Contents
What is pinching tomatoes? The process allows you to get a richer harvest, and is the physical removal of excess shoots. Young plants in the process of growth tend to form extra shoots that can use plant sap, but do not bear fruit. Also, such shoots take on a large amount of energy, however, do not bring results. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to pinching tomatoes.
Why do stepchildren tomatoes
Immediately after planting in the ground, all the forces of the plant go to building green mass, after the formation of fruits, it is desirable to redirect these forces to their development and maturation. For this, pinching is used. How to pinch tomatoes, when it needs to be done, or not pinch a plant at all – everyone decides for himself. Some varieties of tomatoes without pinching sometimes give a full crop in the natural environment, they can do without such a procedure, for example, there are undersized tomatoes that do not require pinching.
The side green branches on a tomato are completely useless. Being an extra green mass, they are undesirable for a rich harvest. If they are removed, the fruits will receive more nutrients. The size of the stepchildren for removal is 3-5 centimeters. If large ones are removed, it can damage and affect growth. Only persimmon, like a variety of tomato that grows on its own, does not require pinching, although many vegetable growers also pinch persimmons.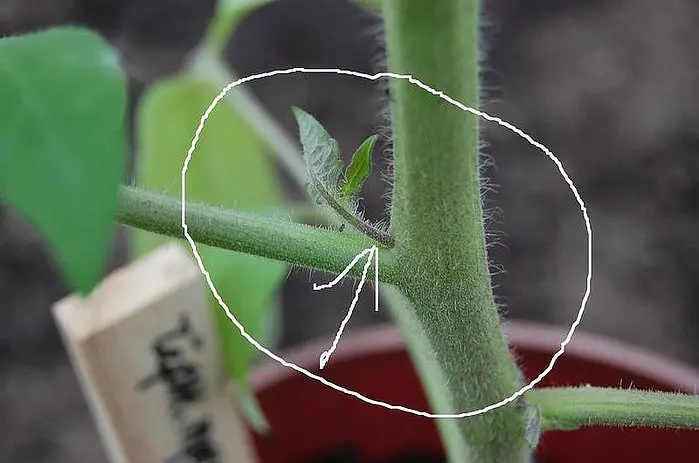 
However, it is worth learning that a rich harvest can only be obtained from healthy plants, and many gardeners fully resort to fertilizers and other ways to achieve the desired result. Accordingly, the removal of excess shoots is a process that can give strength to the sprout, save trace elements and nutrients for the fruit, without wasting extra energy on the germination of side shoots.
Plant care is not limited to controlling the growth process and creating favorable environmental conditions. Lateral stems can grow strongly, from which the yield drops. Almost all varieties of tomatoes without pinching lose in the harvest. Normally, without third-party intervention, only some tomatoes can grow, for example, a persimmon variety, if the owner does not set himself the goal of growing large fruits. Persimmon grows up to 1 m high; when cultivated in a greenhouse, they are usually stepchildren.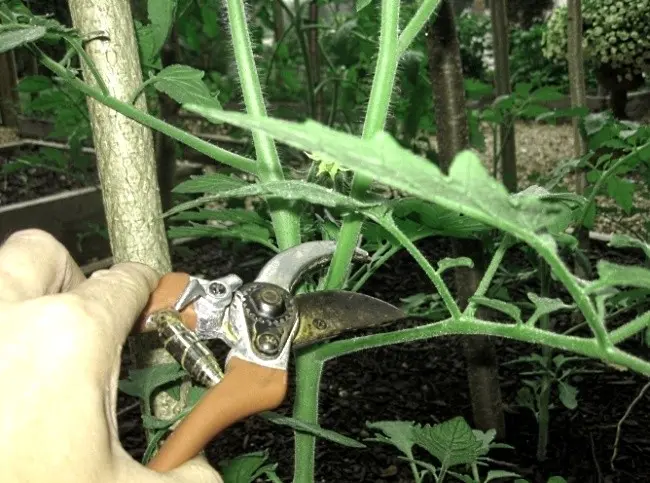 
How to do it right
Determinant varieties of tomato are stepchildren necessarily. They stop their growth on their own, and branch weakly. The ways to achieve the desired result are quite simple. How to do pinching tomatoes? Before 3-4 brushes appear on the plant, the stem should be left alone. After the appearance of sprouts, two stems are left, and one of them should be stronger. The frequency of the brushes is also very important – each after the first brush is located after 2 or three sheets. The fewer such brushes on a plant, the more it needs shaping from the gardener.
Determinate plantings are stepchildren in such a way that one stem remains. A few inflorescences will help to get a harvest earlier. It is not necessary to pinch the growth point. A couple of leaves are left – all this is necessary to enable the inflorescences to ripen at the same time.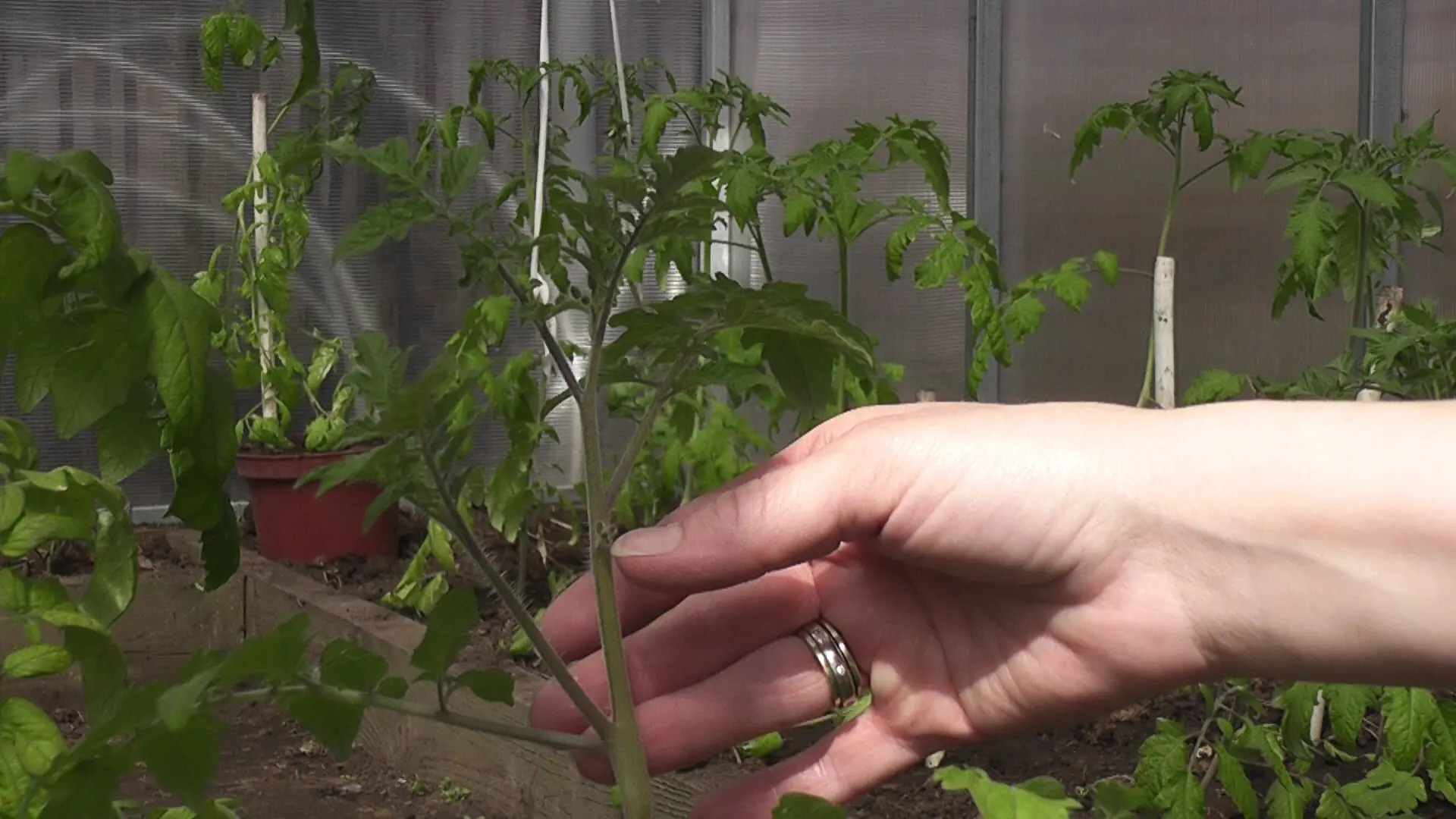
The fewer stems left on each tomato, the better the harvest will be. Low, that is, determinant varieties of tomatoes sometimes grow quite richly, their stems branch quite strongly. Five to seven inflorescences per plant can produce an acceptable yield. The first fruits stop the tillering process. However, these varieties feed their fruits very slowly, since a large number of them need a lot of vitamins of the same type.
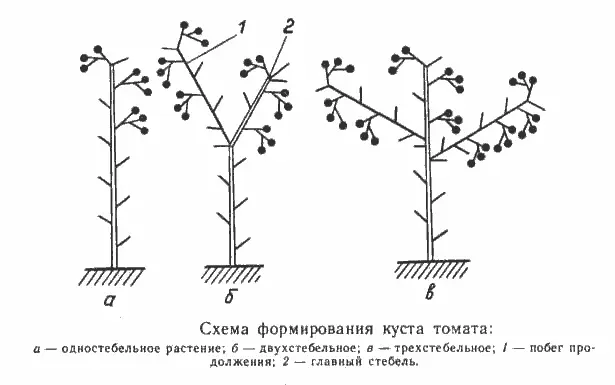
Scheme of the formation of a tomato bush
The harvest is given much later – one bush is obliged to feed the already grown tomatoes, and at the same time provide a complex of minerals and vitamins for the same small fruits, which can be from 10 to 15. For the same reasons, the size of the fruits may also suffer – we get very small ones, although we win in their number.
Indeterminate varieties of tomato have a very strong one main shoot, give more yield and ripen later than undersized ones. Almost all varieties of tall tomatoes lend themselves to pinching. 2-3 stems form the full growth of the plant. More sprouts require subspecies – “cream”, and the like. They also depend on weather conditions, if the summer lasts longer than usual, then you can leave more fruit brushes, as well as grow stems. Indeterminate tomatoes bush very strongly on their own, so the growth process must be controlled in order to get a rich harvest.
It is important to have time to remove the shoots even before the appearance of the first brush with fruits. 6, 8 or 10 leaf is a sign that the fruit brush will appear soon.
Branches appear in the axils of each leaflet, and may grow quite large before the time we require. Shoots that grow lower try faster – the benefits of them in this case are obvious. Therefore, tall indeterminate types of tomato are stepchildren necessarily – after all, a tall stem makes it possible to grow very strongly, bush and create lateral processes that require moisture and energy.
When is the best time to stepchild
The best option for pinching tomatoes would be to carry out the procedure once a week. However, this period is not exclusive or mandatory. When grown indoors, extra shoots should be removed more often. The process of mechanical removal of such shoots in undersized species is a little more difficult, because they are more magnificent and it can be difficult to get to the required sites.
When to start pinching tomatoes? Sprouts are best cut or removed with gloved hands while still small, 3-5 centimeters long. A large shoot can cause problems in plant growth. The tomato does not notice the removal of the shoot with its small size, and will not get sick.
In the greenhouse
Carrying out pinching of tomatoes when grown in a greenhouse should have its own separate goal – to extend the fertility of each plant. Another task is to increase the yield. In the greenhouse, determinant tomato varieties are bred most often. Greenhouses can be used for almost six months, hybrids and indeterminate varieties are suitable for greenhouse cultivation to the fullest. Different varieties are processed in different ways.
Determinate varieties grow in such a way that the main stem should be left for them. How and when is it right to pinch in a greenhouse? This should be done much more often than on open ground. Medium and tall tomatoes should not have reserve shoots, since the development of inflorescences does not affect growth. Since in the greenhouse there will be fewer inflorescences on the main stem than usual, you can plant tomatoes closer to each other.
In open ground
In the open field, it is correct to remove the sprouts even before the appearance of the fruit part. Usually it appears after the appearance of 6-8 or 10 sheets. The sinuses of each leaflet are capable of producing lateral processes. How to pinch tomatoes in the open field? The answer is simple – as soon as the first fruit brush appears, such stepchildren can already be quite large. In addition, the lateral stems are located below the shoot, and are fed faster.
If you do not follow the established pattern, the fruit brushes will be forced to lay through the leaf, and in the bosom there will be a stepson sufficiently developed for growth. Thus, the gardener can get a huge amount of green mass and very little yield. Therefore, stepchildren should not be neglected. Tomatoes that do not need pinching will not create a critical mass that qualitatively affects crop growth.
In especially undersized shoots, 1-2 stems are left after the processing process. So the fruits will ripen only on the first inflorescences. One shoot is left on one stem, one stepson is left on two, and one more below is left on three. Each of them should create up to three inflorescences. Three stalks create the possibility of getting green unripe tomatoes among the fruits.
Video “Staging different varieties of tomatoes”
A note on how to properly pinch tomatoes in a greenhouse. After watching the video, you will learn how to form bushes of indeterminate and semi-determinate tomatoes.









