Contents
Few would disagree that human life would be impossible without our senses. All of them are important to us, but if you ask a person which one he is least willing to lose, then most likely he will say: eyes.
The eyes are one of the most basic human senses. It is thanks to them that we know what the world looks like and we can navigate it. However, the way they function, as well as their capabilities, is not fully known even today.
People are trying to unravel any mysteries related to the human eye, but there is still a lot to be explored in this regard. What known and unknown possibilities of the human eye can surprise us? We present you 10 interesting facts about the eyes and human vision.
10 Vision is the main human sense
 It has been established that about 80% of information enters the brain through the eyes.. Interestingly, people who have lost their sight continue to “see” during sleep. This is achieved through the storage of images in memory and the ability to create „new movie” based on previous information.
It has been established that about 80% of information enters the brain through the eyes.. Interestingly, people who have lost their sight continue to “see” during sleep. This is achieved through the storage of images in memory and the ability to create „new movie” based on previous information.
This is not available to people who were born blind, because the brain has never received any images from the organ of vision that could be processed, remembered, and then used.
9. Upside down
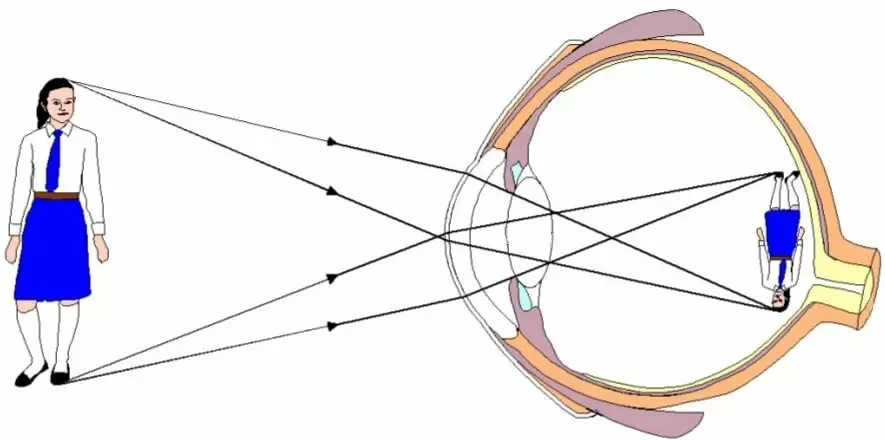 The image that appears on the retina of the eye appears there inverted and reduced. It is then corrected and converted into information by the brain so that we can perceive it correctly.
The image that appears on the retina of the eye appears there inverted and reduced. It is then corrected and converted into information by the brain so that we can perceive it correctly.
Also, it should be noted that the lens in our eye works faster than any photographic lens. Try to look around the room quickly and think about how many different distances you focus your eyes on. Every time this happens, the lens is constantly changing its focus, all unconsciously. Compare this to a photographic lens that takes several seconds to change focus from one distance to the subject to another.
8. Pupil dilation and constriction
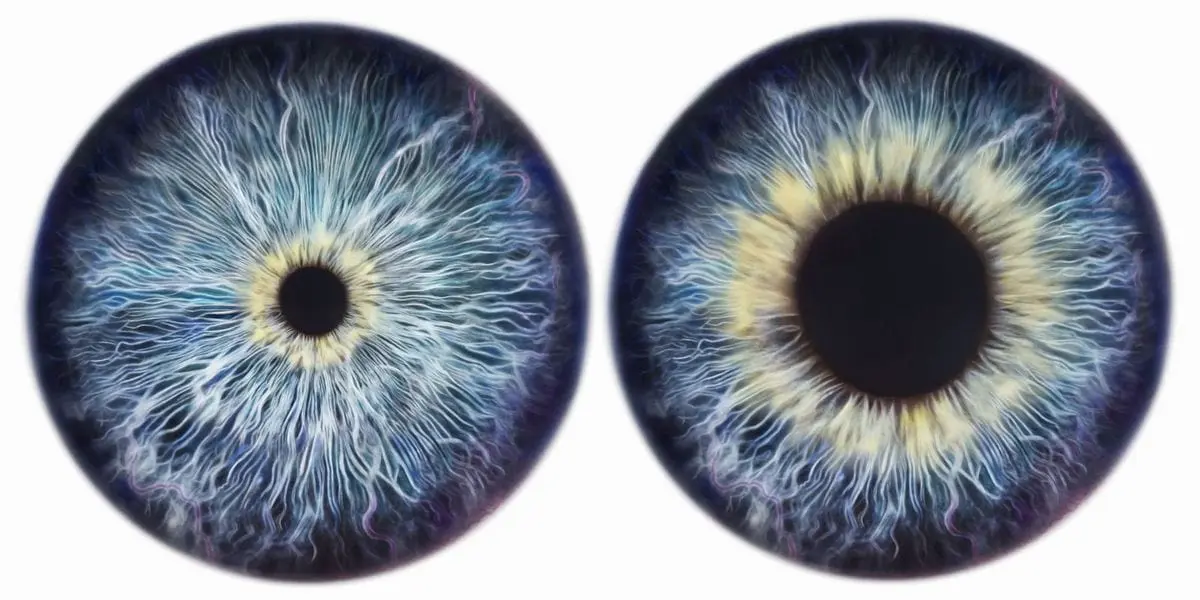 The pupil of the eye reacts to light. It narrows when there is very light around, and expands in the dark.. However, not only in such situations, its size changes.
The pupil of the eye reacts to light. It narrows when there is very light around, and expands in the dark.. However, not only in such situations, its size changes.
At many times when a person experiences specific emotions, pupil size may change. For example, it expands if we experience fear, joy, sexual desire, and excitement. Interestingly, the pupil reduces its diameter when a person feels uncomfortable, being strongly suppressed by the circumstances surrounding him.
7. Colors and shades
 Photoreceptors located in the retina of the eye allow a person to recognize 160 colors and about 600 of their shades.. Statistically, one in twelve men is colorblind and is completely blind or can only identify a few colors.
Photoreceptors located in the retina of the eye allow a person to recognize 160 colors and about 600 of their shades.. Statistically, one in twelve men is colorblind and is completely blind or can only identify a few colors.
6. We blink every few seconds
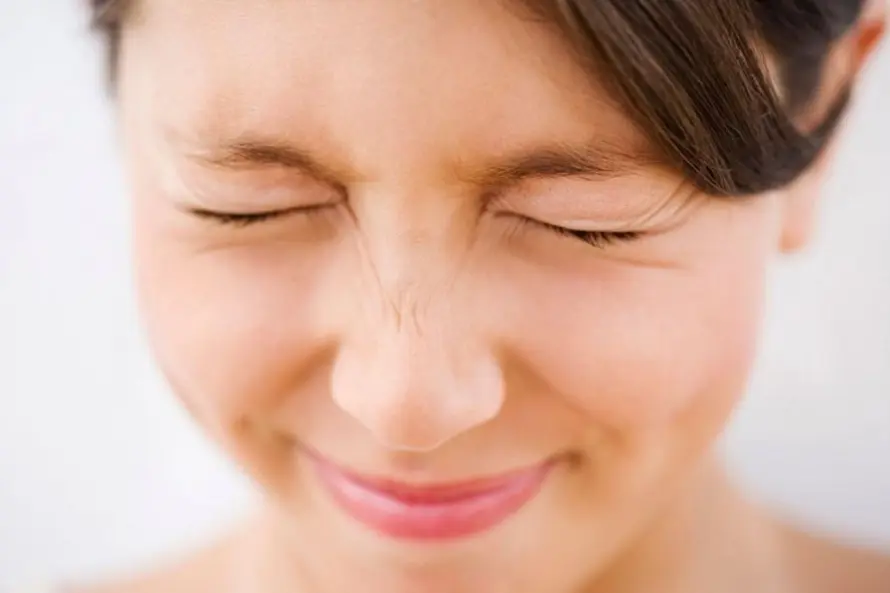 Scientists have calculated that an adult blinks 12 to 17 times per minute.. It is also known that if you sum up the time that the eyelids droop during blinking, then it can be concluded that the eyes remain closed for 9 days a year. Interestingly, newborns blink much less often – up to about 4 times per minute.
Scientists have calculated that an adult blinks 12 to 17 times per minute.. It is also known that if you sum up the time that the eyelids droop during blinking, then it can be concluded that the eyes remain closed for 9 days a year. Interestingly, newborns blink much less often – up to about 4 times per minute.
5. Pirate eye patch
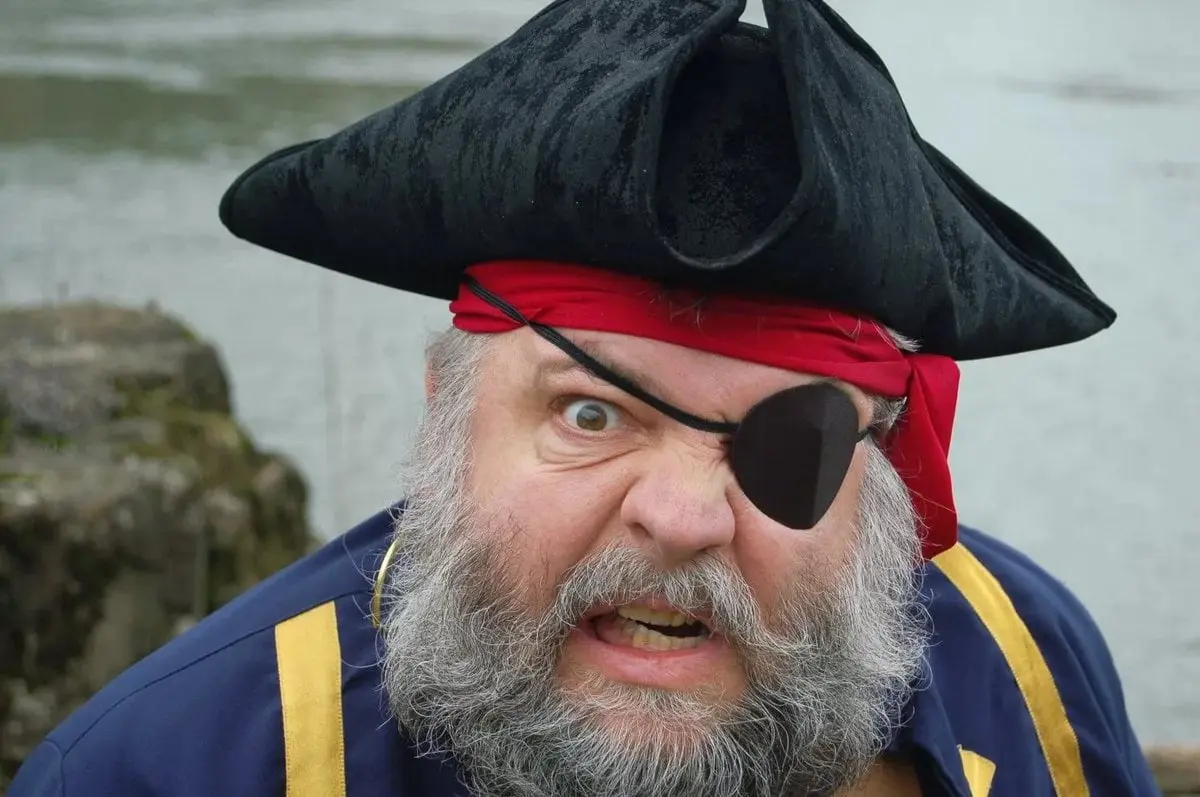 The eyes must adapt to the amount of light around it. Often, when we move from a bright room into a dark one, we need to wait a while before the eye adjusts and recognizes the environment and objects. Also in a situation where from a dark interior, we move into a light one.
The eyes must adapt to the amount of light around it. Often, when we move from a bright room into a dark one, we need to wait a while before the eye adjusts and recognizes the environment and objects. Also in a situation where from a dark interior, we move into a light one.
Exactly because of this reason Pirates wore an eye patch. She usually closed … a healthy eye, allowing you to quickly adapt to variable lighting conditions. The pirate, descending below the deck, where there was not enough light, put on a bandage over his open eye. Thanks to this habit, he could quickly adapt to changing the degree of illumination of the space without wasting a second on getting used to his eyes.
4. Eyes must rest
 The human eye can perform its functions without rest. However, the muscles that are responsible for the movement of the eyeball and eyelids need a break.. If they are tired, people begin to experience great discomfort. Because of this, symptoms can subsequently develop that interfere with good vision. The eyes begin to burn, watery, or there is a feeling of “heavy eyelidsand even a headache. This is a signal that it’s time to rest your eyes.
The human eye can perform its functions without rest. However, the muscles that are responsible for the movement of the eyeball and eyelids need a break.. If they are tired, people begin to experience great discomfort. Because of this, symptoms can subsequently develop that interfere with good vision. The eyes begin to burn, watery, or there is a feeling of “heavy eyelidsand even a headache. This is a signal that it’s time to rest your eyes.
3. Change in eye color in babies
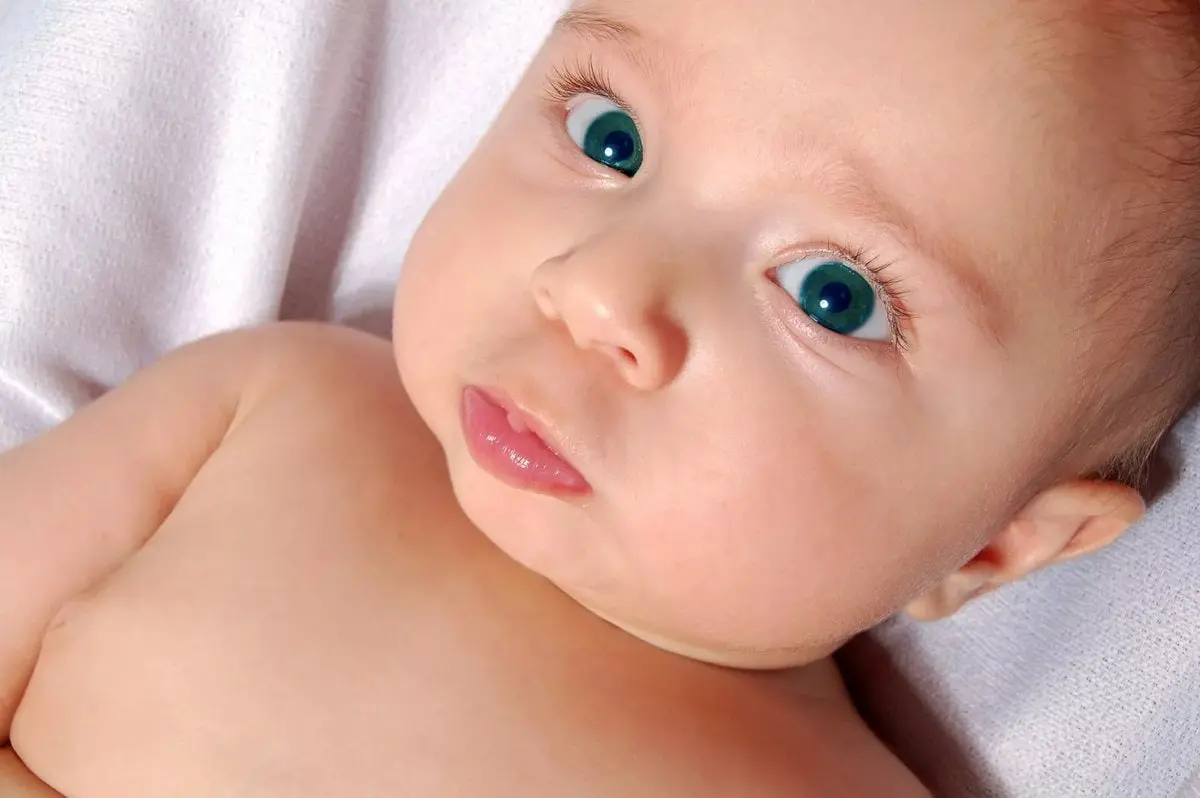 A feature that may surprise new parents is that babies don’t always end up with the same eye color they were born with. It is characteristic of our climate that newborns often come into the world with blue eyes, while for some it darkens over time. Sometimes you need to wait a few years to see the real color of the child’s eyes – it may later turn out that his eyes are not blue, but green or brown.
A feature that may surprise new parents is that babies don’t always end up with the same eye color they were born with. It is characteristic of our climate that newborns often come into the world with blue eyes, while for some it darkens over time. Sometimes you need to wait a few years to see the real color of the child’s eyes – it may later turn out that his eyes are not blue, but green or brown.
This is due to the production of melanin, which is found in the iris, which gives color to our eyes. In our climate, its production does not start immediately after the arrival of the child in this world, but after a while, it can affect the change in eye color.
It is interesting that in the world there are no two identical eyes. Each iris, like fingerprints, has its own original and unique pattern. Differences can be seen even between the right and left eyes of the same person. Even identical twins do not have identical irises.
It is also hard to believe that all blue-eyed people descended from the same distant ancestor. Scientists have established that all our blue-eyed contemporaries are descended from one forefather, who, most likely, lived about 10 thousand years ago in the Black Sea region.
Researchers studying the genetics of eye color have found that more than 99,5% of blue-eyed people who consent to having their DNA tested have the same small mutation in the gene responsible for the color of the iris. This, according to Professor Hans Eiberg and his colleagues from the University of Copenhagen, suggests that this mutation originally occurred in just one person, who became the ancestor of all blue-eyed people in future generations.
2. Night vision correction
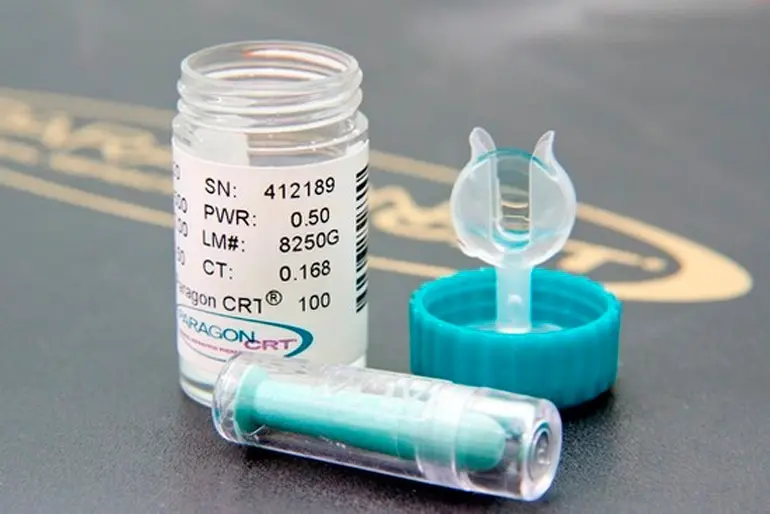 Few people know that during a night’s sleep, you can completely correct the defect of vision. Thanks to this method, in the morning, after waking up, a person can see clearly without wearing glasses. And all this thanks to one of the modern methods, which is called orthocorrection.
Few people know that during a night’s sleep, you can completely correct the defect of vision. Thanks to this method, in the morning, after waking up, a person can see clearly without wearing glasses. And all this thanks to one of the modern methods, which is called orthocorrection.
The whole secret of this method lies in special orthokeratological lenses that must be worn at night. During sleep, they model the eye and give the cornea a shape that allows you to see clearly for about 10 hours from the moment the lenses are removed.
Orthocorrection can correct visual defects such as nearsightedness and slight astigmatism. And at the same time, it is a completely non-invasive method – the eye returns to its original shape after using the lenses.
1. red eye
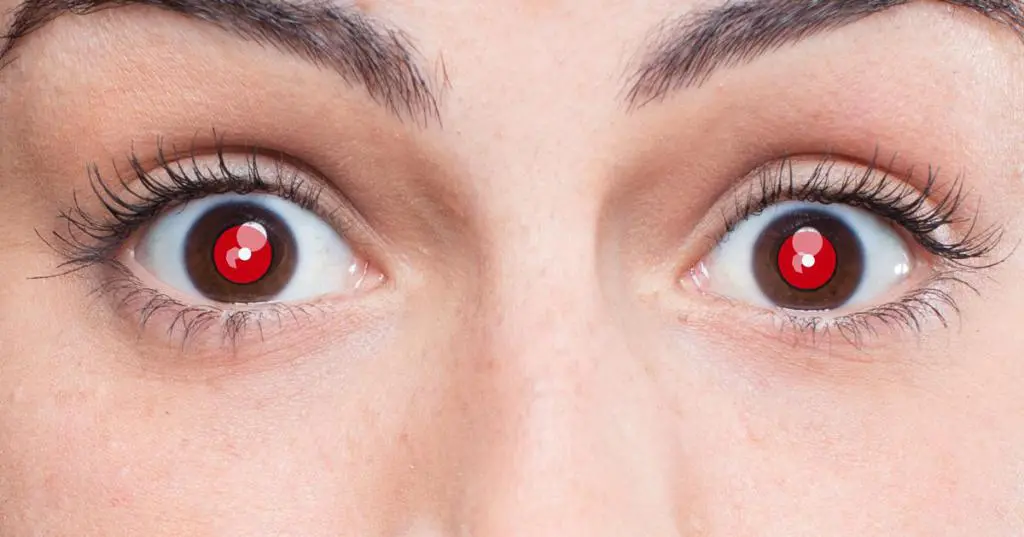 Photographers have certainly encountered red-eye on more than one occasion., which can ruin even the best shot. Actually, this is a side effect of using the flash in a shaded room or at night.
Photographers have certainly encountered red-eye on more than one occasion., which can ruin even the best shot. Actually, this is a side effect of using the flash in a shaded room or at night.
At the time of shooting, the flash light falls on the eyeball, more precisely on the pupil, which is in an expanded state in the dark. As a result, it does not have time to decrease and passes a large amount of light into the eyes, which, after reflection from the retina and passing through numerous blood vessels, gives a red color.










