Contents
Actinomycosis in cattle is a disease known since the 1970s. The causative agent of the pathology was identified by the Italian scientist Rivolt. Later this discovery was confirmed by German researchers. In the modern world, actinomycosis is spreading more and more, affecting a huge number of cattle (cattle). All about the symptoms, methods of diagnosis and treatment of the disease further.
What is actinomycosis in cattle
Actinomycosis occupies a leading position among cattle diseases. This disease has been known since ancient times. Scientists examined the jaws of a rhino that lived in the Tertiary period. On them, they found changes characteristic of actinomycosis.
The main target for infection is cattle. Sometimes pigs get sick, and most rarely other animals. Most often, the disease affects such areas of the body of a cow:
- lower jaw;
- gum;
- sky;
- space between jaws;
- throat
- The lymph nodes;
- salivary glands.
Separately allocate the defeat of the udder, tongue. In the photo, actinomycosis of cattle looks like this.
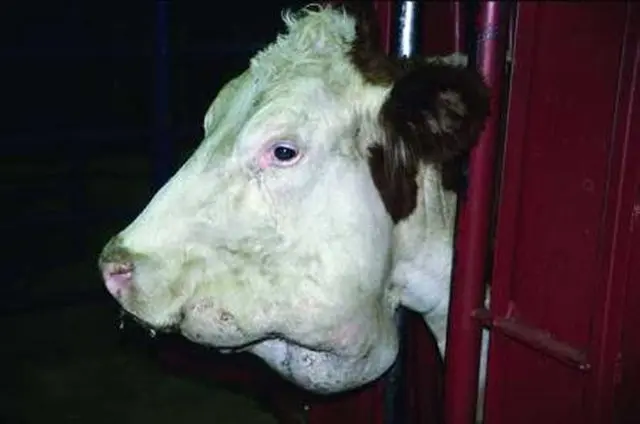

Causes of actinomycosis in cows
The causative agent of actinomycosis is the fungus Actinomyces bovis. In atypical cases, other types of fungus are isolated. In the exudate (inflammatory fluid), the pathogen is isolated in the form of small brown grains, which are also called drusen. They are gray or yellow in color.
When examining smears of sick cows under a microscope, the fungus looks like tangled threads. Moreover, their diameter is uneven: there is a thickening on the periphery and a thin area in the middle.
But the fungus is not the only causative agent of actinomycosis. Sometimes, when examining pus, bacteria are isolated:
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- protea;
- staphylococci or streptococci.
Some researchers argue that actinomycosis causes an association of fungi and bacterial flora.
Actinomyces bovis actively develops under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. This means that the fungus does not care if there is access to oxygen. When heated to 75 ° C, the causative agent of actinomycosis is destroyed within 5 minutes, and the formalin solution kills it in 3 minutes. In the environment, actinomycetes survive for 2 years, they are resistant to low temperatures.
The causative agent of actinomycosis enters the body of a cow through damage to the skin, wounds in the mouth, nipples in the udder. The infection can enter through the respiratory tract, rectum. Sometimes cows become infected endogenously. Actinomycetes, which are present in the intestines and oral cavity of healthy cattle, are suddenly activated and cause an inflammatory process.
In the case history of actinomycosis in cattle, in most cases there is a history of trauma, which served as a gateway for infection. The source of infection with actinomycosis can be food contaminated with pathogenic fungi, water and other objects with which cows interact.
From the gate of infection, the pathogen spreads through the connective tissue and subcutaneous fat. Therefore, actinomycosis is most often local. Sometimes it spreads through the blood throughout the body.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations of actinomycosis in cows depend on the localization of the pathological process, the state of the animal’s immune system, and the aggressiveness of the pathogen. But all varieties of cow disease have several common features. Any form of actinomycosis is chronic. The disease begins with an incubation period. It represents a period of time when the pathogen is already active in the body of a cow, but clinical manifestations have not yet been observed.
Another common symptom is the formation of actinomycomas in cows. This is a volumetric formation, which in its essence is a benign tumor. It grows slowly, does not hurt, has a dense texture.

When the head is affected in cows, dense knots are formed that grow both outward and inward, into the pharynx. Soon, fistulas form on the actinomycomae. Through them, yellowish pus is released, which contains grains. These inclusions are the drusen of the fungus. After a certain time, small areas of the skin begin to die off, so impurities of torn tissues appear in the pus. The color of the discharge becomes reddish. The fistula then opens, then overgrows.
With the growth of the tumor in the pharynx, the cow begins to breathe with difficulty, it is difficult for her to swallow. As a result, due to a violation of the act of swallowing, the animal loses weight. Despite the abundant discharge of pus, the temperature most often remains normal. The increase is typical only for generalized actinomycosis.
With the defeat of the jaws or the space between them, the shape of the head of the cattle changes. The jaw of cows increases several times. Sometimes inflammation spreads to surrounding tissues, which causes fistulas (holes) to form in the sky, gums. A purulent mass flows out of them.
Actinomycosis of the udder of cattle is characterized by a predominant lesion of the posterior lobes. It is manifested by massive necrosis of the skin. First, dense ridges with a purulent cavity in the center are formed on the udder. Then fistulas develop in their place, from which a yellowish secret flows.
Actinomycosis of the tongue is characterized by widespread or limited inflammation of this organ. In the people it is called “wooden language”. In cows, an ulcer on the back of the organ is most often formed. The ulcer has a gray-white bottom with rollers along the edges.
Diagnostics
Treatment of actinomycosis in cows involves making a correct diagnosis. Most of the time it’s not in doubt. A professional veterinarian, already on the basis of clinical manifestations, may suspect actinomycosis. But in any case, laboratory confirmation is necessary for the selection of effective therapy.
Additional diagnostics consists in the study of pathological secretion under a microscope. To do this, take pus, granulomatous tissue, swabs from the oropharynx. Diagnosis of actinomycosis is carried out as follows:
- They take a secret or part of a tubercle suspicious for pathology.
- Wash them under water.
- Treated with an aqueous alkaline solution.
- Placed on a glass slide.
- Fix with 50% glycerin solution.
- Cover the top with a glass slide.
Only after all the preparatory stages have been completed, you can be sure of the quality of the study. But decisive in the diagnosis of actinomycosis is the sowing of the pathological secretion on nutrient media. However, bacteriological research is difficult.
Determination of the level of antibodies to the pathogen is not widely used in veterinary medicine, although it is widely used in the diagnosis of diseases in humans. Thus, the most commonly used method is microscopy.
When making a diagnosis, actinomycosis should be differentiated from other diseases of cows:
- actinobacillosis;
- streptotrichosis;
- young;
- epizootic lymphangitis;
- tuberculosis of the lymph nodes.
The most similar are actinomycosis and actinobacillosis. But in the first case, the bone is most often damaged, in the second – the soft tissues of cows. Pathogens under microscopic examination are excellent. The causative agent of actinomycosis has the form of long threads, actinobacillosis – sticks.
Tuberculosis of the lymph nodes differs from actinomycosis in that in the first case, the formation of an abscess is not characteristic. Cows infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis react during tuberculinization.
How to treat actinomycosis in cows
The main goal of disease therapy is the elimination of the pathogen. This implies the complete elimination of the fungus from the body of cattle.
In the initial period of the disease, iodine compounds are used. They are given to cows in the oral cavity and in the form of parenteral injections. Solutions of iodine and calcium iodide are injected intravenously. They are mixed with distilled water or saline sodium chloride solution. For 1 ml of iodine, take 2 ml of potassium iodide and 500 ml of water. But with such treatment, relapses of actinomycosis are possible.
To completely cure the cow, they turn to antibiotic therapy. The course of treatment is from 4 to 6 days. The duration depends on the severity of the course of the disease, the state of immunological resistance of the cow, the resistance of the pathogen. The most commonly used drug is Oxytetracycline. In the treatment of actinomycosis in adult cattle, the dose of the drug for one application is 400 IU, calves are given 000 IU.
Locally actinomycomes are chipped with “Polymyxin”. It also belongs to the group of antibiotics. 900 units are dissolved in 20 ml of novocaine. The latter is used for pain relief. The procedure is carried out 1 time in 10 days.
The course of treatment should be strictly the same as determined by the specialist. As a rule, therapy is continued for several more days after the complete cessation of clinical manifestations. This is the only way to completely get rid of the pathogen.
In the treatment of actinomycosis of cattle with antibiotics, potassium iodide is used as concomitant therapy. The dose for 1 injection is 100 ml of a 10% solution. Ultrasonic irradiation is becoming more and more widespread.
In localized forms of the disease, surgical removal of the tumor is considered the most effective. Actinomicoma is excised completely together with the capsule. To increase the effectiveness of therapy, the cow is preliminarily given a course of antibiotics. Moreover, drugs are administered both locally into the formation and intravenously. Below is a video of the surgical treatment of actinomycosis in cattle.
The room in which the sick cow was located must be disinfected without fail. To do this, use a 3% alkaline solution or freshly slaked lime.
Inexpensive but effective drugs for the treatment of actinomycosis in cattle
Preparations for etiotropic therapy (aimed at eliminating the pathogen) are inexpensive in most cases. At the same time, they are highly efficient. For the treatment of actinomycosis of cows, you can use the following antibiotics:
- “Penicillin”;
- “Benzylpenicillin”;
- “Okitetracycline”;
- Erythromycin;
- “Metronidazole” (effective for anaerobic infections).
Together with antibiotics, drugs of other groups are used. Among antiseptics, the drug “Monoklavit-1” is highly effective. This product contains iodine. It is effective for both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Its mechanism of action is to form a film on the surface of the wound, which protects it from environmental pollutants. External processing is carried out 1 time per day.
Zinaprim is another inexpensive but effective drug for the treatment of actinomycosis in cows. It is sold in powder form. The medicine is given to cows inside at the rate of 1 g per 10 kg of body weight. The course of treatment is from 3 to 5 days. “Zinaprim” also acts on gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. The drug should not be given to cows with hypersensitivity to sulfamethazine, the active substance of the drug.
It is impossible to ignore the biologically active additive “Polyfit-propolis”. The course of treatment of the drug is long. It is from 16 to 21 days. Therefore, it is used in combination with other drugs.
Forecast
The prognosis of actinomycosis depends on the form of the disease, the severity of its course, the timeliness and adequacy of the treatment of the cow. The earlier antibiotic therapy is started, the greater the likelihood of complete recovery of cattle without relapse. With localized forms, the prognosis is favorable. It worsens with generalized varieties of the disease or with the involvement of the joints in the process.
Some cured cows develop re-infection. Often this is due to the inadequacy of antibiotic therapy. Farmers stop treatment as soon as symptoms disappear. As noted earlier, this is fundamentally wrong.
preventive measures
Actinomycosis, like many other diseases of animals and humans, is easier to prevent than to cure. Therefore, it is very important to carry out the prevention of this disease on farms. To reduce the risk of infection in cows, you must follow these rules:
- Regularly disinfect the stall with cattle. An effective treatment agent is freshly slaked lime.
- Do not graze cows in damp places or lowlands if the farm is located in an unfavorable area for fungus.
- Prepare roughage before consumption by cows. To do this, they should be poured with boiling water and kept for 5-10 minutes. You can also add salt (10-15 g per 10 liters of water).
- Calcinate the straw before feeding the cow.
- Cattle that have already become infected with actinomycosis must be urgently isolated.
- Cows that have been ill should be under constant supervision, as a relapse of the disease is possible.

Conclusion
Actinomycosis in cattle is a disease that requires the earliest possible diagnosis and treatment. With the timely start of therapy, it is possible to achieve a complete recovery of cows. The main thing is not to self-medicate, but to seek help from a veterinarian. Only a specialist can determine the exact dosage and duration of the course.









