Contents
Everyone knows that man is endowed by nature with five main senses that ensure his orientation in space. They are known to almost every one of us – this is sight, hearing, smell, taste, touch. However, not everyone knows that in reality there are much more feelings. And here we are not talking about a feeling of love, pride, revenge, and so on. Now let’s talk about the physiological side of our being, that is, about the feelings inherent in most of us that provide us with normal interaction with the environment. Some of them are present in the body of each of us in equal “volume”, others manifest themselves in different people depending on their individual characteristics.
Here are 10 little-known human senses.
10 Feeling nauseous

In the human body there are special nerve formations, which, when irritated, cause a feeling of nausea. Due to their activity, at some point, vomiting may occur and the contents of the stomach will move into the esophagus, regardless of the person’s desire. When for some reason there is a failure in this system, vomiting can become indomitable or, conversely, a person will completely cease to be capable of vomiting.
9. Feeling of lack of oxygen

There is a type of receptor called peripheral. These structures respond to changes in the concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body. With a lack of oxygen or an increase in carbon monoxide in the external environment, the body switches to another mode of breathing – more rare. It is these receptors that regulate the process of filling the lung tissue with air.
8. A sense of balance

This mechanism is controlled by a small formation that is located in the inner ear of a person. How this feeling works can be understood by the example of what a person who is in a state of intoxication feels: he loses his sense of balance for a while, while his hearing remains intact, despite such a close proximity of these organs.
7. Feeling warm/cold

Someone will say that the receptors responsible for touch are responsible for this. However, it is not. In fact, the parts of the spinal cord and the brain are involved in the process of perception of environmental temperature.
The clarity of the sense of temperature differs in different parts of the skin. In some zones, a person feels a difference in temperature by half a degree, in others – by 75%, and in others – it remains completely invisible. The more the object is heated, the stronger it affects the thermal nerve and, accordingly, the more intensely the person feels heat at that moment. However, this happens to certain limits: if the object is too hot, the person will perceive its effect as pain, and not as heat. In the same way, an object that is very cold can cause pain.
6. Proprioception
Proprioception is a sense that allows you to feel the spatial position of your body parts and their movement. Every person has this property. Without it, the existence of each of us would be very difficult. Unfortunately, quite rarely, however, there are people who, for one reason or another, have this mechanism disrupted, and because of this they have to consciously control any of their actions that healthy people can perform without even thinking about them.
5. Feeling full

Each person always feels when he needs to eat or drink, as well as when his stomach is full. These impulses are sent by the brain. While eating, the walls of our stomach gradually stretch and when the physiological limit comes, the necessary signal is sent to the brain. This mechanism can be clearly explained with a simple example. When a person chews food measuredly and thoroughly, he absorbs exactly as much as he needs to get rid of the feeling of hunger. If the same amount of food is eaten very quickly, then the feeling of fullness will not have time to come and, most likely, we will want supplements, and after a while we will realize that we have gone too far. This can be explained by the fact that the signal from the receptors located in the wall of the stomach, in this case, does not have time to reach the brain in such a short time, so the feeling of satiety occurs with some delay.
4. Feeling itchy
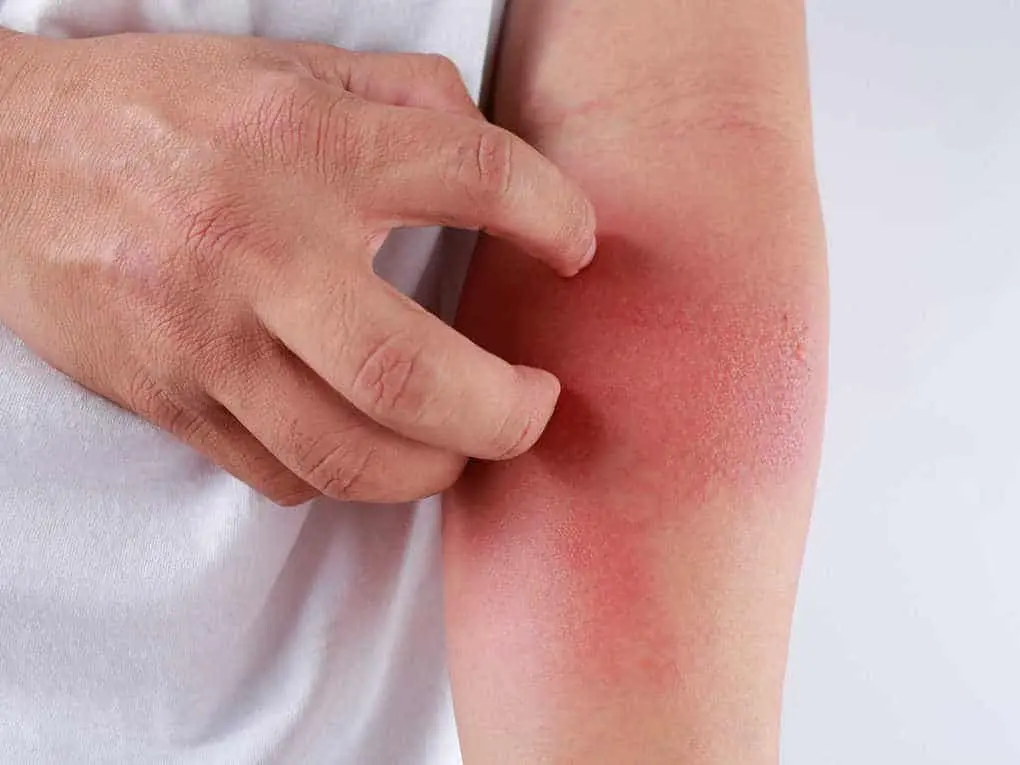
First of all, it should be said that itching is not related to touch. If one or another kind of irritants (including insects that can harm a person) get on the surface of the skin, the receptors send a signal to the brain that indicates danger. A person begins to scratch the irritated area, thereby, possibly, removing the cause of itching from there.
3. Sense of direction

It has been proven that human nature has the ability to subconsciously feel the direction of movement. Although, it should be noted that in the vast majority of people this ability is poorly developed, unlike representatives of the animal world, for example, birds know where the “warm edges” are on an instinctive level.
2. sense of time

This ability is most pronounced in young people. To say that this feeling does not exist is stupid, because each of us feels it to one degree or another. However, it is also quite possible to deceive this very feeling.
1. Feeling pain
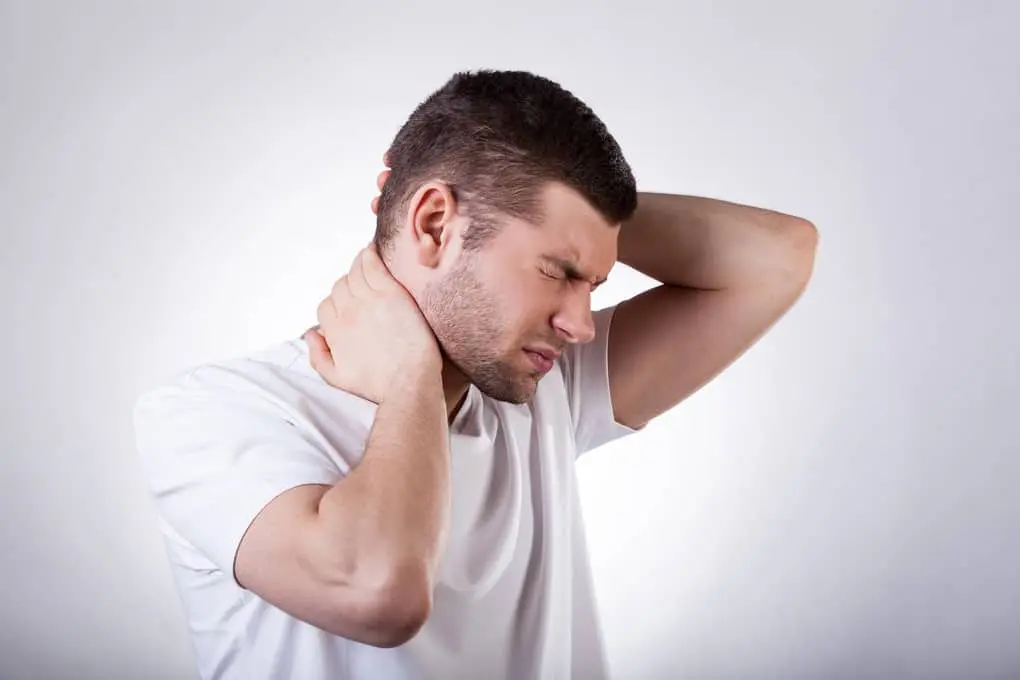

The occurrence of pain also cannot be attributed to the mechanism of touch. This feeling has a different, more complex, process of formation.
A person can feel pain from skin damage, burns, pathological internal processes, etc. The receptors located in the skin structure provoke the movement of an impulse to the spinal cord. The spinal cord can “quench” or convert this signal before it reaches the appropriate center in the brain.
The main purpose of pain is to draw a person’s attention to any dangerous endogenous or exogenous processes that require rapid elimination. Without the ability to feel pain, we would be defenseless against the outside world, because we could not feel the outgoing danger.










