Contents
The yellow body in cows often leads to infertility. It happens that after insemination, pregnancy does not occur, the cow remains dry. In this case, it is necessary to establish the exact cause of the pathology, otherwise the animal may remain infertile.
What is a corpus luteum
Before artificial insemination, a favorable time is chosen – the period when the female is in heat and the follicle is formed. At some point, the follicle matures and the egg is released. Reaching one of the horns of the uterus, the egg is fertilized. At the site of the rupture of the follicle, a certain cavity appears, which subsequently becomes overgrown with vessels. Further, it turns into a temporary endocrine gland – the corpus luteum.
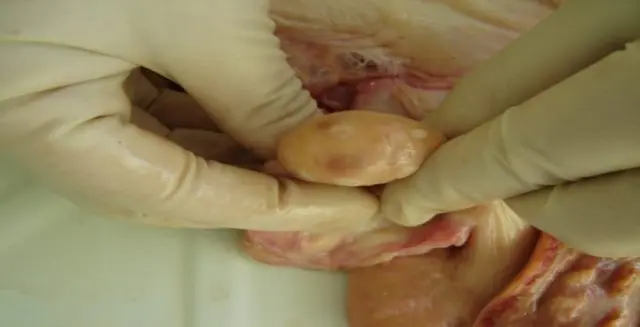
After fertilization, iron begins to produce biologically active substances that contribute to the development of pregnancy and fetal growth:
- steroids (progesterone, estrogen);
- peptides (oxytocin, relaxin);
- inhibin;
- cytotoxins;
- growth factors.
progesterone and inhibin – sex hormones that positively affect reproductive function.
Peptides – amino acids that regulate all physiological processes.
Cytokines – biological molecules that can coordinate the work of the immune, endocrine and nervous systems.
The gland continues to work in cows throughout pregnancy, until the appearance of a calf.
In the event that fertilization has not occurred, the formed corpus luteum has no further development, gradually disappears. After the next sexual cycle, when the individual is again in the hunt, the formation of a new follicle begins.
Causes of the formation of a corpus luteum
The corpus luteum sometimes, for various reasons, can linger in the ovary, because the action of hormones does not allow the follicle to ripen and release the egg. Although ovulation has occurred, but for some reason the egg does not enter the uterus. In such cases, experts declare the persistence of the corpus luteum.
The corpus luteum is formed, works, regresses due to the interaction of the pituitary gland, ovary, immune system. With pathology, a failure occurs in the entire hormonal system.
The main reason for the formation of the corpus luteum, which is stated by veterinarians, is puerperal paresis.
In some individuals, the disease recurs after each calving. Cows suffer from birth paresis mainly in the winter season, in the feed of which proteins predominate. It is possible to avoid the recurrence of labor paresis by properly balancing the diet of pregnant cows. It is useful to give pregnant cows vitamin D, which contributes to the proper functioning of the entire genital area of the animal and a favorable hormonal background. Mandatory active exercise of cows before the first harbingers of childbirth. The disease can affect some parts of the brain, as well as the pituitary gland. If its work is disturbed, the hormone progesterone is released into the blood, which affects the formation of the corpus luteum.
There are a number of other reasons for the occurrence of persistence of the corpus luteum:
- lack of active walking;
- poor feeding ration, which leads to metabolic disorders and hormonal disorders in the cow’s body;
- lack of vitamins A, E, D, which are necessary for the proper development and bearing of the fetus;
- lack of mineral supplements in the diet, many of which have a positive effect on the nervous and reproductive system of the cow;
- increased content of concentrates in feed.

The reasons for the development of the corpus luteum also include a history of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
Signs of a persistent corpus luteum
More often than not, there are no signs of a delay in the exit of the corpus luteum in cows. On the contrary, outwardly the animal looks healthy, has a good appetite. Moreover, all signs of hunting appear: mucus comes out of the vagina, the cow makes attacks on animals in the herd. But after insemination, pregnancy does not occur.
The diagnosis of persistent corpus luteum is made only after several unsuccessful attempts at insemination. Then the cow is examined using an ultrasound machine and a rectal method, which is carried out 2 times with an interval of a month. The fact is that one examination may not reveal pathology, since the veterinarian needs to determine the difference in body size.
When examining, it is important to establish:
- the presence or absence of inflammatory processes in the genital area;
- the size and density of the ovary;
- the consistency of the gland;
- the density of the walls of the uterus, its shape and size;
- condition of the cervical canal;
- color and condition of the vagina.
Only after the second examination is an accurate diagnosis established.
It is necessary to treat the corpus luteum in cattle
Most often, the prognosis of the disease is favorable. It is necessary to identify the cause of persistence and cure associated deviations in the genital area, eliminate hormonal failure, correct errors in the care, maintenance and feeding of the cow. Usually, after well-conducted therapy, healthy calves are born.

How to treat a corpus luteum in a cow
Immediately after the diagnosis is confirmed, therapeutic measures begin. The main task of treatment is to increase the tone of the uterus, restore the basic functions of the genital organs:
- the cow should be allowed to approach the probe bull more often in order to bring the female into the hunt;
- use hormonal preparations according to a special scheme under the supervision of a veterinarian;
- physiotherapeutic procedures are used, for example, ovarian massage, after which the corpus luteum comes out on its own after 4-5 days.
Sometimes they resort to surgical intervention, removing the contents of the gland through the vagina or rectum. Such an operation does not require anesthesia and suturing, but can lead to some complications.
Often veterinarians squeeze out the contents of the corpus luteum. This is an easy procedure. To begin with, the intestines of the cow are cleaned of feces. Then the veterinarian carefully inserts his hand into the rectum and gropes for the ovary. Then he grabs the gland and puts pressure on it. When its contents come out, the veterinarian clamps the cavity and holds it for about 5 minutes. This procedure does not interfere with the normal functioning of the ovary in the future.
During the treatment, it is worth paying attention to the age of the cow. If she had more than 15 calvings, she is considered old, it makes no sense to prescribe therapy at this age, despite the positive result of the treatment.
disease prevention
Since the persistence of the corpus luteum in cows is a frequent occurrence, the owner needs to think about the prevention of the disease. First of all, it is necessary to provide the animal with balanced feed, vitamin supplements, microelements, and arrange daily active exercise. A cow requires careful attention and special care during pregnancy, otherwise it will not be possible to avoid various complications during and after calving. Late discharge of the placenta is also the cause of the delay of the corpus luteum, so a qualified specialist must be present at the hotel.
Conclusion
The yellow body in cows often leads to infertility. Therefore, the owner needs to diagnose the disease in time and cure the animal of all inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system in a timely manner. Otherwise, it may lead to reduced productivity.









