Contents
- 10 Russian literature from the 11th to the 17th centuries
- 9. Almost entirely handwritten
- 8. Originates in the Byzantine and Bulgarian literary traditions
- 7. The highest goal of literature is the salvation of the soul
- 6. Books tend not to surprise the reader with novelty, but to “bewitch” with familiarity.
- 5. Literary collections are the most common type of manuscripts
- 4. The Old Church Slavonic language was created on the basis of the Bulgarian-Macedonian
- 3. The oldest monuments of writing – agreements with Byzantium
- 2. The Invasion of Batu had a great influence
- 1. Inseparable connection with folklore
Old Russian literature can be compared to the soil on which Russian culture of the XNUMXth-XNUMXth centuries grew. Old Russian literature differs from modern literature in its purpose – modern artistic literature exists in order to “raise” the reader above the ordinary. Old Russian included the foundations of the ideals of moral principles, faith in man and his ability to change the world.
Why is it important to know the literature of Ancient Rus’? Firstly, because without knowing it, we will not understand the full depth of the work of the brilliant poet A.S. Pushkin, the moral search of the writer Tolstoy, the deep philosophy of Dostoevsky’s thoughts, etc.
We invite you to set aside some of your time to get acquainted with some interesting facts about ancient Russian literature. Everything is written in simple words – it will be useful for general development.
10 Russian literature from the 11th to the 17th centuries

In the development of the literature of Ancient Rus’, 3 periods are distinguished: Kievan Rus (XI-XII centuries) – on the literature of the XI-XII centuries. the development of the literature of Belarus, Ukraine, Russia was based.
The collapse of North-Eastern Rus’ (XII-XV centuries) and the centralized Russian state (XVI-XVII centuries) – during this period, the literature of the forming Russian nation was created. From the 14th century distinct book traditions that led to the formation of Russian literature are clearly manifested, from the 15th century. to Belarusian and Ukrainian.
9. Almost entirely handwritten

The manuscript of Ancient Rus’ can now be found quite often (there are even special publics on social networks that have borrowed the form of writing). You can see that the books were decorated with different animals or figurines – the color varied from red to brown.
A notable feature of Old Russian literature is the way it is distributed and existed – it is handwritten, while this or that work was a collection (that is, a separate manuscript was not distributed), pursuing different goals. The value of the manuscripts was judged from their practical side, and not for the sake of embellishment.
8. Originates in the Byzantine and Bulgarian literary traditions

Old Russian literature brought spirituality and morality to the world – these are its most important goals, and also taught Christian ethics. It was she who became the ancestor of all subsequent Ukrainian, Russian and Belarusian literature.
Books brought up in people such qualities as generosity, warmth, kindness, etc. The development of writing in Rus’ formed the basis for the emergence of literary creativity.
It is worth noting that the authors adhered to the Bulgarian as well as Byzantine traditions in literature, taking an example from sources that indulged in translations.. But there is one caveat – the authors did not plagiarize, but with the help of their creative abilities they created something completely new. The translated literature served as the basis for the formation of their own traditions.
Interesting fact: in 1564 the first printed book “Apostle” was published in Russia.
7. The highest goal of literature is the salvation of the soul

The Purpose of Literature Was the Salvation of the Soul. Nowadays, few people are interested in the literature of Ancient Rus’, and even at school only some works are included: “The Tale of Igor’s Campaign”, for example, or “The Tale of Bygone Years”, etc., but even here they try to quickly talk about these books, and even completely replace it with the literature of the XNUMXth century.
Perhaps the whole point is that the characters from these works are no longer relevant, and the plots are not of interest to modern readers. Perhaps this is true – for us this literature is ancient, but for the people of that time it was very new and reflected the spiritual values of the people.
The central theme of all the works was, as mentioned earlier, the salvation of the soul. If you have read The Tale of Igor’s Campaign, you will understand what it is about.
6. Books tend not to surprise the reader with novelty, but to “bewitch” with familiarity.

New demands constantly arose, so it is not surprising that new works were written in connection with this circumstance. Many of them were copied for several centuries, and, of course, read – especially liked parts were included in other works, because few people were familiar with the feeling of authorship.
A literary work does not at all have the task of presenting something new to the reader, on the contrary, there is a goal to calm him down and “intrigue” with familiarity, which shows a commonality with folklore. The author, creating his work, performs, so to speak, a kind of ritual, as you know, the presence of surprises is undesirable in rituals.
5. Literary collections are the most common type of manuscripts

It should be noted that there were no separate manuscripts as such, most often a literary work was a collection.
The scribe was engaged in rewriting works, and the notebooks that were written by him could later be connected by a binder. He, in turn, could collect notebooks written by different arctic foxes and at different times, after which they were connected.
All literary materials were of the same format and were combined according to their content. Collections in our time are called convolutes.
4. The Old Church Slavonic language was created on the basis of the Bulgarian-Macedonian

The Bulgarian-Macedonian dialect served as the basis of the Slavic literary language, the task of which was to preach the Christian doctrine.. Initially, the language was conceived specifically for literary purposes, it was not used in everyday communication.
Cyril and Methodius became the creators of the alphabetical system, in addition, they translated it from the Greek language. Slavic peoples of the Middle Ages: Serbs, Bulgarians, Russians, etc. adopted this language as a literary language.
3. The oldest monuments of writing – agreements with Byzantium

The Bulgarian monk Khrabrachernorizets (9th-10th centuries) wrote in his legends that the Slavs did not have a system of written signs, and they carried out counting and divination with the help of cuts and features.
Scientists agree that the Slavs, even before the introduction of Christianity in Kievan Rus, used a primitive script. El Masudi, a writer who lived in the 10th century, saw prophecies in the temple that were embodied on stones. In Kyiv, Slavic translations of treaties with Byzantium have been preserved: 911, 944 and 971.
2. The Invasion of Batu had a great influence
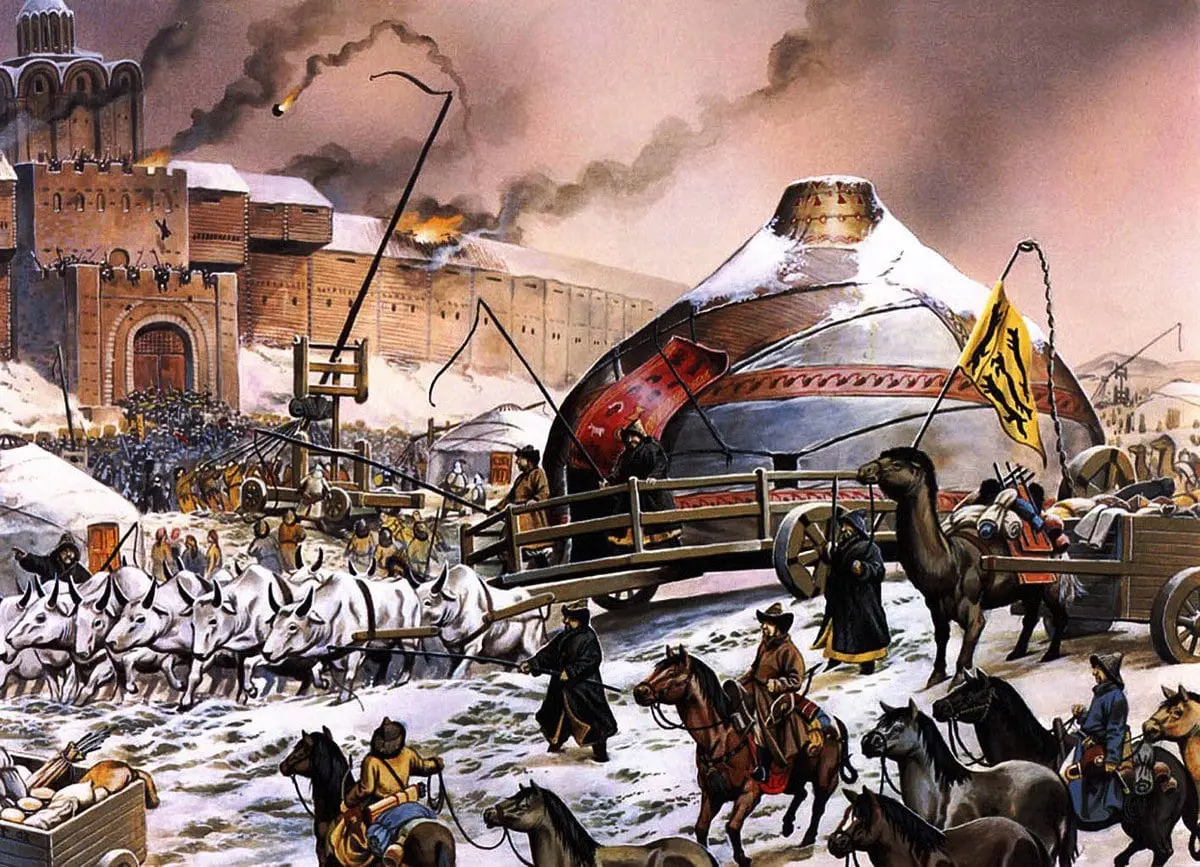

Kievan Rus at the beginning of the XII century was fragmented into separate principalities. Separate territories did not recognize the Kyiv prince and waged internecine wars. That is, in those days, Rus’ was exhausted and fragmented.
The invasion of Batu, of course, had a negative impact on the entire history of Rus’, freezing its development. Since that time, the lag behind European countries began, both in the economic and cultural spheres, which also affected literature.
1. Inseparable connection with folklore
Ancient Rus’ is closely intertwined with folk poetry – folklore. It was thanks to him that people understood artistic means of expression: through symbols and images, as well as the surrounding reality.
Each literary work included folklore, in which allegories, traditional symbols, figurative expressions, and so on were used.
Writing was intertwined with the genres of folk art, this includes legends (stories about important events transmitted to the younger generation), proverbs (folk poetry), fame, etc.










