked menstruation.
To cope with the problem, you need to minimize the impact of stress on the body. Hormones are most often not used in such situations. If the stress does not go away for a long time, you should consult a specialist, since the absence of menstruation can cause an early menopause.
Ovarian hyperinhibition syndrome
OHTS develops after a woman has taken hormonal drugs for a long time, including:
Oral contraceptives.
Gonado-releasing hormone agonists (Goserelin, Buserelin).
Gestagens (Visanna).
Most often, after some time after discontinuation of the drug, menstruation returns to normal on its own. If menstruation does not occur 2-3 months after the end of taking hormonal drugs, then you need to consult a doctor. Moreover, the lower the body weight of a woman, the higher the likelihood of developing amenorrhea.
Patients will be assigned an analysis to determine the level of prolactin. If there are no failures, then Clomiphene citrate can be used to restore menstruation. This drug stimulates ovulation. It is used within 1-4 months. When the situation stabilizes, the drug is canceled.
Bromocriptine is prescribed to patients with high prolactin levels. The drug is taken until the hormone levels drop to 5430 mIU and below.
Disorders of the hypothalamic-pituitary system of organic nature
A delay in menstruation against the background of a tumor growing in the brain can happen, but this does not happen often. Growing neoplasms put pressure on the pituitary and hypothalamus, which entails a whole cascade of reactions: hormonal imbalance occurs, menstruation stops. The only way to deal with the disease is through surgery. After removal of the tumor, menstruation resumes. This happens after six months or a year.
Sheehan’s syndrome is a vascular spasm or hemorrhage in the pituitary gland. Such a violation most often occurs in women after childbirth, when the pregnancy itself was complicated by preeclampsia. Nursing mothers may not notice the absence of menstruation, as amenorrhea is covered by lactation. However, after the refusal of breastfeeding, menstruation does not begin. After 2 months of their absence, it is necessary to contact a specialist.
If the doctor detects Sheehan’s syndrome, he will prescribe the patient Metipred or Prednisolone, thyroid hormones, or hormone replacement therapy with Angeliq, Divina, Femoston. You should not take drugs on your own, since it will not be possible to restore the cycle without understanding the cause of amenorrhea, but it is quite possible to gain excess weight.
Empty Turkish Saddle Syndrome
The Turkish saddle is located in the brain near the pituitary gland. It becomes empty when the pituitary gland is under pressure for a long time and atrophies. Frequent pregnancies or complex labor activity can provoke a similar situation. Treatment is carried out in a similar way as the treatment of Sheehan’s syndrome.
Ovarian amenorrhea
Sometimes the cause of amenorrhea is a malfunction of the ovaries. In this case, the hormonal system as a whole will function properly.
With resistant ovary syndrome, these organs of the reproductive system simply stop responding to stimulation by sex hormones. The disorder develops in women under 36 years of age. Often a similar situation can be traced in a grandmother, mother, daughter, that is, it is of a family nature. You can cope with the problem only with the use of hormonal preparations of combined action. A woman cannot give birth on her own. IVF will be required using a donor egg.
Premature ovarian failure syndrome leads to the fact that the eggs stop being produced and the patient develops menopause. Moreover, this can happen at an early age (up to 43 years). This syndrome can be caused by severe infections (flu, rubella, mumps, measles), or undergoing treatment for cancerous tumors.
Other types of amenorrhea

false amenorrhea. This type can be attributed, for example, when the process of menstruation proceeds normally, but, for one reason or another, the blood does not leave the body. This can be, for example, some kind of congenital pathology, as well as deviations acquired in the process of life. A fairly striking example of this is the overgrowth of the hymen or vagina. Here we are talking about acquired mechanical obstacles. Some deviations can only be diagnosed with the help of ultrasound, in any case, the word “mechanical” is decisive here.
True amenorrhea – the absence of a monthly cycle in girls. Here, the absence of the menstrual cycle is manifested, but without visible hormonal signs and changes in the reproductive system. The ability of a woman to become pregnant is completely lost.
Physiological amenorrhea called the absence of a cycle due to various age deviations. Deviations can occur both during the maturation of the body, and at its end, the disease can manifest itself and end by itself. We are not talking about the disease here, as this is completely normal. For example, some women lose the ability to menstruate while breastfeeding. Or after pregnancy, while the body is recovering.
Pathological amenorrhea This is the most serious type of amenorrhea. Here we are talking about a violation in the body. In this case, the reproductive opportunity may be completely lost. Most often this happens in those girls who have never had a monthly cycle, that is, in young women or, conversely, in women in middle age. Violations are both functional and organic in nature.
Diagnosis of amenorrhea
Diagnosis of amenorrhea begins with the collection of anamnesis and examination of the patient. The doctor necessarily finds out the state of women’s health of the mother. This will allow you to trace the family history of the disease. It is important to clarify exactly when a woman’s period began, whether she was exposed to radiation, or whether she is overweight. If the patient suffers from other chronic diseases (cardiovascular pathologies, obesity, joint diseases), she should inform the doctor about this.
The doctor draws attention to the woman’s body type, hair growth, the degree of development of the mammary glands and other characteristics of sexual health.
The next stage of diagnosis is the examination of the patient on the gynecological chair. The doctor assesses the condition of the pelvis, external genitalia. If the girl is a virgin, then examination using mirrors is not practiced.
Ultrasound of the genital organs and the mammary gland provides information about the size of the organs, their functioning, and the maturation of the ovarian follicles. The study allows to identify cysts and tumor neoplasms.
Blood sampling for hormones is mandatory. Determine the level of thyroid hormones (T4 and TSH), as well as sex hormones (FSH, LH, DHEA, AMH, prolactin, testosterone, etc.).
A woman may need to consult narrow specialists: an oncologist, geneticist, endocrinologist, neurologist, neurosurgeon, nutritionist, pediatrician. Ultrasound of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland, MRI of the brain, X-ray of the skull are performed. All these studies in the complex are rarely prescribed. The doctor chooses certain diagnostic techniques that are needed to confirm the diagnosis and find out the cause of amenorrhea.
Treatment of amenorrhea

Medicines that can be used to treat amenorrhea include:
Preparations containing estrogens: Folliculin, Estrogel, Divigel, etc. They are prescribed in a situation where amenorrhea develops against a background of estrogen deficiency.
Progestogens: Utrozhestan, Prajisan, Duphaston, Norethistron. They are prescribed for deficiency of hormones of the second phase of the cycle, or gestagens.
Antiestrogens: Clomiphene citart. This drug is used to stimulate ovulation.
Combined hormones: Femoston, Angelik, Divina. They are prescribed to restore ovarian function
Thyroid hormones: L-thyroxine, Euthyrox.
Glucocorticosteroids: Prednisolone, Metipred. They are prescribed to restore adrenal function.
Bromkriptin (Parlodel). This drug lowers prolactin levels.
The operation is prescribed for gynecological pathologies, as well as for brain damage by tumor neoplasms.
Amenorrhea is a serious disorder in the body that should not be ignored. If a woman of childbearing age does not have periods, then she needs to see a doctor and receive treatment.









