Contents
Hello my dear readers! Today we will talk about motivation again, namely, we will consider what is interesting about Alderfer’s theory. I will tell you who its founder is and what is the value of his judgments.
Who is Clayton Alderfer and what is motivation?
Clayton Paul Alderfer is an American humanist psychologist. He was born on September 1, 1940 in the USA. Became a psychologist at Yale University. In many ways, his views were similar to those of Abraham Maslow.
For many years, scientists from different areas of psychology have been studying the phenomenon and concept of motivation. Can we define this word? Can. Simply put, motivation is what drives people to act.
Psychologists distinguish many types of motivation, study what exactly induces a person to do something or not to do something. They also take a deep look at the hierarchy of needs and how they influence our behavior.
What is Clayton Alderfer’s Theory of Motivation?
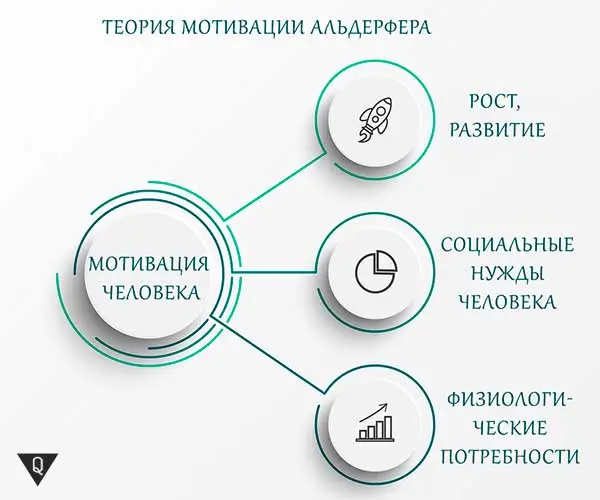
As I said, Alderfer strongly supported Maslow’s ideas. However, in the 70s of the last century, he put forward his own interpretation of the theory of needs. His brainchild was the theory of motivation, which is known as the ERG theory.
Why are three capital English letters used here, you ask? Everything is simple. For the name, the capital letters of the category names used by the psychologist were taken:
- E — existence, existence;
- R — relatedness, which translates as «connectedness», but implies communication and relationships in society;
- G — growth, growth, development.
I would like to note that Alderfer took the pyramid of needs of his predecessor as a basis, identified a number of shortcomings in it and presented his concept to society. Unlike Maslow’s theory, in Alderfer’s development, human needs are divided into 3 main groups, which were discussed above.
It is worth saying that the new judgment has many advantages that the previous one did not have. But I would like to highlight two of them:
- Firstly, the number of categories has been reduced from 5 to 3.
- Secondly, there is no clear hierarchy of needs.
As you know, with Maslow it is possible to move to the next level only after all the needs of the previous (lower) level are satisfied. Alderfer, on the other hand, allows movement both from the bottom up and in the opposite direction. If the movement is upward, then the person is satisfied, and if downward, then he is in a state of frustration (in short, the person fails in trying to satisfy his needs).
I draw your attention to the fact that Alderfer’s pyramid of needs shows the way to meet specific needs to more abstract ones. Top-down movement (or regression) occurs due to the transition from an abstract need to a more specific one, if the first has not been satisfied.
Existence, connection and growth
Next, we will talk about each of the Alderfer categories in more detail.
So, we have 3 main groups, which include the needs for existence, connection and growth:
- The psychologist refers to the first group physiological needs — food, water, air, sleep, sexual desire, etc. It also includes factors that ensure both safety and working conditions.
- The second group reflected the social needs of a person, including group security, the desire to obtain social status, to be realized in the family, to receive recognition from others for success and achievements, to assert themselves in the team (at work, in the family circle and among friends).
- Needs group number 3 is a combination of self-realization, self-esteem, the desire to develop and improve, as well as the desire to express yourself in the workplace and in creativity.
Practical Approach
Alderfer’s theory has found its practical application in many organizations, as it allows you to use a wide range of opportunities for motivating staff.
Next, I propose to consider the behavior of people, according to each of the groups of needs:
- Existence. A person who cares about the satisfaction of the desires of this group will have little interest in the subtleties and content of his profession. The main thing he will focus on is the amount of wages, the conditions where he works, as well as opportunities for recreation in the process of work.
- Connection. In the collective, the needs of this group can be realized when all kinds of events are organized. In the presence of connections, the worldview of a person changes. Here he works not only for the sake of material reward, but also for the sake of feeling his value as a specialist, as part of the whole, because now he belongs to a certain team.
- Growth. People who satisfy the needs of the highest category strive to become leaders in order to be recognized for their qualities. Such people need encouragement and rewards.
Conclusion
I draw your attention to the fact that each of the needs can become relevant at any moment, regardless of the level at which it is located.
Visit my blog. Here you will find a lot of interesting information for yourself and not only. Subscribe and bring your friends.
Finally, we recommend reading an article about the theory of 10000 hours.
See you soon friends.









