Contents
General description of the disease
Torticollis is a disease caused by changes in the soft tissues of the nerves of the neck and skeleton, due to which the head is tilted to the side and turned to the other (opposite) side.
Types and causes of torticollis
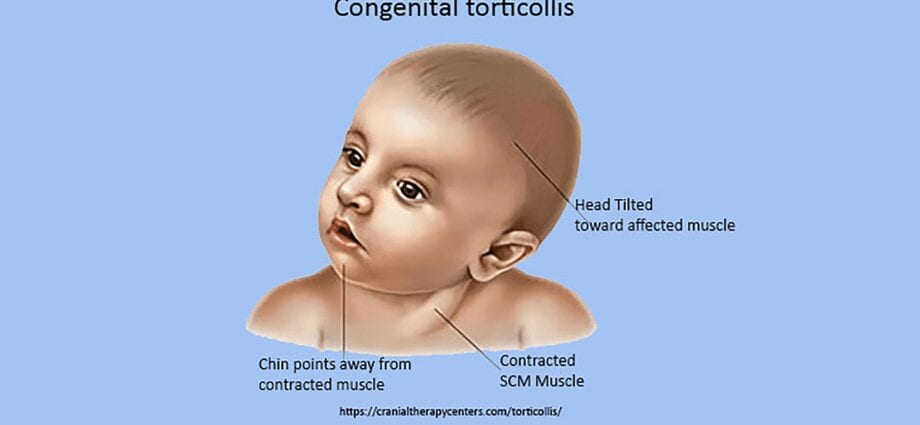
Congenital – the cause is incorrect placement of the fetal head in the womb or injury during childbirth, which causes hypertrophy of the clavicular-sternum muscle (it scar and shortens) or a defect in the development of the cervical spine.
Acquired torticollis. There are several of its subspecies:
- arthrogenic – occurs due to subluxation or dislocation of the vertebrae of the neck;
- hypoplastic – the cause is underdevelopment of the muscles of the trapezium or sternoclavicular muscle;
- dermatogenic – its appearance is based on changes in the skin of the neck due to scars;
- compensatory – this type of torticollis can develop due to decreased visual acuity or hearing;
- bone – various lesions of the vertebrae will cause torticollis;
- neurogenic torticollis occurs when the nerve and muscle formations of the neck are damaged;
- spastic (reflex) – excessively intense contractions of the cervical muscles contribute to the development of this disease.
In rare cases, torticollis can develop due to a prolonged stay of the head in a tilted form due to the peculiarities of a person’s professional activity.
The main signs and symptoms of torticollis:
- 1 acute, paroxysmal pain in the form of spasms (mainly tormenting from the side to which the head is tilted);
- 2 impaired posture;
- 3 the characteristic location of the head to the side (turning and tilting the head depends on which cervical muscle is damaged);
- 4 limiting movement and turning of the head;
- 5 in rare cases, spasms can be in the muscles of the upper limbs, eyelids, jaw, and in the facial muscles.
Complications
If torticollis is not treated, serious complications can develop, such as: facial hemipoplasia (asymmetry), scoliosis of the skull and plagicephaly, curvature (deformity) of the spine.
With the early development of torticollis, the pathology of PEP (perinatal encephalopathy) develops and intracranial pressure is increased.
To diagnose torticollis, it is enough to look at the position of the patient’s head. To find out the cause of the occurrence, it is necessary to make an X-ray of the cervical spine.
Useful foods for torticollis
To strengthen muscle tissue, the patient should eat right and focus on the use of: non-fatty meats, liver, sea and dairy products, eggs, cereals and sprouted grains of wheat, oats, barley, on the consumption of fresh fruits, berries and vegetables, legumes , vegetable oils and butter. Eat more greens and nuts. These foods contain vitamin B, which helps to develop and strengthen muscle tissue.
Traditional medicine for torticollis
Conservative methods of treatment include corrective gymnastics, therapeutic massage of the injured muscle, and the so-called “treatment position”.
If torticollis is of a congenital nature, then it is necessary to start treatment from the first days of the baby’s life, so that the clavicular-sternum-mastoid muscle does not heal. After all, if you start the disease, in the future, conservative treatment may not help and you will have to resort to treatment with the help of surgical intervention.
To correct the position of the head, special cotton wool rolls or sandbags, paraffin applications are applied.
Treatment by the position consists in the fact that the patient lies for an hour / one and a half in the correct position with a repetition rate of 3 times a day. To do this, a roller can be placed under the head, and sandbags are placed on the sides of the patient (this is done in order to maintain the correct body position). The treatment mattress should be semi-rigid. In severe cases and if the child is too small, the head should be placed at an angle of 10-15 degrees (this can be achieved by folding the edge of the mattress). This is done so that the patient does not choke. Another effective position will be when the patient is placed directly on his back, the head is turned on a healthy side and kept in this position while there is strength. If a small child has torticollis, then in order to interest him, you can put toys or objects of interest to him on that side.
Massage is needed to relieve muscle spasm and stretch the neck muscle. Movements should be circular, light and fluid. To correct on the diseased side, it is necessary to massage the facial muscles, and on the healthy side – the muscles of the trapezium.
After the massage, in order to consolidate the result, it is necessary to do therapeutic exercises, which includes all exercises where the muscles of the neck and trapezium are involved (these can be various alternate tilts and turns of the head in different directions).
Important!
Before resorting to a conservative method of treatment, you need to make an appointment with a surgeon and orthopedist so that they tell and show you how to properly perform certain procedures and exercises. Also, you need to visit a professional massage therapist or chiropractor who will show you what movements should be used during massage.
Dangerous and harmful foods with torticollis
- pickles, smoking, marinades;
- fatty food;
- foods that contain large amounts of caffeine
- sweet sparkling water;
- food with artificial fillers, additives;
- fast food with convenience store canned foods.
These products lower muscle tone, pollute the body, which leads to the accumulation of toxins, blood clots form, and blood supply to the muscles is disrupted. This can lead to their atrophy.
Attention!
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to use the information provided, and does not guarantee that it will not harm you personally. The materials cannot be used to prescribe treatment and make a diagnosis. Always consult your specialist doctor!