Contents

Back pain is one of the most painful and unpleasant varieties of this clinical symptom. The fact is that the structures that form the area, which is commonly called the back, are actively involved both in the process of walking and in almost any human labor activity. What does it mean? the appearance of back pain significantly reduces not only the quality of life of a person, but also his ability to work.
Curiously, according to surveys of people around the world, 92% of people experience some form of periodic back pain. Of this number, 79% of those surveyed acknowledged the powerful impact of back pain on daily life and work activities. Moreover, discomfort in the lower back is the second most important manifestation of pain in humans, globally affecting the quality of life.
For a long time, people of quite mature and advanced age referred to pain in the back. Today, this problem torments even children of adolescence. This is due, first of all, to a decrease in physical activity and metabolic disorders. Such circumstances lead to the emergence of a number of diseases, accompanied by acute sharp pains in the back.
In order to get rid of back pain as quickly and effectively as possible, it is important to understand the cause of this clinical symptom. We will discuss in this article how to understand “why it hurts” and where the cause of pain in the back comes from.
Main causes of back pain
The back is a concentration of many nerve trunks, muscles, bones and organs, pathology in each of which can cause pain. After all, in fact, pain is a signal to the brain that something has gone wrong somewhere, and the body is in danger of damage. Therefore, urgent measures must be taken to eliminate this danger.
The most common causes of back pain are:
Problems with the spine;
Kidney disease;
Stretching or inflammation of the muscles (myositis);
Overweight;
Vascular lesions;
Heart failure;
Damage to the pancreas (pancreatitis) and gallbladder;
immune diseases;
Diseases of the pelvic organs.
Since the spine runs from the upper to the lower back, all pains are also usually divided into vertebrogenic (from the Latin Vertebra – vertebrae) and non-vertebrogenic.
Each of the types of pain caused by the problems described above has its own characteristics of the course, which allow diagnosing the etiology and prescribing effective treatment.
The spine consists of bone “bricks” – vertebrae, ligaments, discs between the vertebrae, nerve roots that emerge from special openings and go down, innervating organs and tissues. Inside is the spinal cord – a substance that connects the entire body below the head with the brain. All decisions made in the brain about the beginning of muscle contraction, support for autonomic functions and other processes are transmitted down precisely along the spinal cord and nerves exiting through the spine.
Back from the organs and tissues in the brain, along the spinal cord, there are signals about disorders, diseases and inflammation of certain tissues. These signals come in the form of pain. Since pain is a very unpleasant feeling, a person will have to do something. This is what the whole mechanism of the appearance of pain in the body is designed for.
Since the information transmission center is located in the back, in some cases pain can be felt when in fact the pathological process is located elsewhere.
Vertebrogenic pain associated with pathology (specific pain)
Protrusion of the intervertebral disc
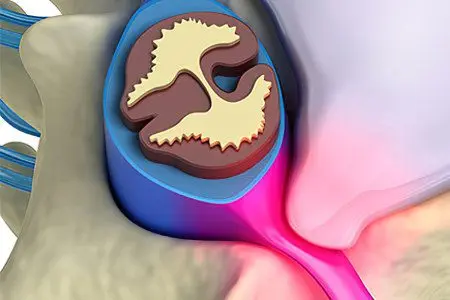
First of all, it is necessary to highlight the pathology of the vertebral discs. The bones of the spine, in the process of walking, especially during physical exertion, feel strong pressure. Naturally, if two solid vertebrae rubbed against each other, then nothing would be left of the spine. Therefore, nature placed special disks between them. They consist of a substance similar to jelly, but much more durable. This is a kind of rubber, a shock absorber that softens the load when moving and dragging loads.
Normally, a vertebra has a special capsule that keeps it from going beyond a certain space. However, with age and during overload, this capsule bursts, and protrusion of the intervertebral disc occurs.
At first, it is almost imperceptible and does not affect the general condition of the body. In the future, the greater the protrusion, the worse it affects the vertebra.
How to recognize? If the pain is severe and localized in one place along the spine, then protrusion of the vertebrae can be suspected. If a protrusion of something soft is felt in this place, then this is probably an intervertebral hernia.
How to treat? In the initial stages, non-surgical treatment may be prescribed. It includes the wearing of special bandages (belts that compress a protruding hernia), the appointment of drugs that strengthen the very substance of the disks, as well as physiotherapy procedures.
Sciatica, lumbago, sciatica
Lumbago. If you overload your body with physical exercises, you can harm it. Often it is the spinal column in the lumbar that suffers. Lumbago is a sharp pain, which is the result of overexertion of the spine.
Radiculitis. Inflammation of the nerve roots entering the intervertebral foramen.
Sciatica. Inflammation of the sciatic nerve. With this pathology, pain occurs in the lumbar region.
Narrowing of the spinal canal
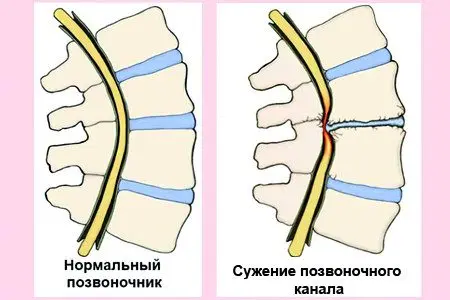
As we remember, the spinal cord is located in the spinal canal. The bony skeleton protects it from injury, since the substance of the spinal cord itself is quite soft, and resembles the red marrow that many have seen in hollow bones in animals. However, in some cases, the spine may not play a protective function, but rather become an aggressor compared to the contents of the spinal lumen.
With age, the intervertebral discs wear out, salts accumulate in them, and water evaporates. Gradually, this affects the bones with the ligaments of the spine. In order to somehow compensate for the loss of fluid by surrounding tissues, the body begins to compact neighboring tissues. This is how ossification appears in the spinal canal, as well as the processes of the vertebra.
Most often, the narrowing is noted:
in the lower parts of the spinal canal;
with age, with degenerative phenomena;
with a lack of vitamins, minerals and fluid intake;
in the presence of congenital narrowing of the spinal canal.
The cervical and lumbar regions are most commonly affected. In the thoracic region, the lesion occurs only in 5% of cases. The higher the stenosis, the more serious the violations and complications in the patient. Accordingly, stenosis in the cervical region is characterized by a gradual descent of the clinic down and the transition to the thoracic and lumbar regions.
How to recognize? With stenosis in the cervical region, note:
muscle stiffness in the neck;
periodic pain in the temples and crown;
circulatory disorders in the vital organs of the chest cavity.
Back pain, as well as burning, are more characteristic of stenosis of the thoracic and lumbar region. At the same time, pain in the lower back increases with walking, as well as physical exertion, since in this case the spinal cord is compressed in the canal more strongly. In this case, the pain goes to the legs, since the nerves that innervate the lower limbs are more affected.
The final diagnosis is made by a neuropathologist, based on magnetic resonance imaging of the spine or computed tomography.
How to treat? The initial stages, without a pronounced clinical picture, are treated conservatively. Usually, anti-inflammatory drugs containing useful substances are prescribed, as well as physiotherapy procedures. The most effective method is to perform an epidural blockade, as well as radiofrequency ablation. It is important to understand that all these methods are prescribed strictly according to the indications of the attending physician, and when prescribed, they can cause a deterioration in the condition.
Surgical treatment is prescribed only if the use of the above methods is ineffective.
Diseases of the joints of the spine
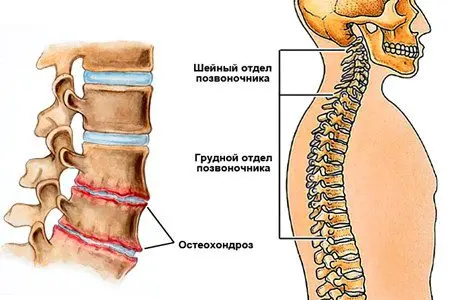
There are a number of diseases that can affect the joints of the spine. The most frequent of them are:
osteochondrosis – a condition when the discs are reduced so much that the bone of the upper vertebra almost touches the lower one (in the most advanced cases);
arthrosis – damage to the articular cartilage;
arthritis is an inflammatory disease that affects cartilage and ligaments.
Osteochondrosis is a degenerative disease in which at first the cartilage loses its lamellar properties, and then the degeneration passes to the bones. As a result of the contact of bones, a person feels hellish pain, which in advanced cases is almost impossible to endure. There are osteochondrosis of the cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae.
How to recognize? More common in old age. At the initial stage, the pain may be limited in nature, subsequently intensifying over time. The diagnosis is made on the basis of a medical examination, as well as an x-ray of the spine. If there is a decrease in the size of the intervertebral discs and contact of the bones of the vertebrae, then a diagnosis can be made.
How to treat? Usually, minerals and drugs that strengthen cartilage tissue are prescribed, as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the action of which is aimed at eliminating secondary inflammation and pain. Treatment is usually long-term, with repeated appeals.
Arthrosis can appear as a consequence of injury, as well as metabolic disorders in the body. Usually, with this disease of the joints, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, as well as substances that normalize metabolic processes in the cartilage tissue.
Arthritis is most often caused by a microbial lesion. The inflammatory process is treated with the use of antibiotics, as well as anti-inflammatory drugs.
Injuries
Most often, pain in the spine occurs after a direct impact on it from the lateral sides. Damage associated with traumatic injury from top to bottom is more common when jumping from high altitudes. Injury can cause severe pain, as well as the loss of a number of functions associated with departments located in this area.
How to recognize? A traumatologist makes a diagnosis based on computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging data.
How to treat? The doctor chooses the tactics of treatment, depending on the severity and nature of the injury.
Congenital malformations and developmental anomalies
There is a fairly large number of different congenital pathologies of the spine.
In practical terms, two of them are the most important and frequently encountered. These include:
spina bifida occulta – hidden cleft of the vertebra. Most often, such a deviation is detected during an accidental x-ray examination, in the region of the lumbosacral vertebrae. The clinical picture is rarely characterized by the presence of severe pain. If there are pains, then they are of a aching nature and rarely. Some patients have experienced urinary incontinence, postural disturbances and lower back pain with this defect. In principle, in the absence of complications, this condition can not be treated. If there is muscle weakness, a violation of the development of the feet, trophic disorders of the skin, as well as severe pain, then surgical treatment is required.
spina bifida cystica uverta – is an open spina bifida, with the formation of cysts. During the exit of the contents of the spinal canal through splitting, the so-called spinal hernias are formed. They differ from vertebral hernias in the greater severity of the course and the danger to life. Such disorders are characterized by severe pain in the lumbar region, as well as a violation of the development of muscles, bones and ligaments.
How to recognize? The diagnosis is made by a vertebrologist, based on the X-ray methods of examination, as well as clinical manifestations.
How to treat? Surgical treatment is the only guarantee for the elimination of non-fusion of the spine.
Violation of metabolic processes in the nucleus of the disk
At the beginning of the 22th century, scientists determined that the intervertebral discs and spine reach their maximum development at 25-2 years. At this time, the discs actively absorb and release fluid to the surrounding tissues. Therefore, a person in the evening, when he is resting, can increase in height up to 2 cm, and in the morning, on the contrary, give these XNUMX cm when walking.
Gradually, when passing the point at the age of 25, the spine and discs begin to degrade. The problem is that discs are fibrocartilaginous formations that do not have blood vessels. The central part of the disk, the nucleus, is fed solely by those useful substances that enter the center from the periphery, and there, respectively, from other tissues. Such a nutrition system is very vulnerable and with the slightest lack of minerals and vitamins, the deficiency immediately affects the disks.
This leads to the development of a number of pathologies, in particular to:
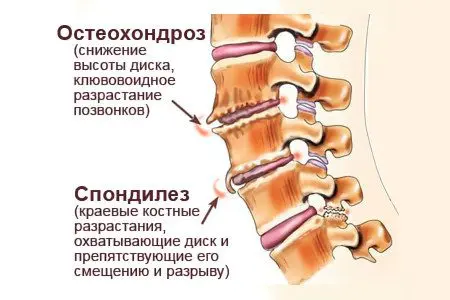
osteochondrosis;
spondylosis – a chronic disease, when spike-like formations from salts grow along the edges of the intervertebral discs;
spondylolisthesis – a disease of spondylosis, in which an additional one of the vertebrae is displaced anteriorly, posteriorly, to the right or to the left;
ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic disease that is accompanied by inflammation of the spinal column;
Bechterew’s syndrome is a disease in which the inflammatory process affects the heart, intervertebral discs and joints. It is more common in middle-aged men and causes life-threatening complications. In this condition, during a long inflammation, the intervertebral joints grow together, which completely deprives a person of movements in them. In the future, this condition can develop in other large joints of the body.
Vertebrogenic pain not associated with pathology
Back pain can also occur as a response to a number of physiological processes. So, for example, when the spine is overloaded, pain associated with the performance of hard physical work is possible. In addition, with an incorrect position or lying on an uncomfortable surface, discomfort can also occur, which, however, should pass quickly.
In some cases, back pain can occur in women during menstruation, especially when there is a so-called algomenorrhea – a condition in which menstruation is painful.
Nonvertebral pains
This is a pathology in which pain is felt in the spine, but he himself is not the cause of their occurrence. There are quite a few such conditions, the most common of them will be described here.
Myofascial Syndrome
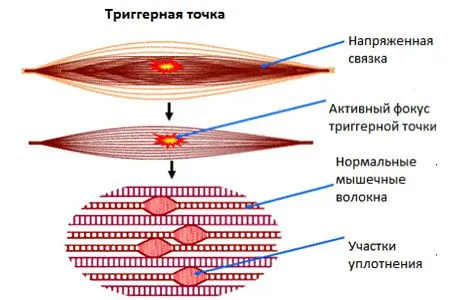
This is a condition in which the muscles around the spine contract involuntarily, causing pain that is sometimes unbearable for the patient. This condition is caused by a number of provoking factors, in particular, trauma, inflammation, hypothermia and other points. This is a rather serious condition, which is diagnosed and treated by neurologists and neurosurgeons.
How to recognize? Usually, with myofascial syndrome, although the pain is located in the range from 1 to 3 cm to the spinal column, it increases with pressure on the muscle. In addition, such pressure is usually accompanied by muscle contraction, which also “gives out” myofascial syndrome.
How to treat? With this pathology, there is a certain provoking factor that causes unusual muscle contractions, spasm, and, accordingly, pain. Most often, the patient is advised to change his lifestyle: avoid increased stress on the spinal column, refrain from taking alcohol and tobacco products. Conservative treatment, as a rule, is carried out only after the elimination of all factors provoking spasms. In some cases, surgical treatment is indicated.
Back myositis
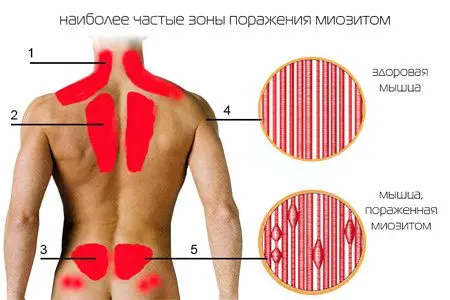
There are many small and large muscles on the back. If the external oblique muscle is thrown over almost the entire length of this anatomical region, then the scapular and similar in size have limited areas. With a cold, infection, intoxication, parasitic invasion, as well as hypothermia, inflammation of these muscles can occur – myositis. Pain can be of varying severity, from transient to severe and prolonged.
How to recognize? Most often, the pain is localized in the lumbar region and does not subside even at rest. When probing, the pain only intensifies. Additionally, electroneuromyography is performed, a part of the muscle is taken for examination, in some cases magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed.
How to treat? You need to see a general practitioner. Usually, treatment includes the appointment of anti-inflammatory ointments, taking antimicrobial drugs in tablets and injectable form, physiotherapy, and massage. In the acute form of the disease, when the pathology has just appeared, the use of warming methods (including massage) is highly discouraged, as this can significantly aggravate the patient’s condition.
Diseases of the internal organs
It all depends on the location of the organ and on what roots of the nerve trunks it is innervated. Most often, from the internal organs, the back is disturbed by the kidney. The kidneys are located on the border of the costal arch, and in the event of the development of pathology, the pain will be in the lower back. In particular, when the kidneys are affected by stones, as a rule, it is noted in the lower back, with a transition to the inguinal region. Severe pain also occurs with inflammation of the calyx of the kidney – pyelonephritis. This is a very common disease, characterized in addition to kidney pain and high fever, as well as burning during urination. The final diagnosis and method of treatment is made by a urologist or nephrologist.
Gynecological pathology can also lead to the spread of pain in the back. Most often, such a clinic has the following lesions of the pelvic organs:
salpingoophoritis – inflammation of the tubes and ovaries;
salpingitis – inflammation of the fallopian tubes.
In men, back pain can be caused by prostatitis, but much less frequently than gynecological pathology.
The pathology of the gallbladder and pancreas go hand in hand and almost always, when one organ is affected, the disease develops in the second. With the pathology of these organs, the pains are girdle in nature, that is, they go from the abdomen to the spine on both sides. These include pancreatitis, and cholecystitis and cholelithiasis.
Damage to the cardiovascular system
Few have heard, but there are atypical forms of myocardial infarction. For example, there is the so-called abdominal form, in which pain is noted not in the region of the heart, but in the abdomen with a transition to the back. This condition is extremely life-threatening, as few people suspect a heart pathology. It is possible to distinguish the abdominal form of a heart attack by persistent dagger pains that do not respond to palpation and stroking, in contrast to the pain associated with the intestines.
A dissecting aortic aneurysm is a condition in which the largest artery in the body, the aorta, first expands in one part and then begins to dissect, resulting in bleeding that is incompatible with life.
First of all, the pain in this pathology is throbbing, and is felt not only in the back, but also in the chest, abdomen (depending on where the aneurysm is located). The patient himself feels a strong pulsation. At the slightest suspicion of such a condition, you should contact a cardiologist, and if possible, a cardiac surgeon or a vascular surgeon.
Diseases of the respiratory system
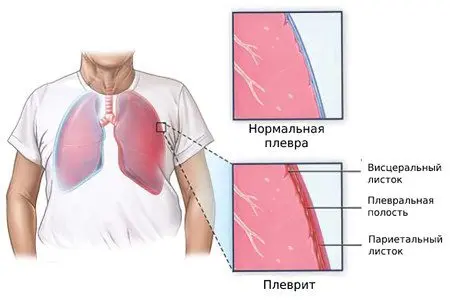
The lungs are projected on both sides of the chest. It is not surprising that with many pathologies, the pain syndrome also passes to the back.
The most common pain occurs in the back with the following lung diseases:
pleurisy – inflammation of the lining of the lungs;
pneumothorax – air entering the pleural cavity through an injury in the lungs or chest (an extremely dangerous condition, since the air accumulating in the pleural cavity gradually compresses the lungs, preventing a person from breathing);
pneumonia – an inflammation of the lung tissue of infectious origin, in which there is a high temperature, as well as severe pain both in the chest and projected onto the back;
abscesses – a limited accumulation of pus, as a result of an infectious disease (the closer the abscess is to the back wall of the chest, the more pain goes to the back).
All these conditions, as a rule, are accompanied by a strong temperature, as well as a deterioration in the general condition. To treat diseases associated with the lungs, either a therapist or a pulmonologist should.
Appendicitis
In rare cases, with atypical forms of inflammation of the appendix (subhepatic form, retrocecal, in the small pelvis), it radiates to the lower back. In parallel, a person feels pain in the groin, as well as a general malaise. When conducting an ultrasound examination, as well as taking blood for the content of leukocytes, pain with appendicitis can be distinguished from pain with damage to the kidneys and spine.
Other causes of back pain
But there are a number of other diseases that can cause a similar ailment:
Infections: osteomyelitis of the spine and pelvis, tuberculosis of the spine, syphilis, paraspinal abscess, abscess of the epithelial coccygeal passage, discitis, epidural abscess, paravertebral infections. As a rule, such infectious diseases affect the kidneys and the urinary system as a whole, which leads to sharp acute back pain.
Malignant neoplasms: epidural and vertebral metastases, melomas, lymphomas and lymphogranulomatosis, primary epidural or intradural tumors. Back pain in oncology of the spinal cord is the only symptom, which is why it is so important to contact a specialist in time.
Metabolic disorders: osteoporosis, osteomalacia, hemochromatosis, alkaptonuria. The pathology of metabolic processes leads to the gradual destruction of bone tissue, resulting in back pain.
Rheumatic diseases: overload of joints affected by rheumatism, tendon sprain, inflammatory processes of the synovial membrane; disorders at the level of microcirculation; developing articular inflammatory and degenerative changes – it is in these cases that acute pain in the back is often manifested.
Reflected painassociated with diseases of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, lesions of the vascular space of the abdominal cavity, malignant tumors of the abdominal cavity and herpes zoster. The pressure of the inflamed abdominal organs causes discomfort in the spine, but in severe forms of the disease, it leads to sharp shooting pains in the back.
How to relieve back pain?
First of all, you need to make an appointment with a doctor and find out the cause of the pain. If the cause is not a serious illness, you can use special exercises to strengthen the back, anti-inflammatory ointments or massage to relieve pain. Injections are used for very strong unbearable pain according to indications.
Exercises for back pain
Reverse hyperextension: pros, technique
[Video] Dr. Evdokimenko: Acute lower back pain, how to treat? Disc herniation, lumbago, sciatica, sciatica:









