Contents
Acute pharyngitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the throat of an acute course. Acute pharyngitis can act as an independent pathology, or be a consequence of other diseases.
As an independent disease, pharyngitis develops when the infectious agent directly affects the mucous membrane of the throat, or when it is exposed to external and internal stimuli (lack of nasal breathing, alcohol intake, smoking, etc.). As for the fact of the development of acute pharyngitis as a secondary disease, inflammation often manifests itself against the background of disorders in the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract infections, etc. It is extremely rare that acute pharyngitis occurs in isolation. As a rule, the inflammation process includes departments in contact with the pharynx (nasal sinuses, larynx, trachea).
Causes of acute pharyngitis
The causes of acute pharyngitis are varied, among them:
Viral infection. It is viruses in 70% of cases that cause inflammation of the mucous membrane of the throat. Rhinoviruses, influenza viruses, adenovirus, enteroviruses, coronaviruses, parainfluenza virus, etc. have etiological significance.
bacterial infection. Various bacteria provoke the development of acute pharyngitis in 30% of cases. These are pathogenic microorganisms such as Haemophilus influenzae, streptococci, diplococci, gonococci, chlamydia, mycoplasmas, etc.
Fungal microorganisms. As a rule, in order to develop acute pharyngomycosis, it is necessary to influence disease-provoking factors, among which are treatment with glucocorticoids, long-term use of antibacterial drugs, diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency states.
Irritant effect of allergens on the mucous membrane of the throat. Allergens can be present both in the inhaled air and ingested with food and medicines. If it is not possible to identify components that irritate the mucous membrane, then gradually the acute phase of pharyngitis will turn into a chronic one.
Acute pharyngitis can develop against the background of a throat injury. These include chemical burns with acetic and other acids, alkalis, alcohols, thermal burns with steam or boiling water, as well as mechanical injuries. The latter can be obtained as a result of a foreign body entering the throat, when injured, during surgical interventions.
Separately, it is worth noting that in order for a person to develop acute bacterial or viral pharyngitis, it is necessary not only to become infected with the infection itself, but also to drop local immune defenses.
Therefore, additional risk factors predisposing to the formation of acute inflammation are:
Adherence to various diets that lead to metabolic disorders, to the depletion of the body.
Hypothermia of the body. Both local and general hypothermia matter.
Taking drugs that suppress the immune system.
Severe chronic diseases.
Increased concentration of dust, gases, smoke and other irritating substances in the air. Often the impact of this factor is explained by occupational hazards.
Abuse of alcohol, smoking.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, for example, gastroesophageal reflux, hiatal hernia, gastritis.
Chronic inflammation in the nasal cavity, in the paranasal sinuses, in the nasopharynx.
Dysbacteriosis.
Symptoms of acute pharyngitis
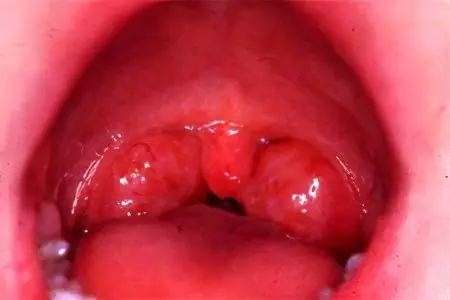
Symptoms of acute pharyngitis develop against the background of pathomorphological changes in the mucous membrane of the throat. So, it becomes edematous, the vessels expand and are injected, the epithelium of the throat undergoes desquamation (desquamation of scales). Often the auditory tubes are involved in the pathological process.
The reaction of mucosal inflammation is especially pronounced in those places of the throat where there is an accumulation of lymphoid tissue – this is the back wall, side ridges. In acute pharyngitis, as well as in the chronic form of the disease, granules can form, represented by inflamed and swollen follicles in the back of the throat. Objective symptoms of acute pharyngitis are:
There was a burning sensation, perspiration, dryness and soreness in the throat.
Hoarseness of voice.
Ear congestion.
Sensation of a foreign body in the throat.
Increased pain in the throat when swallowing, their irradiation to the ear.
Body temperature most often remains normal, although sometimes it can rise to subfebrile levels. If the inflammation is severe, then the mark on the thermometer will reach a value of 38 ° C and above. At the same time, signs of general intoxication of the body are added with weakness, fatigue, muscle pain, etc.
Perhaps an increase in regional lymph nodes, the appearance of headaches.
It causes pain when an empty sip is taken to swallow saliva. The intensity of pain in this case will be higher than during meals.
A mucopurulent secret flowing down the back of the throat makes the patient cough. In order to get rid of sputum, the patient will constantly cough, trying to get rid of a thick secret. Especially strong cough in the morning or during a long conversation.
Diagnosis of acute pharyngitis

Diagnosis of acute pharyngitis for a specialist is not difficult. The diagnosis is made on the basis of the patient’s complaints, after his examination.
With pharyngoscopy, the doctor visualizes the hyperemic mucous membrane of the throat, its swelling. In some places, mucopurulent plaque accumulates. The tonsils, palatine arches, orifices of the auditory tubes are often inflamed.
It is important to make a differential diagnosis with catarrhal angina, diphtheria and other respiratory tract infections, as they give similar symptoms.
To clarify the diagnosis and to determine the type of causative agent of pharyngitis, in some cases, a swab is required from the back of the throat. The smear is sent for microbioscopic examination.
Treatment of acute pharyngitis
Treatment of acute pharyngitis, which has a mild course, can be limited to symptomatic therapy. This includes a sparing diet, taking hot foot baths, applying warm compresses to the neck, steam inhalations, nebulizer inhalations, gargling with antiseptic solutions and irrigation with special medicinal formulations.
At the time of treatment, it is important to minimize all factors that irritate the throat mucosa. To do this, first of all, you need to stop smoking. If the disease is not bacterial in nature, then taking antibiotics is not advisable. Systemic administration of antibacterial drugs is required for complicated acute pharyngitis. In all other cases, local antimicrobial therapy can be limited.
Antimicrobial agents are prescribed in the form of rinses, inhalations, lozenges.
When choosing a drug, it is important to consider the following points:
The tool should have a wide spectrum of action and fight not only bacteria, but also viruses.
The drug should not have a toxic effect on the body.
Absorption of the drug from the mucous membrane of the throat should be slow.
The selected agent should not have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane.
For the treatment of a mild form of acute pharyngitis, you can use antiseptic agents in the form of tablets. These can be drugs Geksaliz, Faringosept, Septolete, Strepsils, etc. However, it is worth remembering that lozenges and lozenges for resorption have weak antibacterial activity, which requires an integrated approach to treatment. In addition, their intake cannot be uncontrolled, since the active ingredients of such tablets are medicines and can be harmful to health. This is especially true for pediatric patients.
Iodine preparations should be used with caution, as they are highly allergenic and can strongly irritate the mucous membranes. This applies to drugs such as: Povidone-iodine, Vokadin, Iodinol, etc. The same rule applies to products with propolis – Proposol and sulfonamides – Ingalipt, Bicarmint.
Also for local treatment, you can use the drug Imudon, which contains lysates of 10 bacteria and two mycotic microorganisms. Getting on the mucous membrane of the throat, the drug activates phagocytosis, increases the number of immune complexes, which allows the body to actively fight inflammation. Imudon can be included in the scheme of complex treatment of pharyngitis with the use of systemic and local antibiotics. This has been proven to promote a speedy recovery.
In the form of a solution for gargling and in the form of an aerosol for topical application, Hexoral can be used. It is non-toxic and highly active against most bacteria that cause pharyngitis. In addition, irrigation of the throat with Geksoral helps to get rid of pain due to the analgesic included in its composition.
Octenisept has the widest spectrum of action against not only most gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, but also against mycoplasma, chlamydia, fungi and viruses. However, it is used mainly in the conditions of medical institutions, since there are no convenient forms for the release of this drug for independent use.
The composition of the complex therapy of acute pharyngitis can include antihistamines (Suprastin, Diazolin, Zirtek, Zodak, etc.) that well relieve swelling from the mucous membrane. To increase the body’s resistance to other infections, the patient is prescribed immunocorrector drugs – these are IRS-19, Tonsilgon, Imudon and others.
If body temperature rises, there is a risk of descending infection or other complications, and the inflammation itself is severe, then systemic antibiotics are recommended. The drugs of choice are the penicillin group, in particular Phenoxymethylpenicillin. It is this drug that has the maximum activity against group A streptococci, which provoke rheumatic heart disease.
As for nutrition, it is important to refuse spicy, pickled and salty dishes. Food and drink should only be consumed while warm, making sure they are neither too hot nor too cold.
It is advisable to adhere to bed rest during an exacerbation of the disease and minimize contact with other people. This will reduce the recovery time and prevent the transition of the disease into a chronic form.









