Contents
Botanical description of calamus

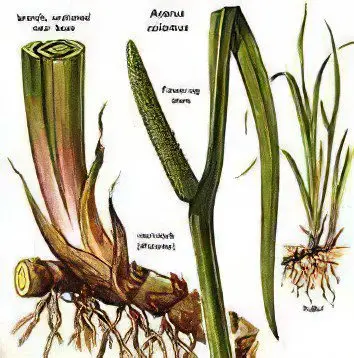
Calamus marsh is a tall perennial herbaceous plant that belongs to the Aronnikov family. This plant has a brown color, its rhizome is thick and creeping, the leaves are sharp, reach 1 meter in length and are shaped like a sword, they cover each other with their bases. The stem, on which there are flowers, begins at the top of the root. This green root has a rib on one side and a groove on the other. Above the cob is the upper part of the cob, also called the spathe, because it looks like a leaf. This cob has the shape of a cylinder, it deviates from the stem. The ear has many flowers, which are located on the fleshy axis.
Calamus marsh grows on highly moist soil, it is strengthened in the soil with its strong root, which has many branches. The length of the root reaches 150 cm. Calamus marsh grows near water, on the banks of lakes and rivers, in swamps, it forms large thickets, which are pure, and sometimes with mixtures of sedges and horsetails. It grows in the middle and southern strip of the European part of Russia, it can be found in Eastern Siberia and the Caucasus. It grows well in the steppe and forest-steppe zones, along the banks of reservoirs, on swampy soils, flooded fields and in gullies.
Collection and preparation of calamus
Today, not everyone can find and collect calamus, but many still find it and make blanks out of it. To make it easier for people, special farms have been created that grow calamus. From the beginning of autumn to the beginning of winter, calamus is prepared: it is pulled out of the silt with a rake or pitchfork. Then the already collected roots must be washed from contamination, cut off the remaining leaves. After that, the roots should be wilted, leaving the plant in the open air. Next, you need to cut the roots into pieces, the length of which is 10–20 cm. And if the root is very thick, then it needs to be split along.
The raw materials are dried under an iron roof at a temperature of + 30–35 ° C, the temperature cannot be raised, since the essential oil quickly disappears. Rhizomes are considered well dried when they break easily. The essential oil in the calamus rhizome is approximately 5%, it also contains tannins, ascorbic acid, resins, copper, and starch.
Dried calamus blanks are spongy pieces of roots that are very light. Unpeeled roots are flattened, slightly curved, the outer color is yellowish-brown, with a reddish or grayish-green tint. For the most part, the dried roots are split. The peeled and split roots of the plant at the break and on the outside should be white or pinkish. The dried raw material smells peculiar and has a spicy-bitter taste.
Useful properties of calamus
Since ancient times, people have known that calamus has many medicinal properties. This plant is very often used in folk medicine. A vodka tincture is made from the roots of calamus marsh, which is used for medicinal purposes. A decoction of calamus helps with liver diseases, diseases of the bladder, nervous system, and tuberculosis. And also tincture of calamus is used for rheumatism. If a person has heartburn, then calamus root will help him, which you just need to chew.
A decoction of calamus roots is used by people who want to strengthen the hair on their heads, as well as those suffering from lichen. Women’s diseases can also be cured with the help of calamus – douching should be done with its decoction.
Putrid wounds are sprinkled with calamus powder. People who complain of stomach pains can take a decoction of calamus inside.
The roots of the plant have an effect that increases appetite, improves digestion, and also enhances the reflex separation of juice in the stomach.
Today, calamus is used in medicine as a remedy for peptic ulcer. And in veterinary medicine, the roots of calamus have found application as a gastric remedy.
The chemical composition of calamus
Calamus root contains: essential oil, tannins, acorin glycoside and calamine alkaloid. Calamus leaves also contain tannins and essential oil. The essential oil consists of a mixture of terpenes, sesquiterpenes, and the odor carriers are azarylaldehydes.
Also in the roots of calamus there is a little unscented soap, and the root of calamus also contains vitamins, starch, protein, minerals – all of them are related substances.
Application of calamus
The use of calamus in alternative medicine is quite diverse. Fresh roots are used to disinfect water. Decoctions are prescribed for diseases of the teeth and gums. Calamus bog is effective in diseases of the biliary tract and liver, kidney stones. For leukemia, a therapeutic herbal collection is used, which includes calamus root, nettle and elecampane. Calamus is useful for improving digestion and raising appetite.
Calamus rhizomes are sometimes used for diseases of the central nervous system. Powdered, they help with heartburn, diarrhea and bad breath. Calamus preparations reduce blood pressure and increase sputum secretion. They are useful to take with gastritis with low acidity of the stomach. The plant is also used for the rapid healing of wounds. In gynecology, a decoction of calamus is used for diseases of coccal and trichomonas etiology, secondary amenorrhea, and ovarian failure.
Video: medicinal properties and contraindications of calamus, and how to use it?









