Contents
Acetoacetic acid is a metabolite formed in the transformation of fatty acids. When insulin levels are lowered, there are difficulties in utilizing glucose in cells. It leads to incomplete fat burning with the formation of ketone bodies, including acetoacetic acid.
What is acetoacetic acid?
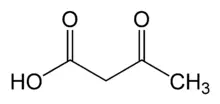
Acetoacetic acid, like acetone and β-hydroxybutyric acid, is classified as one of the chemical compounds called ketone bodies. It is an indirect metabolite of the metabolism of fatty acids, mainly produced in the liver. Acetoacetic acid is an energy alternative to glucose that is needed by many organs, incl. kidneys, muscles and heart. In a healthy person, ketone bodies are released into the blood in small amounts. Only when the metabolism is disturbed (e.g. due to diabetes and impaired glucose consumption) is the excessive production of acetoacetic acid and other ketone bodies. In addition, their concentration in the blood increases and they are excreted more in the urine. She develops ketoacidosis, which in turn leads to a dangerous keto coma. Acetoacetic acid testing is performed in people with suspected conditions that may be associated with ketoacidosis, e.g. hypothyroidism, diabetes or alcohol intoxication.
When do we test acetoacetic acid?
Acetoacetic acid testing is performed when there is a suspicion of diabetic ketoacidosis, alcohol intoxication, fever, hypothyroidism, fasting, and a low-carbohydrate and high-fat diet. In people with diabetes, there are some symptoms that may suggest the need for a test, including:
- a sweet smell from the mouth,
- excessive thirst
- bad mood,
- polyuria
- dehydration,
- diarrhea
- high temperature,
- vomiting,
- dry mouth.
Research
Acetic acid test material: serum or urine.
Preparation for the acetoacetic acid test: on an empty stomach (at least 8 hours).
The course of the study: one-time blood sampling from a vein in the arm or testing a urine sample.
Time to wait for the result: 1 Day.
There are no contraindications for the test.
Standard:
– in serum – from 0,03 to 0,22 mmol / l (0,3-2,0 mg / dl),
– the presence of acetoacetic acid in urine is always considered pathological.
Comments: Fatty acids can only be completely burned in the presence of glucose. The consequence of incomplete burning of fats is the formation of ketone bodies. Acetoacetic acid is one of the constituent ketone bodies. Its production is intensified in the absence or reduction of insulin concentration and difficult utilization of glucose. Ketone bodies, including acetoacetic acid, are absent in normal urine.
What does elevated acetoacetic acid and other ketone bodies indicate?
Increased levels of these substances in the blood and urine can cause:
- diarrhea,
- vomiting,
- high temperature,
- alcoholism,
- alcohol poisoning,
- pregnancy (especially its other half),
- diabetes (type I and II),
- acute kidney failure,
- starvation diet,
- low carbohydrate content in the diet.