Contents

Acidosis is a violation of the acid-base balance of the blood with the accumulation of hydrogen ions and acidic components in its composition. If the body is healthy, then the buffer systems of the blood quickly neutralize the excess of these substances. However, with some diseases or malfunctions in its work, acidic products begin to accumulate in excess in the blood, enter the urine, and can even provoke the development of a coma.
Acids begin to accumulate in the body when it produces them in too large a volume, or is not able to fully utilize them. The pH level drops, acidosis develops. Moreover, acidosis is not an independent pathology, this condition is only a consequence of various diseases or disorders in the normal functioning of the body.
The pH of 7,35-7,38 is considered the boundaries of the norm of blood acidity for a person. If these boundaries are exceeded, then a person has serious health problems: hemostasis suffers, the work of internal organs is disrupted, sometimes there are such violations that pose a direct threat to human life. Therefore, it is important for doctors to know the level of blood acidity of those patients who are in serious condition, for example, in the intensive care unit, in the oncology department of hospitals. Sometimes regular measurements of the level of blood acidity in women who are expecting a child are required (if there is a predisposition to such disorders).
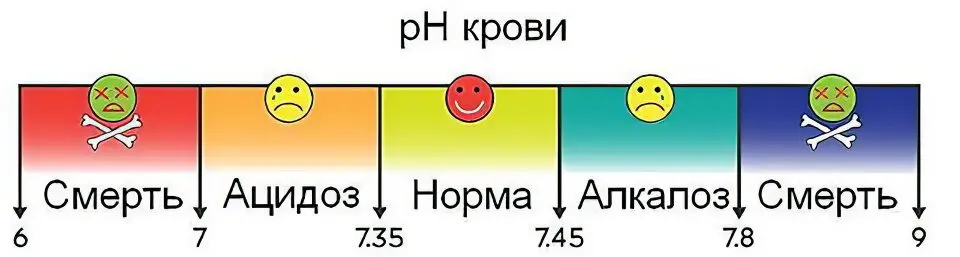
There is acidosis compensated and decompensated, relative and absolute. Sometimes the level of acid-base balance changes in one direction or another due to stress, strong emotional excitement, too fast metabolism, etc. However, such fluctuations are quickly eliminated by the body’s own reserves (kidneys, lungs, blood buffer systems). In this case, a person does not even have time to notice that he has had a shift in the pH of the blood, since there will be no pathological symptoms.
Poor nutrition and serious errors in the menu can lead to acidification of the blood of a chronic course. Such acidosis can be present in a person throughout life. Symptoms of chronic acidosis are either absent at all or mildly expressed, while the quality of human life does not suffer. Insufficient physical activity, stress, constant hypoxia – all these are risk factors that can lead to the development of mild acidosis.
If a person enters the intensive care unit or intensive care unit, then the level of blood acidity in him is measured without fail. This indicator characterizes the vital activity of the body, and an increase in acids in the blood requires emergency medical care. If you do not provide it, then acidosis will lead to disturbances in the functioning of the brain, to coma and death.
Why does acidosis develop?

Acidosis is a symptom of a disease or disorder in the human body.
Therefore, it is so important to establish the cause that led to the acidification of the blood:
Feverish conditions that develop against the background of any diseases or other pathological conditions. With an increase in body temperature, metabolic processes are launched, which is accompanied by the production of immunoglobulins (proteins produced by the body itself for its own protection). If the body temperature exceeds 38,5 ° C, then these proteins begin to break down, at the same time, fats and carbohydrates are destroyed. As a result, the internal environment of the body becomes acidic.
Disorders in the work of the kidneys.
Protracted diarrhea.
Unbalanced diet or starvation. If the body does not receive enough nutrients from food, then it seeks to cover the deficit from its own reserves: glycogen, fats, muscles, etc. The destruction of these substances leads to the fact that the pH is disturbed, and the amount of acids increases, as the body itself begins to produce them. Not only starvation, but also the predominance of animal fats, salt, refined foods and carbohydrates in the menu can lead to the development of acidosis. The pH is negatively affected by the lack of fiber and trace elements in the diet.
Childbearing period. When a woman is pregnant, all her internal organs work in an enhanced mode. Metabolic processes are accelerated to provide the baby with the maximum amount of nutrients. The level of breakdown products naturally begins to rise, which can lead to acidosis.
Inflammatory processes in the body, which caused a violation of hyperventilation of the lungs. The worse the ventilation of the lungs, the stronger the acidosis. Respiratory failure, asthma, pneumonia, emphysema can lead to its development. All these conditions provoke the so-called respiratory or respiratory acidosis.
Heart diseases.
Diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis.
Types of acidosis

Depending on the pH level of the blood, the following types of acidosis are distinguished:
Compensated acidosis, in which there are no symptoms of disorders in the body. In this case, the pH level is equal to 7,35.
Subcompensated acidosis, which is expressed by arrhythmia, shortness of breath, diarrhea and vomiting. In this case, the pH level is equal to 7,25.
Decompensated acidosis, which is characterized by serious disruptions in the work of the heart, digestive system, brain, loss of consciousness. In this case, the pH level is 7,24.
Depending on the cause that led to the development of acidosis, the following types are distinguished:
Metabolic acidosis, which manifests itself in case of failures in metabolic processes. When the blood cannot bind normally, or its acids are destroyed, for example, against the background of diabetes mellitus.
Gas acidosis, when there are violations in the process of gas exchange in the lungs. The reason for this is diseases of the respiratory system. In addition, respiratory acidosis is observed with hypoventilation of the lungs, with an excessive content of carbon dioxide in the air, with chest injuries, etc.
non-gas acidosis.
Excretory or excretory acidosis, when the kidneys lose the ability to normally remove acids from the body (those acids that are dissolved in the blood). Also, excretory acidosis develops when the stomach or intestines secrete too much alkali.
Exogenous acidosis, which develops under the condition that acids come from the external environment in such volumes that the body is not able to absorb them.
Mixed acidosis develops when the internal environment of the body is acidified due to several factors at once. For example, against the background of heart disease, which is accompanied by damage to the lungs or kidneys.
metabolic acidosis
More often than other types of violation of the acid-base balance of the blood, it is metabolic acidosis that occurs. At the same time, the level of lactic, acetoacetic and beta-hydroxymolar acids in the blood increases. The disease has a more severe course, as it is accompanied by an increase in the level of potassium in the blood and a decrease in hemoperfusion in the kidneys.
In diabetes mellitus, the body most often develops ketoacidosis and lactic acidosis, which are characterized by the accumulation of certain types of acids in the blood. So, with lactic acidosis, a lot of lactate accumulates in the blood, and with ketoacidosis, the level of acetoacetic acid, or rather, its decay products, increases. These types of acidosis can cause the patient to fall into a coma. Therefore, assistance to a person should be provided as quickly as possible. Also, lactic acidosis can develop in people who do not play sports, but at the same time have experienced strong physical overload. Lactic acid settles in the muscles, causing them pain, and also rises in the blood, making it acidic.
Thyrotoxicosis, refusal of food, excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages can provoke metabolic acidosis.
Acidosis symptoms

If acidosis is compensated by the adaptive mechanisms of the body, then its symptoms may be absent altogether, or be mild. As acids accumulate in the blood, signs of acid-base imbalance will appear, such as: increased fatigue and weakness, breathing problems. Shock and coma develop with severe acidosis.
Often the symptoms of acidosis go unnoticed for the reason that they are dominated by the symptoms of the underlying disease from which the person suffers. This does not allow a correct diagnosis. Severe acidosis is accompanied by respiratory failure, a decrease in the number of heart contractions, cardiogenic shock and coma.
With metabolic acidosis, there are violations of the organs of the respiratory system of the Kussamaul type: inhalation becomes deep, and during exhalation, an excess amount of carbon dioxide is released into the external environment. Thus, the body tries to get rid of excess acid.
Against the background of respiratory acidosis, alveolar gas exchange decreases, breathing becomes shallow, but frequent. It is enough for a specialist to assess the nature of the patient’s breathing to determine the presence of acidosis. The next step is to find out its cause.
Respiratory acidosis is easier to diagnose than others. Often it is accompanied by emphysema, pneumonia, edema of the interstitium of the lung. To detect metabolic acidosis, laboratory and instrumental studies are required.
If a person has compensated acidosis, then it can be detected only after taking a blood test to assess its buffer systems, passing urine, etc. When acidosis begins to intensify, disorders of the respiratory system appear.
If acidosis is decompensated, then the performance of the brain, cardiovascular system, and digestive organs suffers. These disorders are caused by hypoxia of organ tissues against the background of the accumulation of acids in the blood. Obvious symptoms of acidosis are an increase in blood pressure and tachycardia, which develop against the background of an increase in the level of norepinephrine and adrenaline in the blood.
Vomiting and diarrhea indicate the progression of acidosis, since against its background there is an increase in the secretion of the digestive glands. The pressure can either rise or fall, the pulse quickens, arrhythmia and bronchial spasm develop.
Neurological symptoms are manifested by increased drowsiness and fatigue, consciousness becomes clouded, the person becomes lethargic, experiences a headache. If acidosis is severe, the patient may fall into a coma. At the same time, his pupils will be dilated, there is no reaction to light, reflexes disappear, muscle tone decreases.
Characteristic symptoms of respiratory acidosis: secretion of sticky sweat, swelling of the face, change in skin color from bluish to pink. At first, a person talks a lot, is in euphoria, but as acidosis progresses, he falls into apathy, he can go to bed. Sopor and coma develop with decompensated acidosis. Further progression of disturbances in the work of the respiratory organs leads to more and more pronounced tissue hypoxia, to oppression of the respiratory center. Severe respiratory acidosis will be accompanied by metabolic disorders. Tachycardia increases, heart rate is not restored. If adequate medical care is not available, then the person dies.
With uremia, against the background of a violation in the work of the kidneys, the patient develops convulsions, as the level of calcium in the blood falls. Breathing becomes noisy, and an ammonia odor may come out of the mouth as the level of urea in the blood rises.
Diagnosis and treatment of acidosis

Diagnostic signs that indicate that the blood pH has dropped to around 7,35: an increase in carbon dioxide pressure (respiratory acidosis), a decrease in the level of standard bicarbonate and alkalis (metabolic acidosis). These indicators can be identified by performing a blood and urine test in the laboratory.
If acidosis has a mild course, then the patient is prescribed a plentiful drink, alkaline solutions. Be sure to adjust the menu, removing from it products that contribute to the growth of acids in the blood. The patient must be carefully examined to determine the underlying cause of the acidosis.
The fact that acidification of the internal environment of the body becomes the cause of various diseases has been more and more talked about in recent years. People who are fond of alternative medicine try to use baking soda to treat all diseases without exception, but is it really so universal?
If a person in the body grows and develops a malignant neoplasm, then it is simply impossible to cope with it with the help of soda. Moreover, its use will only aggravate the patient’s condition. With gastritis, soda will complicate the course of the disease and can even lead to the development of atrophy of the gastric wall. Baking soda can help treat alkalosis. However, it must be taken under the control of laboratory blood parameters and in doses verified together with the doctor.
If the acidosis is caused by diabetes mellitus, then the patient should adjust the dose of insulin. Bronchodilators (Salbutamol, Isoprenaline, Theophylline) and mucolytics (Ambroxol, Acetylcysteine) are prescribed for diseases of the respiratory system. It is imperative to sanitize the respiratory organs, carry out therapy aimed at restoring bronchial patency.
To eliminate the symptoms of acidosis, the patient is prescribed plenty of drink and soda. If the patient’s condition is severe, then a sterile bicarbonate solution is injected intravenously. The procedure is carried out in the intensive care unit.









