Contents
Acute adnexitis is one of the most common diseases in women, which is characterized by inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries. These organs are of great importance for women’s health, so adnexitis requires high-quality and timely treatment.
Causes of acute adnexitis
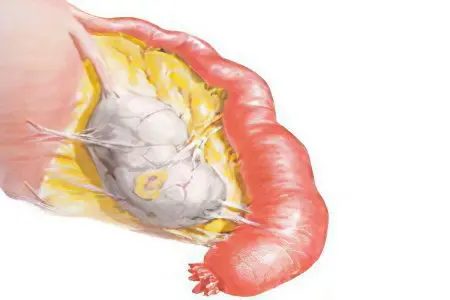
The causes of acute adnexitis can be very diverse:
Infection with microorganisms such as mycoplasmas, gonococci, chlamydia, Trichomonas, etc. Most often, they penetrate the female genital organs through the vagina during intercourse.
Surgery on the organs of the reproductive system can also cause infection. This occurs when sanitary and hygienic measures are not observed in a medical institution and the medical staff is negligent in their activities. In this regard, the medical curettage of the uterus, the installation and removal of the intrauterine device, and the conduct of studies accompanied by the introduction of a contrast agent are of particular danger.
Abortion and artificial childbirth are associated with the risk of infection and the further development of adnexitis. Most often, inflammation develops on the condition that the patient already has an infection, for example, in the intestines or in the vulva.
Even those foci of inflammation that are far from the appendages, for example, otitis media, tuberculosis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, etc., are dangerous in terms of the development of adnexitis. Microorganisms enter the tubes and ovaries with the bloodstream, causing adnexitis.
The weaker the immune defense of a woman, the higher the risk of developing inflammation of the appendages. The body simply will not have enough strength to cope with the infection that has penetrated inside.
Symptoms of acute adnexitis

Symptoms of acute adnexitis can be distinguished as follows:
Pain that is aching or throbbing. It is localized in the region of the ovaries. During the next menstrual bleeding, the pain tends to increase. It also becomes more intense during ovulation, after serious physical exertion, or against the background of a sharp hypothermia of the body.
Discharge from the vagina becomes pathological. Impurities of mucus are found in them, and as the disease progresses, pus appears.
The menstrual cycle is disrupted. Menstruation may be absent for a long time, or it may take longer than usual.
Adnexitis is characterized by symptoms of general intoxication of the body with an increase in body temperature up to 38 °, the appearance of fatigue and weakness.
Patients lose their appetite, which leads to digestive disorders.
Against the background of acute adnexitis, cystitis often develops.
If you experience symptoms that indicate adnexitis, you need to go for a consultation with a gynecologist. This will cure the disease until it becomes chronic.
Depending on where exactly the inflammation is localized, there are:
Adnexitis is bilateral, when inflammation develops in both the right and left appendages. The pathological process is accompanied by severe intoxication of the body, a significant deterioration in well-being. During the examination, the doctor detects increased muscle tone in the lower abdomen. The woman points to pains on both sides of the navel. The blood picture shows leukocytosis with a shift of neutrophils to the left.
Right side adnexitis. In this case, the inflammation affects only the right appendage, so the pain is localized mainly on the right side, in the lower abdomen and near the navel. Often right-sided adnexitis is confused with appendicitis, therefore, in addition to the gynecologist, the patient should be examined by a surgeon.
Left side adnexitis. The inflammatory process affects the left appendage, which is expressed by characteristic pains. They are able to increase during intimacy, as well as during menstruation.
Diagnosis of acute adnexitis

During the first visit to the gynecologist, the doctor will take a woman’s history, clarify whether she had childbirth, abortion, or surgery on the organs of the reproductive system. Then the doctor will examine the patient on the gynecological chair, take a swab from the cervical canal, urethra and vagina. The resulting material is sent for bacteriological examination in order to determine the type of pathogen. During a vaginal-abdominal examination, the doctor will find painful appendages (one or both), which are enlarged.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs in terms of detecting adnexitis is not informative, so it is not prescribed.
Blood sampling for a general analysis will detect an increase in ESR and a jump in the level of leukocytes.
Laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes is one of the most accurate methods for diagnosing adnexitis. It is recommended to those women who definitely need surgical treatment. During laparoscopy, the doctor can not only sanitize the pipes, but also remove adhesions, cysts and other neoplasms.
Treatment of acute adnexitis

Acute adnexitis requires antibiotics. The drug is chosen depending on which microorganism provoked the development of inflammation. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are also used.
These can be drugs such as:
Amoxicillin, Oxacillin (a group of penicillins).
Doxycycline, Tetracycline (tetracycline group).
Azithromycin, Erythromycin (macrolide group).
Ofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin (a group of fluoroquinolones).
The doctor may prescribe a different drug for the woman, depending on the results of the bacteriological examination of the smear. To eliminate inflammation, sulfonamides, for example, Biseptol, can be used.
To increase the patient’s immunity, as well as speed up the process of repairing damaged tissues, biogenic stimulants are prescribed, including Plasmol and aloe extract.
Additional therapeutic measures are physiotherapy: UHF, electrophoresis, mud treatment, magnetotherapy, etc. It is also possible to take vitamins and minerals, which are aimed at improving the body as a whole.
Prevention of acute adnexitis

To prevent the development of acute adnexitis, the following recommendations should be observed aimed at preventing the disease:
Intimate hygiene should be of high quality and daily.
Casual sex should be kept to a minimum. If they do occur, then a condom should be used.
During menstruation, intimacy, swimming in open water and pools are prohibited.
It is necessary to give up bad habits, eat right, which will help maintain immunity.
If a woman is menstruating, then tampons and pads should be changed at least once every 1 hours.
You need to change your underwear every day.
You can not douche on your own, either for therapeutic or prophylactic purposes. Douching can only be prescribed by a doctor. The solutions and the device itself must be sterilized.
Factors such as hypothermia, frequent stress, overwork, poor-quality or insufficient night sleep weaken the immune defense, so they need to be eliminated from your life. You should play sports and spend as much time as possible in the fresh air.
All foci of infection must be treated in time, and this applies to any organs, regardless of their removal from the appendages.
If a woman has unusual vaginal discharge, her lower abdomen hurts, menstruation does not start on time, then it is necessary to consult a gynecologist for advice.
Forecast
If acute adnexitis is detected in time and treated, then the disease does not pose a danger to a woman. When adnexitis becomes chronic, its course is complicated by the formation of adhesions in the fallopian tubes. They, in turn, are the main cause of female infertility, as well as the development of ectopic pregnancy. Therefore, when the first signs of inflammation of the appendages appear, you should not hesitate to visit the doctor’s office.









