Contents
What is alopecia areata?
Alopecia areata characterized by the formation of one or more bald spots on the head, having an oval or round shape and a smooth surface.
One of the characteristic complaints to the doctor is as follows:
“Good afternoon. A 12-year-old child had two areas without hair, round in shape. It looked like the hair was just shaved. The first thought that came to mind was lichen, but the doctor made a different diagnosis, which sounds like “alopecia areata”. However, no treatment was given. The doctor said to come next time if the area of baldness increases. I have a few questions: what is this disease? Will the hair grow back? Is there really no need for any treatment?
In addition to the term “alopecia areata”, you can also find the phrase “alopecia areata” or “alopecia areata”. All these definitions refer to the same pathology.
As for the causes of the development of this disease, they have not yet been precisely determined. In addition, it is not known how the disease will proceed in the future. In some people, hair grows back, and in some, vegetation no longer appears in the foci of baldness. In addition, hair can fall out not only all over the head, but also all over the body.
As for statistics, pathology affects people of different ages, regardless of their gender. The percentage of occurrence among the population is 1,7%.
There are few methods for getting rid of alopecia areata, this is also due to the fact that hair often grows on baldness areas on its own as suddenly as it fell out, without any therapy. This explains the fact that doctors often adhere to expectant tactics.
Symptoms of alopecia areata
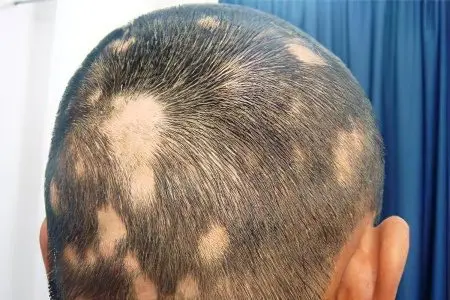
The most striking manifestation of the disease is hair loss in a certain area of the scalp. There can be several baldness zones, their area also varies. As for the loss of hair in the face and on the body, such signs are observed much less frequently.
Among other symptoms of the disease, the following can be distinguished:
The process of hair loss manifests itself with the formation of a small area of baldness. Its shape can be round or oval;
The surface of the affected skin is most often smooth, but sometimes you can find a slight roughness and inflammation;
Patients usually do not experience physical pain or itching. The baldness zone can itch, but this is extremely rare;
A single bald spot occurs in 80% of cases. Two bald spots appear in no more than 12,5% of cases. More than 2 bald spots occur even less often – in 7,7% of cases. They are localized not only on the head, but also on the body;
Sometimes there is loss of eyebrows and eyelashes. The prolapse can be one- and two-sided;
Approximately 10% of patients suffer from deformation of the nail plates on the hands. Their color changes – it becomes more cloudy, falls out, becomes thinner, depressions may appear.
It is worth knowing that it is not always alopecia areata that is the cause of hair loss in foci. A similar clinical picture is observed with fungal skin lesions. In some cases, people pull their hair out on their own. As for mycoses, ringworm is the most common cause of baldness.
Its distinctive features:
The skin in the area of hair loss becomes red, wounds form on it;
The affected areas itch;
The hair does not fall out completely, it breaks at the base. Bald spots in this case are not smooth, black dots are visible on their surface – broken hair.
If a person pulled out his own hair, for example, under the influence of a mental disorder, then there will be pieces of hair of various lengths on his head.
Diffuse alopecia areata
Diffuse form of alopecia areata is a process of hair loss over the entire head. In this case, the hairstyle becomes more liquid, but bald spots do not form. The study of particles of the scalp under a microscope showed that the changes that occur in the epidermis in alopecia areata are similar to the changes that occur in diffuse alopecia areata.
Therefore, scientists came to the conclusion that even with the differences in clinical manifestations, both of these forms of baldness are one and the same disease. It is on this assumption that therapy is based, which boils down to taking drugs that slow down the work of immune cells.
Danger of alopecia areata
Although the pathology leads to the formation of a cosmetic defect, in addition, alopecia no longer poses any health hazard. However, if areas of baldness appear on the head, it makes sense to contact a dermatologist for a comprehensive examination. It is the doctor who will be able to distinguish alopecia areata from a fungal infection of the scalp. After all, ringworm is a disease that is dangerous for the carrier himself and for the people around him.
Is alopecia areata contagious? The disease is not transmitted from one person to another and is not contagious.
Diagnosis of alopecia areata
To determine the type of baldness, the doctor most often needs only one visual examination of the lesion site. To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may use a dermatoscope. In addition, a scalp scraping is performed, which allows you to determine or exclude the presence of a fungus.
Another additional research method is blood sampling. The doctor individually determines which indicators will need to be detected. For example, a test for lupus or syphilis may be done.
Causes of alopecia areata

Scientists suggest that pathology may be the result of autoimmune processes occurring in the body. That is, cells of the immune system block the function of hair follicles and even destroy them. However, there is no clear evidence for this theory. In addition, the suppression of the work of immune cells does not give a high effect in the treatment of alopecia.
Stress and alopecia areata. Some patients who begin to develop alopecia areata, shortly before the manifestation of the pathological process, suffered a severe shock. Some of the people were injured, some suffered ARVI, some experienced certain difficulties. However, the conducted studies suggest that there is no relationship between stressful situations and alopecia areata. Therefore, there are still no clear recommendations on how to avoid the development of this disease.
Heredity and focal alopecia. Studies indicate that alopecia areata occurs with greater frequency in those people whose parents also suffered from this pathology. Therefore, the fact that alopecia areata is inherited is scientifically substantiated.
Prognosis for alopecia areata
The process of developing the disease in each person proceeds differently. In some people, the hair in the affected areas grows back, in the other part of the patients they fall out forever. Therefore, it is difficult to give an accurate forecast.
However, the study of available statistics indicates that if the hair fell out for the first time, then in about 80% of patients they grow back. The recovery process usually takes no more than a year. However, there is not too good news – almost 90% of people in the future have a relapse of the disease. The more episodes of repeated hair loss, the less likely it is to restore the hairline in full.
Sometimes there is an extremely severe course of the disease (in about 18% of cases). At the same time, hair falls out very quickly, a person can lose it completely in just a few weeks. Hair follicles cease to function not only on the head, but also on the face and throughout the body. The prognosis for this course of the disease is unfavorable, the chance for recovery is no more than 10%.
Treatment of alopecia areata
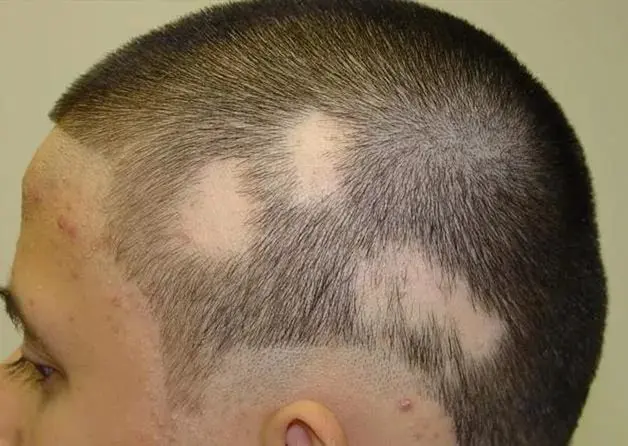
The vast majority of people who have begun to lose hair are wondering about the possibility of treatment and its effectiveness. The results of studies conducted in this area indicate that none of the existing methods of therapeutic intervention is able to give a lasting positive effect. Therefore, no matter how soon treatment is started, the end result will not be better. With a favorable course of the pathology, the hair will grow back, with an unfavorable course, it will be lost forever.
However, it is logical that people do not want to and cannot calmly watch the process of hair loss.
If you wish, you can resort to one of the following types of therapeutic effects:
Using ointments with strong corticosteroid hormones in their composition. These substances have the ability to slow down immune cells, which is why they are used to treat various autoimmune conditions. So, to get rid of alopecia areata, strong corticosteroid hormones are prescribed, for example, an ointment with clobetasol propionate 0,05%. The agent is applied to the affected area up to two times a day. Available data indicate that a positive effect can be achieved with a mild form of alopecia areata. However, after discontinuation of the drug, the hair falls out again. If treatment is carried out, following all medical recommendations, then it will be safe for health. A long therapeutic course is not recommended, as the risk of side effects dangerous to health increases;
Injections of corticosteroid hormones. Injection administration of the drug allows you to create its high concentration in the affected areas. At the same time, hair growth quickly resumes, but after a maximum of 9 months, they will fall out again. Therefore, this treatment method is used as a short-term solution for patients with alopecia areata. To get rid of extensive baldness, this method is not suitable. In addition, an atrophic process may begin in the injection area, the skin becomes thinner, depressions form on it. With long-term course treatment, there is a risk of developing severe side effects;
Oral administration of corticosteroid hormones. If the patient takes the drug in the form of tablets, then its effect will spread to the entire body. A temporary effect will be achieved, however, this method is not recommended for use due to the many side effects;
Application of solutions with diphenylcyclopropenone and dibutyl ester of squaric acid. These substances can provoke severe allergies. The mechanism of their work is not fully understood. The treatment regimen is reduced to applying a more concentrated solution of these chemicals to the affected skin in the first stage – 2%. After half a month, a weaker solution is applied – 0,01%. Then it is applied several more times with an interval of 7 days, gradually increasing the concentration. Treatment continues until a mild inflammatory process occurs on the treated areas. It is with this concentration of the solution that the treatment is continued. The effect of such therapy can be seen after a few months. Treatment is refused if after six months there is no effect. If there is a result, then the frequency of sessions can be reduced. If this leads to subsequent hair loss (which occurs in 60% of cases), then the therapy is resumed. As statistics show, this method of treatment is effective by about 50% in case of mild alopecia. If the baldness is extensive, then this method, as a rule, does not work. As for safety, this method has been used for over three decades, and no side effects have been found;
Minoxidil treatment. The use of this agent for the treatment of alopecia areata is likely to be less effective than for the treatment of the androgenic form of the disease. A good effect can be achieved with a slight baldness. With short-term use, this remedy is considered safe (for more details, see the article: Minoxidil for baldness);
phototherapy method. This procedure is reduced to exposure to the affected areas with ultraviolet rays. There is evidence of a high efficiency of this method of treatment. Hair is restored in 65% of cases. However, there are other data pointing to the absolute ineffectiveness of phototherapy. Therefore, this method of treatment is still in question. As for complications, there is a risk of developing skin cancer, especially after undergoing many sessions. That is why phototherapy can be prescribed as a temporary measure for the treatment of alopecia areata;
Treatment with drugs with Dithranol. Dithranol is a drug used to treat psoriasis. With regard to patchy alopecia, there is a small amount of information about its effectiveness. The safety of the drug has been proven even with its long-term use;
The use of zinc preparations. No studies have been conducted on this treatment modality.
Hair transplant for alopecia areata
The transplantation procedure for this pathology is used extremely rarely. This is because the prognosis of the disease is impossible to predict. Therefore, the effect of the transplant can be quickly lost.
In addition, there is evidence that hair begins to fall out in those places where they were taken from. Sometimes alopecia areata developed even after the hair was taken for transplantation in order to get rid of another pathology. Therefore, before deciding on such a procedure, you should carefully discuss all the points with the doctor (for more details, see the article: Hair transplantation: answers to basic questions).
Gluten-free diet for alopecia areata
There is research indicating that people with alopecia areata may also suffer from celiac disease. So, out of 12 examined sick children, gluten intolerance was found in 5. After the transfer of these children to a gluten-free diet, 4 of them had a complete restoration of the hairline.
Author of the article: Herman Olga Leonidovna, trichologist, specially for the site ayzdorov.ru









