Contents
Many men around the world face the problem of hair loss. Despite the fact that it is the representatives of the strong half of humanity who are most susceptible to alopecia, this pathology is not of an exclusive gender nature. Women are also prone to baldness, but due to the completely different hormonal regulation of the female body, hair loss does not become such a frequent occurrence for them. In this case, we can talk more about an exception to the rule. Alopecia is more of a male disease: according to statistics, the ratio of women and men suffering from baldness is approximately 1:25.
With age, hair thins in both men and women. This can be considered a variant of the physiological norm (unless, of course, one or another pathological process becomes the cause of alopecia). If the hair is rapidly “leaving” the head of a young man, this is all the more worth paying close attention to.
Causes of male pattern baldness
Androgenetic alopecia

Men, as a rule, take care of their appearance no less than women (although they do it in a slightly different way), so baldness, and even earlier, can be a real blow for them. Meanwhile, even early baldness does not always indicate the presence of pathological changes in the body. In the vast majority of cases, there is a so-called androgenic alopecia (about 94-96% of all cases of alopecia). In this case, we are talking about a completely normal, genetically determined phenomenon.
In the normal state, the hair follicle, responsible for the synthesis of fibers and hair structures, has sufficient activity. However, there is a hormone that can suppress the work of hair follicles, and, consequently, reduce their functionality. We are talking about a typical male hormone like dihydrotestosterone. In each man, the level of this substance in the blood, as well as the activity of its secretion, differs significantly. Therefore, some have a chance to maintain thick hair without much effort until old age, while others are more likely to go bald even in the early period (20-30 years). The status of the endocrine system directly depends on the hereditary factor. Therefore, in this case, we can talk about physiologically normal hereditary baldness.
This process is not one-time. Initially, thinning of the hairline is observed (a “bald spot” is formed). The hair at the site of the lesion loses its color, becomes thinner and short. Over time, the process affects other bulbs. The terms of complete baldness vary, on average, we are talking about 8-20 years. Action should be taken in the first few years after a problem is discovered. Otherwise, the hair follicles will “heal” and the bulb will finally lose its functions.
In women, the hormone dihydrotestosterone is also present, but its concentration is so low that it cannot damage the bulbs.
Genetically determined baldness
If androgenetic alopecia is only indirectly caused by a genetic factor (after all, only a predisposition to baldness is transmitted due to the peculiarities of the endocrine system), then in this case the hereditary factor rises to its full height. There is a specific gene responsible for hair loss. It is referred to as SOX 21 and occurs in both men and women. Its inheritance is sex-linked (just remember the basics of biology). However, the male does not have a second X chromosome, and the risk of expressing the gene is much higher.
The foregoing does not mean that in the presence of a gene (even an active one), a man will certainly go bald. You can only talk about the probability, but the probability is great.
Symptomatic baldness
A rarer case is when the hair begins to fall out due to the development of a particular pathological process in the body or due to the influence of an unfavorable factor.
Most often this group of reasons includes:
Poisoning with poisons and other biologically active substances;
Exposure to radiation (for example, during radiation therapy of cancer patients);
Taking certain drugs (For example, drugs used for chemotherapy selectively affect only active cells. But the cells that synthesize hair tissues are precisely such, and therefore receive damage on a par with cancer cells);
Deficiency of vitamins and microelements (often with this cause of baldness there are those who are on a diet, especially on a strict one);
stress;
Diseases of a hereditary nature.
Symptomatic or pathologically caused baldness is typical for both men and women equally.
Alopecia areata
It occurs relatively rarely (no more than 3% of the total number of clinical cases). With alopecia areata, the hair does not fall out completely. The process affects small areas (usually round). The cause of focal alopecia lies in the damage to the bulbs by the person’s own immune system. Focal lesions of the hair follicles can occur due to severe prolonged stress, nervous exhaustion, an infectious disease, as a consequence of anesthesia, etc.
Alopecia cicatricial
It is even rarer (about 1,5%). In cicatricial alopecia, the tissues of the bulbs are replaced by scar tissue that does not have functional qualities. Its only purpose is to “patch” the damage. Cicatricial changes occur as a result of fungal or infectious lesions. The source of the problem is usually damage to the scalp.
Baldness stages
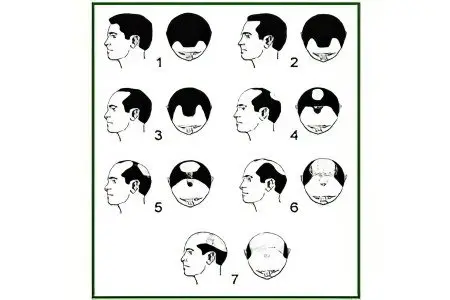
How baldness occurs depends on the cause of alopecia. As already mentioned, baldness most often occurs for genetic reasons (about 95-97%), so the picture is typical in most cases.
The classic is the scheme described by Norwood (the so-called Hamilton-Norwood scale), which allows you to determine the stage of alopecia:
The first stage. Alopecia can go unnoticed for quite a long time. At this stage, thinning of the hairline occurs along the hairline. Hair falls out in the frontal-temporal zone. As a result, two small bald patches are formed.
Second stage. There is a further aggravation of the process. Bald patches become larger, retreating from the hairline by a centimeter and a half (but not more than 2). As a rule, bald areas are symmetrical relative to each other (exceptions are possible). Alopecia also affects the parietal region. The hair is gradually thinning, but at this stage, the baldness of the parietal region is not yet so noticeable.
Third stage. Noticeable areas of baldness are formed in the frontal-temporal region. In some cases, they may be partially obscured by the remnants of sparse hair. Bald patches protrude beyond the hairline by 3-4 cm.
Fourth stage. The process of baldness in the fronto-temporal region, as a rule, stops. The thinning of the hairline on the top of the head begins (usually the hair falls out radially, forming “bald spots”). This stage is most typical for older men, however, depending on individual characteristics and hereditary factors, it can be observed at any age. In some cases, crown alopecia is combined with the progression of the process in the frontotemporal region.
Fifth stage. The border of hair separating the two areas of baldness is rapidly thinning. The absence of hair on the crown becomes distinct. Despite this, a dense strip of hairline remains between the frontal bald patches and the top of the head. Gradually, the hair thinning area takes on an arched shape (from the temple to the central part of the skull, almost reaching the top of the head and back to the temple). The original hairline is almost indistinguishable.
Sixth stage. The border separating the baldness of the crown from the bald patches of the frontal-temporal region is erased. A single bald spot is formed. The process enters a new phase, affecting the lateral areas and the back of the head.
Seventh stage. The final stage of male pattern baldness. Hair loss affects all parts of the head. The only thing that remains is a narrow arched hairline from ear to ear, occupying a small area at the bottom of the back of the head.
It should be noted that this classification of the stages of baldness is applicable only for men. Female alopecia develops according to a completely different type, but in natural conditions this occurs extremely rarely.
Pathologically caused baldness is characterized by individual foci and has no clear staging.
Hair loss shampoos for men

Regardless of the causes of baldness, you can find an effective remedy that will save your hair. Today, there are a huge number of products and services on the cosmetology market. One of the most affordable products is a medicated shampoo. Reasonably, many express distrust of this method of hair preservation and rightly ask the question: how can a regular shampoo help with baldness, especially if it is a genetically determined process? As already noted, doubts are well founded. The number of shampoos for baldness is so great that a non-specialist will immediately be confused. Meanwhile, a huge part of such products are frank dummies, and exist only as a tool to profit from desperate people.
But, fortunately, there are many worthy drugs that really have useful properties.
Shampoos that have the desired effect should contain an extract from the thymus gland (thymus). These products can stop hair loss.
Thymus extract allows you to effectively deal with the hormone that reduces the activity of the bulbs – DHT (dihydrotestosterone). The effect of using such shampoos is achieved after a few weeks or months. The success of treatment largely depends on the characteristics of the body of a particular person, and therefore the severity of the action varies from case to case.
When choosing a shampoo for hair loss, it is important to consider several factors:
The presence in the composition of the thymus gland extract and a large number of useful substances;
Safety – the shampoo must be suitable for the patient, not cause allergies and side effects;
Reliability – the manufacturer must be fairly well-known, and product information must be transparent.
It is not recommended to buy funds from unknown pharmaceutical companies, but you should not chase the brand either, since the composition of such shampoos is almost identical, and the price can greatly depend on the promotion of the brand.
Not all shampoo ingredients are beneficial. So, if the shampoo contains surfactants (surfactants), such as sodium salts, etc., you should not use them. Surfactants cause hair damage and reduce their growth rate.
It is very good if the shampoo contains essential oils of plant origin (lavender, tea tree, etc.) and other useful herbal ingredients.
At the moment, the following shampoos for hair loss have proven themselves best:
Progaine;
Revivogen. Contains a large number of natural extracts. Has the effect of neutralizing the hormone DHT;
Provillas. It has a vegetable-synthetic formula and consists of two products: a solution for external use and a drug for oral administration. Prevents hair loss, and also helps to restore previously fallen hair;
Nizoral. With constant use, it has some effect in the fight against androgenetic alopecia. If the source of baldness is a fungal infection, Nizoral is most preferable;
Nioxin (Nioxin). This is a whole complex of drugs to combat the problem of baldness. Strengthens and nourishes the hair follicles, and neutralizes the DHT hormone.
The choice of a specific remedy depends on the cause of baldness and the individual characteristics of the patient.
best hair loss shampoo
Despite the variety of really effective remedies for combating baldness, one stands out in particular. No matter how comical it may sound, the best shampoo for hair health is not produced for people. We are talking about shampoo-balm Zoo Vip. The product is intended for horses, but you should not be embarrassed at all.
Experienced cosmetologists and hairdressers have long used this particular tool to combat hair loss. The high degree of activity of Zoo Vip is due to the unique composition of the product. The basis of the shampoo is propolis and birch tar. Together, these active substances promote the healing of scalp wounds, stimulate the work of hair follicles, which means they contribute to the growth of new hair and the strengthening of existing ones.
The only drawback is that Zoo Vip has a specific pungent smell (similar to the smell of Vishnevsky’s ointment), but it quickly disappears.
One of the main conditions for achieving a therapeutic effect when using this shampoo is proper application. The product is diluted with water or other shampoo in a ratio of 1:10. Then apply and leave for a few minutes (from 5 to 7). The next step is to wash off the shampoo and use any conditioner.
The frequency and duration of use of this remedy depends on the degree of baldness. If the hair continues to fall out after 1-2 procedures, shampoo should be used regularly until the problem is completely eliminated. If you believe the reviews of those who used this tool, for relatively little money you can quickly and effectively restore hair density.
hair trainer
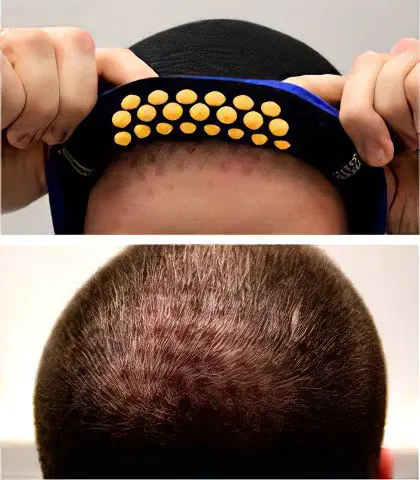
The skin, which during sleep is under the influence of the weight of the head, retains hair even in people who are genetically predisposed to baldness. An analysis of scientific data on the effect of oxygen starvation (occurring in compressed skin) on the metabolism of androgens (sex hormones that disrupt hair growth in men and women) showed that this coincidence is not accidental. The simulator places the top of the head in the same conditions as the non-balding area, training the mechanisms that provide hair nutrition and increasing the resistance of hair follicles to damaging factors. In particular, in response to hypoxia (oxygen starvation) in the follicles, the level of the aromatase enzyme, which neutralizes androgens (testosterone and dihydrotestosterone), increases several times. Where there is a lot of this enzyme, baldness does not develop, since the very cause of baldness is eliminated in the corresponding areas.
The claimed effects of the simulator are in good agreement with scientific data on the role of hypoxia in the development of a network of blood vessels and the regulation of local hormonal status. The fact that hypoxia stimulates hair growth was also noticed by L’OREAL, which created hair cosmetics that mimic individual elements of hypoxia (Vichy Neogenic). Unlike cosmetics, the effect of which is legally limited to a surface layer of skin as thick as a sheet of papyrus paper, a hair simulator creates deep hypoxia, simultaneously activating all the mechanisms associated with an adaptive response to oxygen starvation.
The simulator is designed for men and women of any age and is designed for long-term service in maintenance or episodic mode. The duration of the session is 15-45 minutes (it can be reduced to 10 minutes if at the beginning of the session you press the simulator to the head with your hands so that the relief elements “sit” into the skin faster). Flexibility in the frequency and duration of training is allowed. Hypoxic training can be combined with cosmetics and drugs.









