Contents
Prostatitis is a very common disease of the prostate gland, which affects the entire genitourinary system of a man. Various types of prostatitis are diagnosed in 30-60% of men over the age of 30. Prostatitis is sometimes non-infectious (congestive) in nature, but more often it is an infectious process that is caused by various bacteria entering the gland1.
What is acute prostatitis?
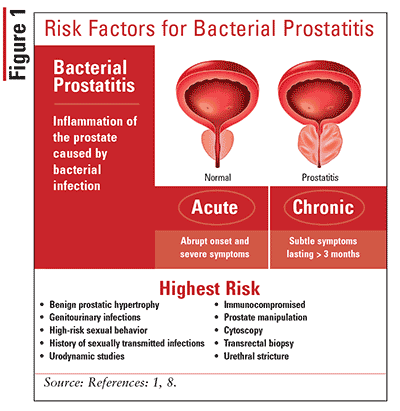
Acute prostatitis is a rather rare (unlike chronic) inflammation of the prostate gland caused by the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into it. At the same time, the development of inflammation always occurs against the background of provoking factors: frequent hypothermia, sedentary work, prolonged abstinence, etc.
Acute prostatitis in men is always a dangerous condition requiring immediate medical attention, as it can lead to serious complications, including sepsis1.
Causes of acute prostatitis
Most often, the development of acute prostatitis causes Escherichia coli (E. coli) – it accounts for more than 80% of cases. Less commonly, acute prostatitis is caused by Proteus, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, and Enterobacteria.
Microorganisms enter the prostate through the urethra, through the circulatory and lymphatic systems. Very often, “reflux” of bacteria occurs during surgical or internal diagnostic manipulations on the pelvic organs – ureteroscopy or the installation of a catheter into the bladder2.
It happens that pathogenic bacteria penetrate the prostate from a chronic infectious focus, which can appear in any organs and tissues. Thus, even a banal sinusitis or bronchitis can become the cause of the disease.2.
However, the entry of bacteria into the prostate does not mean the development of the disease. This requires provoking factors, which include:
- congestion in the prostate gland;
- sedentary lifestyle, which leads to circulatory disorders in the pelvis;
- frequent hypothermia;
- prolonged sexual abstinence;
- frequent change of sexual partners and unprotected sex.
To this list, you can add smoking, abuse of spicy, fried and fatty foods, mental and physical overload.
Symptoms of acute prostatitis
Symptoms and their intensity depend on the form of acute prostatitis and the general health of the man. The most characteristic signs of the disease include:
- soreness in the lower abdomen. Pain can be given to the scrotum, rectum, lower back or perineum;
- temperature increase;
- chills, general malaise, muscle and joint pain;
- urination disorders, frequent urination (especially at night)2;
- intermittent and “sluggish” urine stream;
- pain when urinating;
- impurities of mucus and blood in the urine;
- decreased potency, frequent nocturnal erections, pain during ejaculation3.
Forms of acute prostatitis
Depending on the degree of development of the disease, 4 forms of acute prostatitis are distinguished3:
- catarrhal form. Only the mucosa of the excretory ducts of the gland is affected. It is characterized by a slight increase in temperature, a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen, frequent urination.
- follicular form. The lobules of the prostate are affected. The temperature rises significantly, a dull aching pain appears in the perineum, which radiates to the sacrum and anus. There are painful sensations during defecation and urination.
- Diffuse (parenchymal) form. The whole gland is involved in the process. The temperature and pain syndrome rise sharply (up to 39 ° C and above), the patient’s condition deteriorates sharply. Partial or complete retention of urine appears. When you try to urinate or defecate, excruciating pain occurs.
- Abscess form. Extensive suppuration of the prostate develops – an abscess. This condition requires immediate surgical intervention.
Treatment of acute prostatitis
Treatment of acute prostatitis is rarely performed on an outpatient basis and usually requires hospitalization of the patient in a specialized hospital. The main therapy is aimed at suppressing pathogenic bacteria, combating intoxication of the body and eliminating the symptoms of the disease.
Diagnostics
Since the symptoms of acute prostatitis are very specific and pronounced, the diagnosis is usually straightforward.
First, the doctor, using palpation, determines the degree of involvement in the process of the departments of the gland. Also, the patient is prescribed a general analysis of blood and urine. Bacteriological analysis of urine, secretions or scrapings from the urethra allows you to identify the pathogen and determine its sensitivity to various groups of antibiotics. As a rule, an ultrasound of the prostate is additionally performed. After analyzing the results, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive treatment regimen for the disease.
Therapies
Treatment of acute prostatitis is usually prescribed complex and is aimed at eliminating both the cause and the symptoms of the disease.3.
- Antibacterial therapy (to fight the bacteria that caused prostatitis).
- Detoxification (elimination of manifestations of intoxication of the body).
- Symptomatic therapy (prescription of analgesics, antispasmodics and anti-inflammatory drugs, immunomodulators and vitamins).
- Physiotherapy (after the end of the acute stage, massage, laser therapy and electrophoresis are prescribed).
- In the case of the formation of purulent abscesses of the gland, they resort to a surgical operation.
Folk remedies
In the treatment of acute prostatitis, folk remedies can only be of an auxiliary nature. It is impossible to replace them with medical treatment. Decoctions and infusions of herbs, homeopathy and other remedies can help calm the nervous system, relieve tension, normalize bowel function, increase immunity and saturate the body with vitamins and useful microelements.
Do not self-medicate and remember that sepsis can be a common complication of acute prostatitis. In this case, only a doctor can save the patient from death.
Prevention of acute prostatitis
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle will help prevent acute prostatitis. Eat a balanced diet, avoid gaining excess weight, monitor bowel function. Try not to overcool, do not abuse alcohol and smoking. Lead an active lifestyle, move more, exercise and exercise. Avoid stressful situations and watch your immunity.
A special place in the prevention of prostatitis is the hygiene of sexual relations. Avoid casual sex and unprotected sex. Prolonged sexual abstinence can also lead to stagnant processes in the prostate gland and the development of prostatitis.
Regular preventive examinations by a urologist will help minimize the risk of the disease.
Popular questions and answers
How long acute prostatitis lasts and how to quickly relieve pain, our expert answered general practitioner Mikhail Lystsov.
How long does acute prostatitis last?
How to quickly relieve pain with prostatitis?
Why is acute prostatitis dangerous?
Sources of:
- Medical encyclopedia. — Astrel, 2009. https://search.rsl.ru/ru/record/01000718460
- “Prostatitis. Diagnosis and treatment. Management”. Kulchavenya E. V., Neimark A. I. Publisher: GEOTAR-Media, 2010 Series: Library of a medical specialist. https://medknigaservis.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/Q0111402.pdf
- Pharmacotherapy of acute and chronic prostatitis. Evdokimov V.V. Difficult patient, M., 2010. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/farmakoterapiya-ostrogo-i-hronicheskogo-prostatita/viewer