Contents
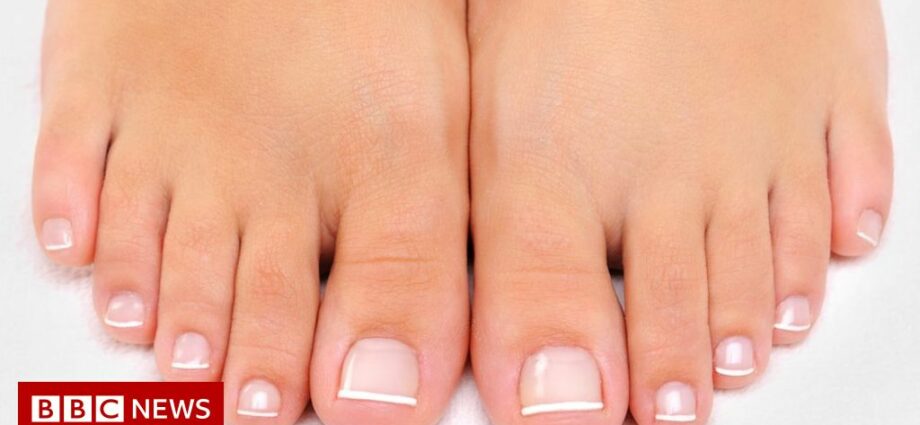
toes
The toe (from the old French arteil, from the Latin articulus, meaning small joint) is an extension of the foot.
Toe structure
Position. The toes are five in number on each foot, and are numbered from the medial face to the lateral face:
- the 1st toe, called hallux or big toe;
- the 2nd toe, called secundus or depasus;
- the 3rd toe, called tertius or centrus;
- the 4th toe, called quartus or pre-exterius;
- the 5th toe, called the quintus or exterius, and more generally the little toe.
Skeleton. Each toe has three phalanges, with the exception of the 1st toe which has only two. The bases of the phalanges articulate with the metatarsus (1).
Musculature. Intervening in particular in the toes, the muscles of the foot are divided into four layers (1):
- The 1st layer is made up of the abductor muscle of the big toe, the flexor digitorum brevis muscle and the abductor muscle of the little toe.
- The 2nd layer is made up of the lumbral muscles, the accessory flexor muscle of the last 4 toes as well as the tendons of the long flexor muscles of the toes.
- The 3rd layer is made up of the flexor digitorum brevis and adductor hallucis brevis muscles, as well as the flexor digitorum brevis muscle.
- The 4th layer consists of the adductor muscles of the toes, with the exception of the abductor muscle of the big toe contained in the first layer.
Vascularization and innervation. The 1st and 2nd muscle layers form the superficial neuro-vascular plane. The 3rd and 4th muscle layers constitute the deep neuro-vascular plane (1).
Protective casing. The toes are surrounded by skin and have nails on their upper surfaces.
Toe function
Body weight support. One of the functions of the toes is to support the weight of the body. (2)
Static and dynamic of the foot. The structure of the toes helps maintain body support, balance, and also perform various movements including propulsion of the body when walking. (2) (3)
Pathologies and pain in the toes
Different problems can arise in the toes. Their causes are varied but can be linked to a deformation, a malformation, a trauma, an infection, an inflammation, or even a degenerative disease. These problems can be manifested in particular by pain in the feet.
Fractures of the phalanges. The phalanges of the toes can be fractured. (4)
Anomalies. The foot and toes can be deformed. For example, hallux valgus is a congenital malformation causing the big toe to shift outward. The off-center area swells and becomes tender, even painful (5).
Maladies of the os. Different pathologies can affect the bones and modify their structures. Osteoporosis is one of the most common diseases. It constitutes a loss of bone density which is generally found in people over the age of 60. It accentuates bone fragility and promotes bills.
Infection. The toes can get infections, including fungi and viruses.
- Athlete’s foot. Athlete’s foot is a fungal infection located in the skin of the toes.
- Onychomycosis. This pathology, also called nail fungus, corresponds to a fungal infection in the nails. The most affected nails are usually the big and little toes (6).
- Plantar warts. Occurring in particular in the toes, they constitute a viral infection leading to lesions in the skin.
Rheumatism. Rheumatism includes all the diseases affecting the joints, especially those of the toes. A particular form of arthritis, gout usually occurs in the joints of the big toe.
Treatments
Medical treatment. Depending on the pathology diagnosed, different treatments may be prescribed to regulate or strengthen bone tissue, reduce pain and inflammation. In case of infection, anti-infectives may be prescribed such as antifungals.
Surgical treatment. Depending on the pathology diagnosed, surgery may be performed. In the event of a fracture, the placement of pins, a screw-retained plate or an external fixator may be necessary.
Orthopedic treatment. In the event of a fracture, a plaster cast can be performed.
Toe examination
Physical examination. Diagnosis begins with an observation of the toes and an assessment of the symptoms perceived by the patient.
Medical imaging exam. The clinical examination is often supplemented by medical imaging examinations such as an X-ray, a CT scan, an MRI, a scintigraphy or even a bone densitometry to assess bone pathologies.
Medical analysis. In order to identify certain pathologies, blood or urine analyzes can be carried out such as, for example, the dosage of phosphorus or calcium. In the case of a fungal infection, a sample may be taken to confirm the diagnosis.
Anecdote
Shape and arrangement of the toes. Different expressions are commonly used to define the shape and arrangement of the toes. The term “Egyptian foot” corresponds to the feet whose toes are of decreasing size from the big to the little toe. The term “Greek foot” defines the feet whose second toe is longer than the others. The term “square foot” is used when all the toes are the same length.