Contents
Vagina
The vagina (from the Latin word vagina, which means sheath) is an internal organ of the female reproductive system. He is involved in reproduction.
Anatomy of the vagina
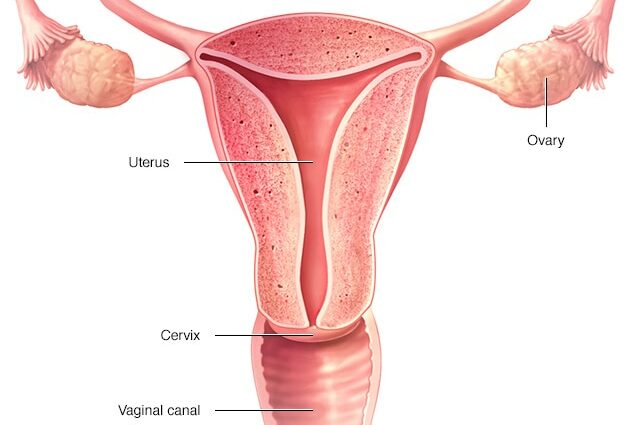
The vagina is a musculo-membranous organ located in the small pelvis. It measures on average between 7 and 12 centimeters long. Its size can vary during sexual life and following childbirth. It is a cylindrical shaped channel that is located between the bladder (in the front) and the rectum (in the back) capable of contracting.
The vagina extends from the vulva, which brings together the external organs of the female genital system (lips, inter-labial space, clitoris) to the uterus, where it will form a cul-de-sac at the level of the cervix. It presents an oblique orientation upwards and backwards (angle of 20 ° with the vertical) of the vulva towards the uterus. The hymen, a thin very elastic membrane, initially marks the border between the vagina and the vulva. It is usually torn during the first intercourse.
Physiology of the vagina
The vagina is the female organ of copulation. He receives the penis and semen during sex. A strongly erogenous organ, it is also responsible, along with the clitoris, for the sensations experienced during intercourse. Conversely, the cervix, which is very poor in nerve endings, is not involved in this feeling. The vagina also plays an important role in reproduction, since it must allow the passage of the newborn. The thin walls of the vagina have many folds and thus allow the necessary expansion during childbirth, mating or tamponade. The vagina is therefore an adaptable organ.
The vagina is also covered with a mucous membrane constantly lubricated by estrogen (hormones secreted by the ovaries). This mucous membrane is made up of different cell layers: basal cells (the deepest), intermediate cells and superficial cells. It allows a self-cleaning of the vagina and its quantity can vary according to the period of the cycle of the woman. We also talk about vaginal discharge. They start at puberty and are usually white or yellow in color. They announce the arrival of the rules. During this period, the vagina also becomes longer.
Pathologies and diseases of the vagina
In general, the female genital system as a whole can be the cause of many gynecological pathologies (sterility, sexually transmitted diseases, pathologies linked to pregnancy, etc.).
In childhood
Vulvo-vaginitis
This pathology can occur after insufficient vulvar toilet after contamination by the stool, after playing on the floor or during acute childhood infections. It results in itching, burning and urinary disorders. The germs responsible for these infections are generally commonplace. However, it can also be more specific germs, such as staphylococci. These infections of the vulva and vagina can be serious in a little girl because her vagina is not yet under the influence of estrogen and does not yet have an infection-fighting lining.
Adulthood
Dyspareunie
Etymologically, this word means “difficulty in mating”. It refers to all the pain felt, both by women and men, during sexual intercourse. Dyspareunia is very common during the first vaginal report because of the tearing of the hymen.
The vaginitis
These infections of the vagina are frequent and essentially harmless. They are manifested by white discharge: leucorrhoea, which can be accompanied by itching, burning and irritation or even pain during sexual intercourse. Some vaginitis have no noticeable symptoms. Vaginitis is favored by hormonal deficiencies, allergies and too much and / or too frequent vaginal injections. Even if they are generally caused by common germs, they can also come from a fungus (we speak then of mycotic vaginitis) or by specific germs (chlamydiae, gonococcus). In the latter setting, vaginitis may be more serious since the infection can reach the fallopian tubes.
Prolapse (urinary leakage)
Urinary leakage is the result of the genitals falling into the walls of the vagina. This fall, or ptosis, is not uncommon and is generally observed following a difficult and traumatic childbirth. This pathology causes a feeling of heaviness in the pelvis, perineum or rectum.
Vaginal cysts
Vaginal cysts are pockets (of air, fluid, or pus) that can form on or under the wall of the vagina. Rare, they are mostly benign but nevertheless cause a feeling of discomfort. There are several types, including Bartholin’s gland cyst.
Vaginal cancer
This is also a rare cancer, affecting less than 1 in 100 women each year. It appears preferentially in gems at risk.
Vaginal diaphragm
In some women, the vagina may contain a transverse septum that is usually less than 1 cm thick. This vaginal malformation is most commonly found in the upper third of the organ.
vaginismus
Sexual dysfunction in women. Corresponds to a contraction of the muscles of the vagina in a painful spasm at the time of penetration.
Treatments and prevention of the vagina
Maintaining pubic hair
The proliferation of hairs in the female genitalia creates a warm and humid environment, more favorable to the appearance and development of microbes and bacteria, which lead to infections. It would therefore be advisable to cut the long hairs. When shaving completely, be careful not to cut yourself to avoid infection.
Effects of antibiotics on the vaginal flora
Antibiotics are used to destroy germs in the body. In their fight against infections, they also destroy the intestinal and vaginal flora. Deprived of its mucous membrane, the vagina is therefore more fragile when taking antibiotics. To remedy this problem and avoid yeast infections, the doctor can prescribe an antimycotic treatment (ovum, cream) in addition to the antibiotic treatment.
Self-defense properties of the vagina
A 6 American study2014 demonstrated the benefits of “lactocillin”, an antibiotic produced by bacteria in the vagina, against vaginal yeast infection. Unlike other antibiotics, it allows targeted treatment.
Douching, to avoid
Vaginal microbes are the cause of the balance inside the vagina. The products used in vaginal douches are thus likely to disturb this osmosis. For intimate hygiene, it is therefore necessary to favor an enema with hot water or mild soap.
Frequent recurrence of vaginal yeast infection
There are behaviors to be adapted to limit the reappearance of vaginal yeast infection. For example, it is advisable to monitor your consumption of sugar, which the fungus feeds on, or to adapt your clothing (for example, prefer cotton or silk underwear).
Gynecological examinations
Vaginal touch
The gynecologist introduces two fingers deep into the vagina. He can thus feel the genitals. He can thus detect a fibroid of the uterus or an ovarian cyst.
Pap smear
A painless test that takes cells from the vagina and cervix. It can detect a gynecological infection, early cancer or even a precancerous condition.
Vaginal biopsy
Performed under local anesthesia, it is performed if a lesion is visible on the vagina.
History and symbolism of the vagina
The vagina is the location of the G-spot, known to cause a major orgasm. According to an internet survey carried out in 2005 by Doctor Catherine Solano among 27 women, 000% of French women have never experienced a vaginal orgasm.
Vaginal yeast infection is not spread! While this is a common symptom in women, yeast infection (a fungus) is not considered a sexually transmitted infection. However, it happens that the sexual partner of a woman with many yeast infections also feels irritation in the penis.
The vagina is an organ that is not well known to women. A study (7) carried out in 13 different countries with 9500 women showed that 47% of them had no idea of the size of the vagina. Gynecologists asking their patients to represent the female genitalia also find themselves with diagrams reflecting a lack of knowledge of the body.
In the same study, 41% of men said they found the vagina “sexy”.
During sports, gymnastics, or during intercourse, the vagina may make a slight noise. We talk about musical vagina or, to put it mildly, vaginal fart. This noise results, during mating, from the air circulation when the penis rubs against the vagina.
THEejaculationis not just a man’s story. Some women ejaculate at the time of orgasm (8). The nature of the fluid, secreted by the Skene glands and light in color and odorless, is not yet well known.