Contents
Almonds are an undemanding crop to care for, but whether a shrub will grow on a site depends on the species. The common almond, which produces edible fruits, and its numerous varieties are very thermophilic. You can get a stable harvest only in the Caucasus or in the Crimea. Planting and caring for the almond bush, the photo of which is shown below, is difficult mainly due to return frosts in the spring that destroy flowers or ovaries. The plant itself can withstand winter temperatures down to -25-30°C.

It is much easier to grow decorative almonds in the country, bred with the participation of other species more resistant to cold, and no one will expect nuts from them. The main thing is that the shrub decorates the site in the spring, when other flowers have not yet had time to open.
Botanical description of almonds
Amygdalus or Almond is a subgenus belonging to the genus Plum, family Pink. It consists of 40 species distributed in Eurasia and North America.
Almonds are deciduous shrubs or low trees no more than 10 m high with gray or brownish cracking old bark and greenish-gray, smooth young shoots. On the side facing the sun, they have an anthocyanin hue. The leaves of all species are greenish-gray, strongly elongated, with a sharp tip and a smooth or slightly serrated edge.
The symmetrical, five-petalled flowers, white or pink, usually open before the leaves and often suffer from recurring frosts. The fruit is a drupe with a fleshy mesocarp, which dries out and cracks after the bone ripens.
The roots of almond bushes are well adapted to the rocky soil of dry mountain slopes. They consist of several powerful shoots capable of reaching the lower layers of the soil in search of moisture, and a small number of fibrous roots.
The lifespan of the shrub depends on the cultivation and care of almonds. Often it is planted in conditions that are not even close to natural. In nature, the culture lives up to 100 years, growing on industrial plantations and in gardens significantly reduces this period.
The most important economic value is the fruit-bearing and very heat-loving Common Almond (Prunus dulcis). His flowers are also unusually beautiful, but the main task of culture is to produce a crop. There are bitter almonds, obtained from the seeds of a species plant, and containing from 2 to 8% amygdalin and sweet (cultivated), in which the amount of this substance does not exceed 0,2%. Amygdalin, when split, releases hydrocyanic acid, so bitter varieties are more used in the pharmaceutical and perfume industries, and sweet varieties are used for cooking.
As an ornamental plant in Our Country, varieties and hybrids of other types of almonds are grown:
- Steppe (Low, Bobovnik);
- Ledebura;
- Georgian;
- Petunnikov;
- Three-bladed (Louisania Three-bladed).
Luizean shrub is especially beautiful in spring, in which even species flowers are terry. Some scientists separate the culture into a separate genus, but most include it in the Almond subgenus.

Optimal conditions for growing almonds
Perhaps, almonds are the most photophilous fruit crop. Not only does the shrub not tolerate shade, it does not tolerate competition for the sun’s rays with other plants. That is why it is impossible to meet almond thickets in nature. Trees and shrubs are located singly or in groups of 3-4 specimens, located 5-7 meters apart.
What at first glance appear to be small clumps in some species are actually root shoots that grow profusely around the main trunk. If annual pruning is not carried out in the culture, then the old shoots, deprived of light, quickly dry out, their place is taken by new ones. That is why even those types of almonds that form a tree become like a shrub.
The soil for growing a crop should be well-permeable and drained, alkaline or carbonate, in extreme cases – neutral. Loams, light clays, stony soils are suitable for shrubs. Standing groundwater close to the surface is unacceptable, the minimum distance is 1,5 m.
The culture is quite drought-resistant. The natural conditions for its growth are mountains, rocky slopes, and a hot climate with poor rainfall. Species plants require very little watering, varieties – more, but still a little. In areas with frequent rains, planting a crop does not make sense.
Those who claim that the almond bush will live where the peach grows and the grapes that do not require shelter are, of course, right. The culture withstands frosts down to -25-30 ° C. But only during and immediately after flowering, even a short-term decrease in temperature to -3 ° C will cause the ovaries to fall off in the Ordinary Almond and its varieties that give edible fruits.
The problem of return frosts has not yet been solved. Therefore, even for the southern regions, it is recommended to choose varieties that bloom as late as possible, with a long dormant period.
How to plant almonds
Actually, there is nothing complicated in planting an almond bush and caring for it. It is much more difficult to find a place on the site and properly prepare the soil.

Planting dates for almonds
Almonds can be planted in spring or autumn. But since the culture grows very quickly and begins to bear fruit early, when placed on the site at the beginning of the season, the shrub can immediately bloom. This will weaken the plant and prevent it from taking root normally. Earthwork in the spring should only be planned as a last resort.
The preferred planting of almonds is in autumn, in November. In a warm climate, the shrub will have enough time to take root, and in the spring it will immediately grow.
Selection and preparation of the landing site
The area for growing almonds should be well lit, protected from cold winds. It is desirable that the planting site of the shrub has a southern orientation. Other trees or buildings should not shade the culture for longer than 1,5-2 hours, but this is highly undesirable.
The soil should be well-drained, if it contains stones of any size, they do not need to be removed. Loams, sandy loams or light clays, heavy and acidic soils, blocking or simply wet, are suitable for almonds. Even in neutral soil, lime or dolomite flour should be added when planting. Groundwater should not lie closer than 1,5 m to the surface.
Planting pits for planting shrubs are prepared at least 2 weeks in advance. Their diameter should not be less than 50 cm, depth – 60 cm. At least 20 cm of drainage from crushed stone, gravel or broken bricks are laid on the bottom. Then they are covered with sand so as not only to fill the voids, but also to make a 5-7 cm layer.
Planting mix should not be too nutritious. Sand, clay and brick chips are necessarily added to the black soil, scarce soils are improved with humus. Acid soil is brought back to normal by adding up to 0,5 kg of lime or dolomite flour to the planting pit.
The recess is 2/3 filled with planting mixture and filled with water.
When planting and caring for almonds in the open field, it will not grow as large as in nature, but it should still be located freely. The distance between plants must be determined based on the height of an adult shrub, it is different for each variety. On average, almonds are planted 4-5 m apart. Rows (if any) should be 7 m apart. An adult shrub should not touch branches with other crops, otherwise the lighting will be insufficient.
Free space between plants is recommended to plan at least a meter. If this condition is ignored, the almond bush will bloom profusely, as the buds open when most crops are bare or have just begun to open their leaves. But the harvest will be meager – the fruits simply do not have enough light for normal development. In addition, almond bush grows faster in shading.

Seedling preparation
Shrubs of sweet and bitter almonds grow well in the Crimea and the Caucasus. In other regions, when choosing seedlings, it is imperative to be interested in whether the variety is adapted to local conditions. It is best to go to a nursery to buy a shrub – at an exhibition or via the Internet you can buy almonds grown in the southern regions on rocky soils. It will be long and difficult to settle down in a different environment.
Almonds should be planted at the age of one to two years – the culture grows rapidly and begins to bear fruit early. In the first year after planting, it is not recommended to let the shrub bloom, and it is not difficult to pluck the buds that abundantly cover the branches in early spring, but for a long time.
When buying a seedling, first of all, you need to pay attention to the root system. It should be intact, elastic, contain at least one strong process and few fibrous branches. In grafted shrubs, you need to take an interest in the rootstock and carefully examine the place of merging of crops – there should not be cracks, peeling of the bark, spots of unknown origin.
Preparing the seedling for planting consists of watering the container plant or soaking the exposed root for at least 6 hours. A shrub can be kept in water for several days if a growth stimulator or a half dose of any potash fertilizer is added to the liquid.
Rules for planting an almond bush
There is nothing complicated in the landing itself:
- Part of the earth is taken out of the landing pit.
Comment! There is no need to make a mound in the center – the young seedling has almost no fibrous roots, but several strong processes have already formed. So, excuse me, there is nothing to straighten around the hill!
- A strong peg for tying a seedling is driven into the bottom.
- The shrub is immediately tied to the support so that the root neck rises 5-7 cm above the soil surface.
- Only after that the root is covered with soil, constantly compacting it.
- Check the position of the root neck.
- Almonds are watered, spending at least a bucket of water on each shrub.
- The trunk circle is mulched with dry earth or lowland (black) peat, but not with humus. The thickness of the shelter should be 5-8 cm.

How to grow almonds
If you choose the right place and plant almonds, the shrub will require a little care. Fruiting varieties need more care than ornamental varieties.
How to water and feed
Immediately after planting, especially if it was done in the spring, almonds need regular watering. As soon as the shrub begins to grow, moisture is limited. Almonds planted in the fall may not require additional watering. It is necessary to focus on the weather and remember that an excess of water is much more dangerous for a culture than its shortage.
This does not mean that a varietal almond bush can grow without watering at all – species plants in this regard are more resistant to drought. With a lack of moisture, the flowering time will be reduced, and since the culture is pollinated exclusively by insects, and it is self-fertile, there may not be enough time for fertilization. Sandy soils require more frequent watering than loams or chernozems.
Home grown almonds are fertilized three times per season:
- in early spring, before the flowering of the shrub – nitrogen, 20 g per 1 sq. m;
- in early May – complex fertilizers according to the instructions (optional);
- August-September – phosphorus-potassium top dressing, 20 g of superphosphate and potassium per 1 sq. m.
Doses of fertilizers should correspond to the age of the shrub and the composition of the soil. If you overdo it, you can just ruin the plant. This is where the “golden rule” of fertilizing any crop comes into play: it’s better to underfeed than overfeed.
On non-irrigated soils, where almond plantations are often planted, the main top dressing is applied in late autumn, when the soil under the bushes is sufficiently moistened. After leaf fall, manure, superphosphate and potassium salt are embedded shallowly into the ground. On chernozems, you can limit yourself to rotted cow dung.
How to trim an almond
To get a consistently fruitful or beautiful ornamental shrub, it is impossible to do without pruning almonds. Immediately after planting, the seedling is shortened to 0,8-1,2 m, all branches located below 60 cm or the grafting site are removed, 2-3 buds are left on the rest.
When the shrub is well rooted and gives new shoots, 3-4 of the strongest are left for the formation of skeletal branches. Up to 4-5 years, the crown of a fruiting almond should be formed in the form of a bowl, with one trunk.
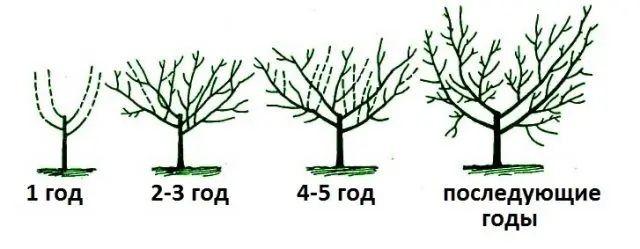
In the future, pruning consists in maintaining the shape of the crown, removing thickening and crossing shoots, fatty branches directed vertically upwards. The entire increase is shortened to 60 cm.
The main pruning of almonds is carried out in the fall, after leaf fall. In the spring, frozen ends of branches, dried and broken shoots of shrubs in winter are removed.
Old and severely frost-damaged trees recover quickly after heavy pruning. If you ignore the procedure for at least one year, the yield and decorative effect will decrease.
It is necessary to work with a sharp sterile instrument. The wound surface, with a diameter greater than 1 cm, is covered with garden pitch or special paint.
How to prepare for winter
Almonds endure short-term frosts, reaching -25-30 ° C. Under the influence of low temperatures, the tops of young shoots may freeze slightly, but after pruning they quickly recover. Returning spring frosts are much more dangerous for shrubs. Even a short drop to -3 ° C will cause the buds or ovaries to drop.
So it is more important to protect almonds from the cold in spring than in winter. Where the frosts are long and severe, planting a crop does not make sense at all.
To increase the resistance of the crop to low temperatures, at the end of summer or early autumn, the plant is fed with phosphorus and potassium, nitrogen is no longer given in June. A mandatory procedure is moisture charging at the end of the season.
In the last days of July or early August, tweezing is carried out – pinching the tips of young shoots. This simple procedure is very important for the almond bush, it significantly speeds up the maturation of the wood and reduces the likelihood of branches freezing.
The only way to protect almonds in the spring is with smoke bombs or building a shelter made of agrofibre or lutrasteel. Grafted standard forms are most sensitive to low temperatures. Where the weather is unstable or significant frosts are possible, the tree is wrapped with covering material from autumn. In any case, it is better to insulate the place of vaccination, but so that the bark does not rot.

Features of growing almonds in different regions
Before embarking on the cultivation of almonds in the Middle Lane, it should be clearly understood that he may live there, but he will not bear fruit in the open field. Even in most regions that are considered southern for Our Country, the culture is cold, the harvest should not be expected there. But ornamental shrubs are more resistant to frost, although they also love warmth.
Growing almonds in the Krasnodar Territory
Sweet almonds can be grown in the Krasnodar Territory. Shrub does not give stable yields everywhere, but only where there are no sharp fluctuations in temperature. The rest period of almonds is short, flower buds awaken in early spring, and sometimes at the end of February. The sun can heat the shrub and cause premature opening of the buds. A decrease in temperature causes abscission of flowers or ovaries.
Sometimes almonds simply do not pollinate due to the fact that at the time of blooming the buds, bees and other pollinating insects have not yet begun their work. So even in the Krasnodar Territory, it is not possible to get a harvest every season everywhere.
In fairness, it should be noted that even in Iran and Morocco, almonds do not bear fruit every year. That is why the United States has become the world leader in the production of nuts. California’s weather is a benchmark for predictability and an even, warm climate ideal for growing most heat-loving crops, including almonds.
Growing almonds in the suburbs
Planting almonds in the Moscow region is possible, but only decorative. Fruiting – only in closed ground. Even if at the cost of incredible efforts to grow and maintain an edible shrub on the site, it will not give nuts.
Decorative almonds will have to be carefully looked after, measures should be taken to increase frost resistance. By the way, it is also useless to plant shrubs of fruit varieties in most of Ukraine, and flowering ones regularly freeze slightly.
Productivity
Growing almonds at home has one feature. All varieties are self-fertile, so you cannot plant one shrub – it simply will not yield a crop. In industrial plantations, it is recommended to grow at least four varieties, or alternate 4-5 rows of the main variety with 1 line of pollinators.
On personal plots, 2, and preferably 3 forms of sweet almonds should be planted. The culture is able to bear fruit annually, but even in Central and Asia Minor, several harvest seasons in a row are considered good luck. The number of nuts is highly dependent on the vagaries of the weather. The best and most stable crop is obtained far from the native places of almonds – in California.

The culture enters full fruiting after 8-9 years for grafted plants or 10-12 years after germination in those grown from seed. The first nuts appear after 2-3 or 4-5 years, respectively. Fruiting under favorable conditions lasts 50-65 years, then the yield drops sharply.
Different varieties of almonds can produce 6-12 kg of peeled kernels from an adult shrub. This is considered a good harvest. Each core weighs an average of 2-3 g, some reach 5 g, but this is very rare.
Early varieties of almonds ripen in late June or early July, late ones – by September. A sign of removable maturity is cracking and darkening of the mesocarp. In ripe nuts, the shell is easily separated from the stone.
The shrub is shaken to bring down the nuts. If necessary, use long sticks or poles. After collecting the bones, they are quickly cleaned of the shell, laid out in a thin layer in a warm, ventilated room for drying. You can store almonds for a year.
Reproduction of almonds
Almonds can be propagated by seed, but since the crop is cross-pollinated, varietal characteristics are not thus inherited. What will grow out of the stone is unknown, one thing is certain: the nuts will be tasty, but it is impossible to predict the content of amygdalin in them. Without heat treatment, the fruits of a shrub grown from a stone should not be eaten.
The easiest way to breed varietal (not grafted) almonds in small quantities is to separate the root shoots and root the cuttings. The latter method does not present any difficulties, but takes more time than other cultures.
On an industrial scale, almond varieties are propagated by grafting.
Grafted Almond Features
Often varietal almonds are grafted onto a species plant. So not only can you quickly get a fruit-bearing shrub that gives high-quality fruits, but also slightly increase frost resistance. Unless, of course, not the species Almond Ordinary is used as a stock, but representatives of the subgenus resistant to low temperatures.
But this does not always make sense – in inappropriate conditions, the almond grows quickly, the old trunk dries up, it is replaced by new shoots that have grown from the root. From this, the tree loses its shape and becomes like a shrub.

Therefore, before growing almonds grafted onto representatives of their own subgenus, you should first find out how it will behave at the landing site. It is possible that in a few years the site will not have a varietal tree, but a shrub formed from root shoots that has nothing to do with the scion (except perhaps the species). You will have to carefully monitor the condition of the bole and, at the first sign of drying out, re-graft young shoots. It is even better to use other crops as a rootstock.
To increase the frost resistance of almonds, it is recommended to use bird cherry, blackthorn, plum, cherry plum as a stock. For growing on stony soils, grafting is best done on bitter almonds. Paper-shell varieties are compatible with peach.
Diseases and pests
Almonds, like peach, are often affected by diseases and pests. It is impossible to get a harvest without preventive measures.
Among the diseases of the almond bush, it is worth highlighting:
- gray rot;
- rust;
- monilial burn;
- Parsha.
The main pests of almonds:
- leaflet;
- aphid;
- plum codling moth;
- almond seed-eater;
- Plum bark beetle.
The main problems of ornamental almond shrubs are aphids and monilial scorch.
For prevention, you should:
- plant almonds freely, so that the branches of an adult plant do not come into contact with other trees;
- thin out the crown annually;
- cut dry and diseased branches;
- in spring and autumn, carry out preventive treatments of shrubs;
- remove plant residues from the site;
- regularly loosen the soil to a depth of about 7 cm;
- choose disease-resistant varieties for planting;
- fight anthills – they are the cause of the appearance of aphids, which, in turn, not only infects the culture itself, but also spreads diseases;
- regularly inspect shrubs, and if a problem is identified, treat with fungicides or insecticides;
- will not overmoisten the soil;
- follow the rules of agricultural technology.

Conclusion
Planting and caring for almond bushes, the photos of which were given in the article, are not a particular problem in the south. In a cool climate, the culture grows, but does not bear fruit, unfortunately, varieties resistant to return frosts have not yet been bred. Ornamental almonds can be grown in the Middle lane.









