Contents
Traditional farming with digging, hilling and weed control is gradually becoming a thing of the past. It is being replaced by new technologies that allow you to equip beds that do not require much time and effort. Such a garden is called “lazy”, because there is little work on it, and there is a lot of time for rest. How to equip a garden for the lazy on your site? More on this later in the article.
What does “lazy garden” mean?
It would be fair to replace the word “lazy” with the word “smart” here, because this technology was invented by very rational people who strive to get high results with minimal effort and time. This is the essence of the idea.

Principles of “lazy” farming
Lazy farming eliminates unnecessary labor and investment. Everything grows on organic matter, it is also used as a fertilizer, the plots for the beds are ennobled, and the yield is growing every year. Yes, this is possible, because in the beds for the lazy everything is done according to the mind and the new rational scheme.
What are the principles behind this approach?
- they do not dig the earth, but only loosen the top layer to a depth of 5-7 cm;
- do not engage in weeding and loosening after rain – mulch copes with this;
- do not water the plants often – the same mulch prevents the evaporation of moisture;
- do not use mineral fertilizers, but increase soil fertility due to organic matter growing on the site.
Following these principles, the gardener significantly saves his time and energy, while receiving excellent harvests, as well as the opportunity to relax more in the country.
Garden organization rules
The organization of lazy farming involves the observance of the following rules:
- reduction of the cultivated area – is achieved by arranging raised beds;
- mulching beds;
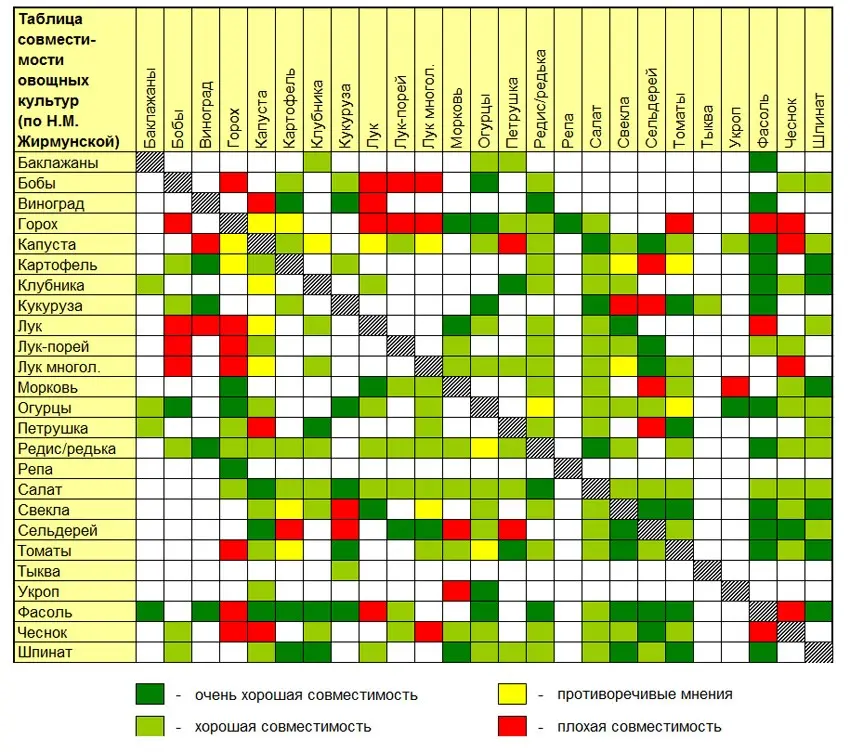
- joint plantings – some plants (garlic, lavender, marigolds) serve as good protection against pests, so they are recommended to be planted between vegetable crops;
- repeated crops – the place should not be empty, so a bed for tomatoes and peppers is planted with radishes, spinach in the spring, and in the summer, after harvesting the garlic, greens are immediately sown;
- sowing green manure – in organic farming, this is the main technique that allows you to increase soil fertility;
- observance of crop rotation – it is impossible to plant crops of the same family in the garden from year to year.
Video “Smart beds: principles of organization”
This video provides helpful tips and tricks for planning and laying out a plot for a vegetable garden.
We are planning a garden
Now let’s figure out what you need to consider when planning the beds.
Area of organized beds
The area of u40bu50bthe beds on the site should occupy no more than a third of the entire territory. The length of the beds can be any, from 60 cm to several meters. But the width should be such that the gardener can easily reach the middle without stepping on the bed itself. The width of the aisles between the beds is calculated taking into account the growing crops. Usually 80-XNUMX cm is enough, but if it is planned to plant potatoes, cabbage, then the passages should be increased to XNUMX cm. In a word, the width of the passages should be such that it is comfortable to walk along them.
We recommend filling the space between the beds with something, otherwise weeds will grow. It is best to fill this area with gravel or sow lawn grass – it will be useful and aesthetically pleasing.
Author’s advice
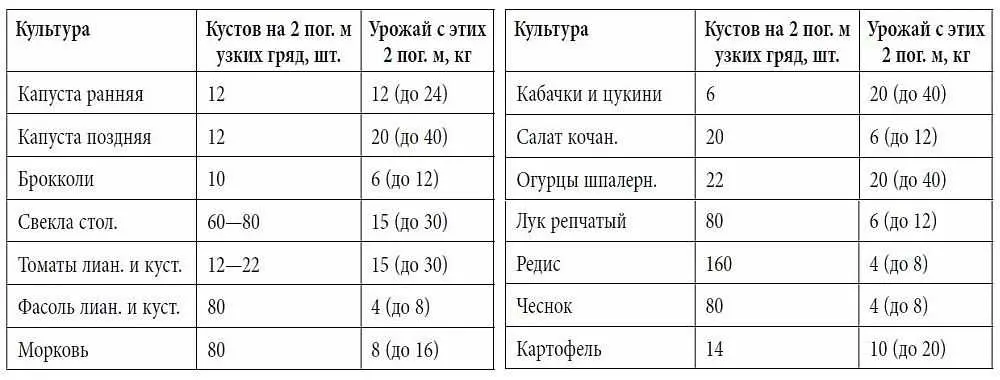
For many summer residents, the problem is the abundance of the crop, which has to be distributed. And this happens due to the fact that vegetables and fruits are tied in a larger volume than the family needs, and at the same time, extra work is invested. Therefore, think in advance what exactly and in what quantity you will grow, taking into account consumption and harvesting, then make a list of crops.
The table of crop yields will help to determine the list of plants and calculate the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe plot for the beds:
Precise location
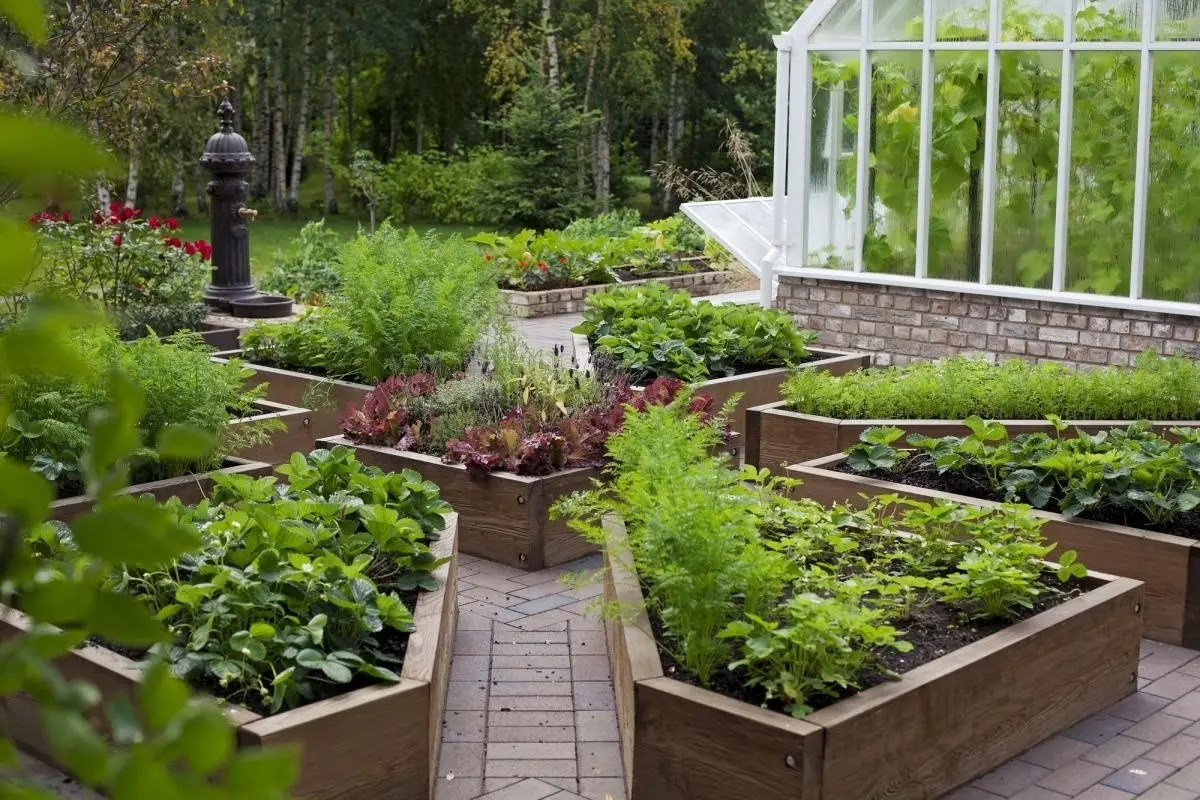
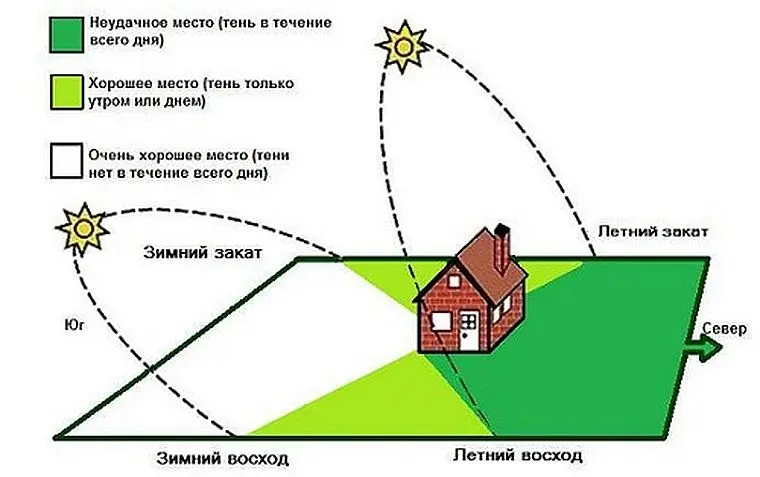
When planning the beds, first of all, the degree of illumination of the site should be taken into account. Almost all plants need a lot of sun. There are no vegetable crops capable of growing in the shade at all, and if they are planted there, the yield will decrease many times over. Therefore, it is better to allocate shaded areas for recreation areas, and for beds to allocate open areas.
You need to decide on the place right away, since moving the beds is not desirable, because a fertile layer is formed there. It is also necessary to choose a location taking into account the cardinal directions. The areas located from south to north are best illuminated; vertical beds on trellises can be placed along the southern walls. To make your plans easier to implement, draw a schematic plan in advance.
Crops to grow
Smart people prefer to get a crop quickly and without unnecessary labor, so they choose crops that do not require complex care. These include: beans, peas, pumpkins, zucchini, corn. These plants can simply be planted and remembered when the crop is ripe. Seedling crops are also easy to care for: tomatoes, peppers, different varieties of cabbage. Be sure to grow greens, radishes, lettuce at hand.
Exotic and heat-loving crops should not be planted on lazy beds – they may not withstand winter frosts, especially in the Urals or Siberia. Always choose varieties suitable for your region, as certain types of cucumbers and tomatoes require the construction of greenhouses, and this is already costly.
By the same principle, you can plan a “smart” garden by choosing unpretentious trees and shrubs that do not need to be cut.
How to make smart beds with your own hands
For beauty and practicality, each garden bed is recommended to be fenced around the perimeter. You can make borders from many improvised materials.
From the boards
The arrangement of the fence must begin with the manufacture of a box of the required size. For strength, fasten the structure in the middle with slats. The boards themselves should be varnished and painted to prevent rotting of the material.
from slate
A slate sheet is cut into pieces 0-4 m high and dug along the perimeter of the beds to half its height. At the corners, the structure is fastened with special puffs; metal reinforcement is placed inside for strength, preventing the walls from curving.
From plastic boxes
If the household has extra boxes for vegetables, they can also be used as borders. First you need to disconnect the walls of the box, then dig them around the perimeter and fix them with wire. You can also use the boxes as a whole, placing them over the entire area and covering them with soil.
From bricks
Such a fence will last a long time, but you need to understand that it is impossible to move a brick structure without breaking it. For stationary beds, it is advisable to pour the foundation, on which then lay the bricks. An easier option is to dig the bricks up to half directly into the ground.
Mobile beds
In this case, all kinds of containers are used: barrels, containers, bags. Any container can be filled with soil and plants can be planted there. The advantage of mobile beds is that they can be moved around the site and, if necessary (frost, rain) brought into the room.
Organization of the irrigation system
Many summer residents organize watering with a hose, watering can or bucket. However, this is hard work that can be minimized. The smart garden uses a drip irrigation system. It is easy to make, even beginners can do it.
The system can be stationary or temporary. For a stationary system, a main pipe is brought to the site. One end is attached to a water tap, and the other end is wired at the level of the beds. Buying a ready-made plastic hose with holes already made will help simplify the task.
Important! The scheme for laying pipes for drip irrigation must be developed at the planning stage of the beds, before the arrangement of the borders.
Site mulching
One of the rules of lazy farming says that there should be no bare earth in the beds. Thus, the evaporation of moisture decreases, a fertile layer is formed faster and, most importantly, weeds do not grow. All this is achieved by mulching. It is better to use organic matter as mulch: rotted sawdust, needles, hay, straw, mowed grass and green manure without seeds. If it is not possible to update the mulch, you can use inorganic materials: black film, cardboard, expanded clay.

Useful tips and reviews
Summer residents who have been practicing lazy farming for a long time have the following recommendations for beginners:
- bring only organic matter into the garden – mineral complexes destroy the fertile layer, which has been formed over the years;
- sow green manure in the fall – as soon as the bed is free, immediately sow mustard, phacelia, oats;
- during autumn sowing, it is not necessary to plant green manure in the soil, it is enough just to cut off the tops and lay them on the beds;
- cut green manure before the budding process begins – the more tender the greens, the faster it rots;
- for an early harvest, cover the bed with white covering material.
“These principles really work. Previously, we gave all the time to the dacha – we dug, weeded, and the harvest was simply ridiculous. Then I heard about lazy farming, studied the literature. We made high beds, we plant, we mulch with grass, we work less, and the harvest is greater.”
“I made some high beds. Now I don’t spend all my time digging in the ground, I just plant seedlings, mulch and get great yields.”
A smart dacha does not happen without lazy beds. However, the principle of lazy farming can be applied not only in the beds, but throughout the entire area: a lawn instead of weeds, green manure and flowers in tree trunks, flower beds from perennials. All this is easy to equip, using the advice of experienced gardeners.









