Contents
Sensitization is when the immune system reacts to a foreign substance, such as pollen, bee venom or pet dander, or a food that does not cause a reaction in most people. Normally, the immune system produces substances known as antibodies, however, when you are allergic, your immune system produces antibodies that identify a specific allergen as harmful, even if it is not. Sensitization may manifest as skin, sinus, respiratory or digestive disorders. In most cases, an allergy cannot be cured, but its symptoms can be relieved.
What is an allergy?
An allergy or allergy is a condition in which the immune system overreacts to a foreign substance that is usually not harmful. When a person is exposed to an allergen for the first time, they usually don’t feel a reaction. It often takes time for the immune system to develop a sensitivity to a substance. Over time, the immune system learns to recognize and remember the allergen. As it does so, it begins to produce antibodies that attack it when exposure occurs.
Sometimes an allergy can manifest itself seasonally through hay fever, which may become worse between April and May, when the number of pollen of trees and grasses in the air is higher.
See also: How does the immune system work?
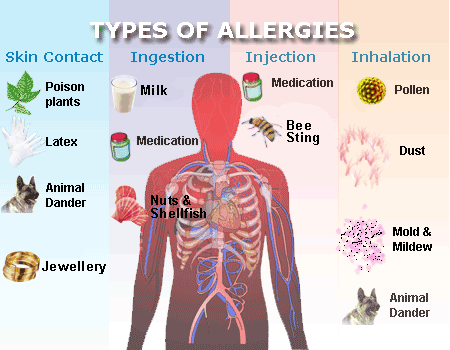
Allergy – types
Man may be allergic to various substances such as pollen, animal hair, mold or mites.
Allergy to pollen of flowers
Flower pollen allergy manifests itself as seasonal allergic rhinitis or hay fever. They cause inflammation and swelling of the nasal mucosa and conjunctiva. If you are allergic to pollen of flowers, symptoms will include frequent sneezing, feeling short of breath, and itchy, watery eyes, nose and mouth. Treatment of this type of allergy consists in the use of oral and nasal antihistamines, anti-leukotriene drugs and nasal steroids.
In some people, the symptoms of allergic asthma (wheezing, shortness of breath, coughing and / or tightness in the chest) may be caused by exposure to pollen. The symptoms of pollen allergy can be reduced by avoiding them. If you are allergic, it is advisable to stay indoors when pollen counts are high, close windows and use air conditioning.
See also: Calendar of plant pollen in Poland [INFOGRAPHIC]
Allergy to dust mites
Some people are allergic to dust mites, which are small organisms that live in dust and in the fibers of household items such as pillows, mattresses, carpets and upholstery. Symptoms of allergy to dust mites are similar to those of pollen allergy. In order to deal with allergy to dust mites, it is recommended to use special plastic / polyurethane covers on pillows or mattresses. In addition, it is a good idea to either get rid of the carpet or vacuum it with a high-performance vacuum cleaner with a filter.
Treatment of allergy to dust mites may include medication to control symptoms for the nose / eyes and chest. In extreme cases, an allergy can be treated with immunotherapy (when other treatments do not bring the expected results).
See also: A vacuum cleaner for allergy sufferers – how to choose the best model?
Allergic to mold
Another type of allergy is mold allergy, which are tiny fungi with spores that float in the air like pollen. Mold can be found in damp areas such as a basement, kitchen or bathroom, and outdoors in grass, leaf piles, hay, litter, or under mushrooms. Mold spores peak in hot, humid weather. Treatment for mold allergy may include medications to control nasal / eye and chest symptoms, or immunotherapy.
Allergic to animal hair
One of the common types of allergy is caused by animal hair. This is due to proteins secreted by the sweat glands in the animal’s skin. The easiest way to get this type of allergy is not to come into contact with animals. If we are allergic and we have pets at home and we do not want to give them up, we should keep them out of the bedroom and use HEPA-filtered air purifiers and wash our pets frequently.
Treatment of allergy to animal hair will involve the use of drugs and, in extreme cases, immunotherapy.
Latex allergy
Sometimes it happens that someone is allergic to latex. In such a case, he should avoid latex gloves, such as are used e.g. for cleaning the house. People who are allergic to latex may experience skin rash, hives, watery and irritated eyes, wheezing and itchy skin. Allergic reactions to latex can be mild, such as red and itchy skin. More severe reactions may occur if the mucous membranes are exposed, for example during surgery or during a dental or gynecological examination.
Treatment of latex allergy is to remove the harmful latex product. There is no cure for latex allergyso the best way to treat this condition is to prevent and avoid anything latex.
See also: Latex and fruit syndrome
Food allergy
You can also be allergic to a given food. An allergic reaction occurs within minutes of eating, and symptoms can be serious. Adults are usually allergic to peanuts and nuts and shellfish, and children are allergic to eggs, milk, soybeans, wheat, and crustaceans, peanuts and nuts. For food allergies, the most common symptoms are itching, hives, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, difficulty breathing, and swelling around the mouth.
An allergic person should avoid foods that trigger allergic reactions. Treatment may be prescribed injection of epinephrine to be worn at all times. This is needed in case you accidentally eat food that causes allergies. There are new treatments for peanut allergy called oral immunotherapy.
Also read: What do swollen lips say?
Allergy to the sun
Sun allergy is a frequently used term to describe many conditions where an itchy red rash develops on skin exposed to sunlight. The most common form of sun allergy is polymorphic light eruption, also known as sun poisoning. Some people have an inherited allergy to the sun, and others only develop the signs and symptoms of an allergy when triggered by another factor such as a drug or exposure to plants such as wild parsnips or limes. Mild cases of sun allergy may go away without treatment. More severe cases can be treated with creams or steroid tablets. People who are severely allergic to the sun may need preventative measures and wear sun protection clothing.
Insect venom allergy
You can also be allergic to insect venoms such as bees, which causes pain, swelling and redness around the site of the sting. Sometimes a major allergic reaction may develop, such as swelling of the leg after, for example, an ankle sting. Other symptoms of an allergy to insect venom include difficulty breathing, blisters (which looks like a red itchy rash that spreads to areas other than the area you have been stung), swelling of the face, throat or mouth, wheezing or difficulty swallowing, rapid pulse and dizziness or a sharp drop in blood pressure.
After such symptoms develop, if the sting re-occurs, another allergic reaction may be life-threatening. Such reactions are treated with adrenaline. In the event of an allergic reaction to an insect sting, testing is recommended to confirm that you are allergic to the venom. Venom immunotherapy is recommended in the case of confirmed allergy to the venom.
See also: Are you allergic to insect venom? You must have these medications with you at all times
Allergy – symptoms
In the event of an allergy, the symptoms depend on the type of allergy and its severity. If an allergic person takes the medication before he has an allergic reaction, he or she will have symptoms but these will decrease.
In the case of food allergies, the symptoms are mostly swelling, hives, nausea, fatigue, etc. A person allergic to a particular food product will usually not be aware of it at first. However, if the person has a severe allergic reaction, see a doctor immediately.
If you are allergic to pollen, the symptoms usually resemble those of the common cold and will include congestion, runny nose and puffy eyes. In most cases, these symptoms can be managed at home with over-the-counter medications. In extreme cases that interfere with everyday functioning, contact a doctor.
Severe allergies may result in anaphylaxis, a condition leading to difficulty breathing, dizziness and loss of consciousness. Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening condition, so if you experience these symptoms after exposure to an allergen, you should seek immediate medical attention.
Sensitization – diagnostics
People who are allergic should not wait for their symptoms to disappear on their own, especially if these persist for more than a week or two and have a tendency to recur, contact an allergist.
Diagnosis of sensitization will be based on allergic skin tests. Thanks to them, it is possible to identify allergens that cause allergic symptoms. The test is performed by pricking the skin with an allergen extract and then checking the skin’s reaction.
In cases where it is impossible to perform an allergic skin test, a blood test is performed. Although it is not as sensitive as these skin tests, it can assess the number of antibodies produced by the immune system. Higher levels of some antibodies suggest a possible sensitization to the allergen in question.
See also: Allergy tests – the course and cost of execution
Allergy – treatment
Of course, it is best to avoid allergens, i.e. what is the cause of our allergy, but it is not always possible. In such cases, the following applies:
Treatment of allergy – drugs
Sensitization can be treated with measures such as antihistamines to control symptoms. Your doctor may suggest over-the-counter or prescription medications in the form of tablets or liquid, nasal sprays, or eye drops.
Allergic medications include:
- antihistamines (e.g., diphenhydramine);
- corticosteroids;
- cetirizine;
- loratadyne;
- cromolyn fine;
- means to open the upper respiratory tract;
- leukotriene modifiers.
Treatment of allergy – immunotherapy
If you are severely allergic, your doctor may recommend allergen immunotherapy. This treatment involves a series of injections of purified allergen extracts, usually administered over several years. Another form of immunotherapy is a tablet that is placed under the tongue (sublingually) until it dissolves. Sublingual medications are used to treat certain pollen allergies.
Treatment of allergy – adrenaline
If you have a serious, life-threatening allergy, you should have an emergency epinephrine injection (EpiPen) with you. It prevents allergic reactions until medical attention arrives.
Treatment of allergy – natural remedies
There are often references to natural remedies that can help in the event of an allergy, but it is advisable to consult your doctor before using them. It should be realized that some of these agents may contain other allergens and thus aggravate symptoms. For example, dried teas contain flowers and plants closely related to plants that can cause symptoms such as sneezing. The situation is similar with essential oils, which are used to alleviate common allergy symptoms, and they may contain ingredients that can cause allergy.
Also read: Allergy medications – types, indications, properties, use
Allergy – prophylaxis
Sensitization cannot be prevented, but its symptoms can be prevented. The best way to do this is to avoid the allergens that cause them.
In the case of food allergy, the so-called an elimination diet, which can help determine exactly what product we are allergic to, and thus help us avoid it. It is better to avoid food allergens, read the labels on the products carefully and do not be afraid to ask questions about a meal, e.g. in a restaurant.
If you are allergic to pollen, pet hair or other allergies, prevention is knowing where the allergens are and how to avoid them. If we are allergic to dust, we can reduce symptoms by installing appropriate air filters in the home, professionally cleaning the air ducts, and vacuuming the house regularly. Proper allergy testing can help pinpoint the exact triggers, making them easier to avoid.
Allergy and other diseases
Allergy and asthma
Asthma is a respiratory disease that makes breathing difficult and can restrict the airways in the lungs. Sensitization can worsen asthma or trigger asthma in a person who has never had the disease. If someone is allergic and has asthma at the same time, this is referred to as allergy-induced asthma or allergic asthma.
Allergy and colds
Usually, symptoms of allergy may be runny nose and cough. There are also symptoms of colds and sinus infections at times. Sometimes it is difficult to recognize what we are dealing with. In such cases, you have to look at other symptoms. For example, allergies can cause skin rashes and itchy eyes. A cold, in turn, can lead to body aches or fever, and a sinus infection usually causes a thick yellow discharge from the nose.
Sensitization affects our body for a long time. In such a situation, our immune system is at risk and the likelihood of catching an infection increases. This includes the virus that causes the common cold.
Allergy and allergic cough
One of the common symptoms of an allergy is a persistent cough, which is caused by the body overreacting to allergens. It is important to know that allergy-induced coughing is temporary and usually occurs at certain times of the year when plants bloom for the first time.
An allergy to pollen can cause asthma, which in turn can cause coughing. People allergic to pollen, in case of contact with the allergen, have narrowed airways, which may lead to coughing. Other possible symptoms include shortness of breath and chest tightness.
Allergy and bronchitis
Bronchitis can be caused by allergies or viruses. Acute bronchitis usually ends after a few days or weeks. Chronic bronchitis, however, can last for months, possibly longer. It can also come back frequently. Allergens that can cause bronchitis include cigarette smoke, air pollution, dust, pollen, or chemical fumes. Many of them are found at home or at work on a daily basis, and this makes chronic bronchitis more persistent and more likely to relapse.
See also: Home air purification – how to start?
Allergic in children
Allergies, especially when manifested on the skin, are more common in younger children. Fortunately, they decrease with age, but pollen or food allergies become more common as children get older. A study like that published in 2017 in the Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology suggests that those born via caesarean section may also be at higher risk of allergies because they are not exposed to the mother’s microbiome during delivery.
As for allergies manifested on the skin of a child, these are usually:
- Eczema – an inflamed skin that causes slowly developing red itchy rashes.
- allergic contact dermatitis – often occurs immediately after a child comes into contact with an irritant. More severe contact dermatitis can develop into painful blisters and cause the skin to crack.
- hives – manifested by red bumps that develop after exposure to an allergen. They won’t peel or crack, but they can make your skin itchy and bleed.