General description of the disease
This is a disease, a mental disorder in which a person has a violation of the sense of reality. It can be accompanied by hallucinations, delusions, very serious mood swings, deep and abrupt, a state of deep depression, despondency, or vice versa – uncontrolled excitement. In psychosis, disturbances in thought processes are also observed. A critical attitude towards one’s painful condition is completely absent. In psychotic episodes, a person can see, hear something that does not exist, and believe in it. At times, these symptoms can cause him to react aggressively to others or harm himself. This definition is often identified with schizophrenia. Although not the same, the presence of psychosis, along with other symptoms, is one of the defining criteria for schizophrenia.[1].
Causes of psychosis
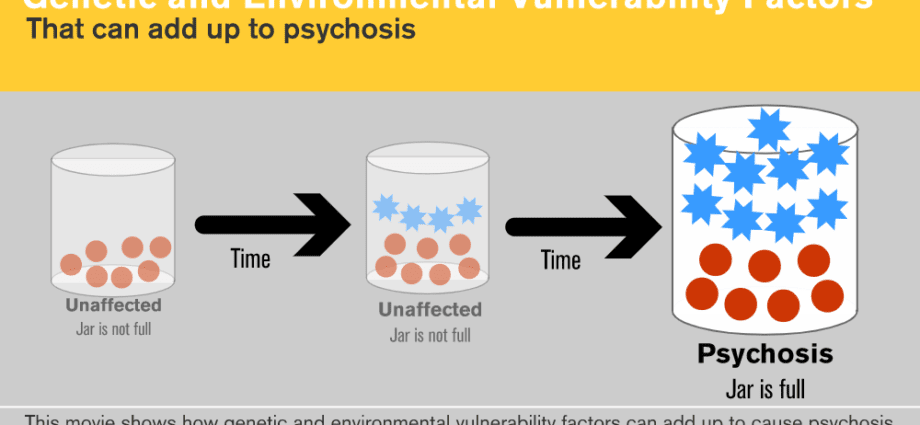
Doctors and scientists are still studying the question of why people develop psychosis. But a number of reasons and factors have already been identified that, individually or in combination, can influence the development of the disease.
- Genetics. Many genes can cause psychosis. But at the same time, the simple presence of this or that gene in a person is not an absolute guarantee that a person will develop this disorder.
- Psychological trauma.A traumatic event, such as the death of a loved one, war, or sexual assault, can trigger a psychotic episode. The type of injury, the damage it causes, and the person’s age, affect whether a traumatic event will lead to psychosis.
- Drug and alcohol use. LSD, marijuana, amphetamines and other drugs, and drinking can significantly increase the risk of active development of psychosis in people who already have a tendency to this disease.
- Physical illness or injury.Traumatic brain damage or tumors, stroke, HIV, and certain brain diseases such as Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease and dementia can also trigger psychosis.
- Teenage years.Adolescents and young adults are at increased risk of experiencing an episode of psychosis due to hormonal changes in their brains that occur during puberty.
Sometimes psychosis develops as a specific condition in certain other disorders: schizophrenia, depression, bipolar disorder[3]… We focus on this in the section of the article devoted to the types of psychosis.
Symptoms of psychosis
Psychosis usually does not develop suddenly. However, in the early stages, symptoms may be subtle. Sometimes its manifestations are no different from those behavioral features that occur in adolescents in the transition period, and therefore the development of the disorder is difficult to notice. As a rule, close people, family members are the first who can witness the appearance of some deviations.
Early signs of psychosis include:
- Alarming decrease in performance, lethargy;
- Difficulty concentrating
- Suspicion or concern;
- Apathy for self-care, personal hygiene;
- Spending a lot of time on familiar things, with which a person previously coped much faster;
- Strong, inappropriate emotions, or vice versa – the complete absence of such[2].
Symptoms of advanced disease can vary from person to person. Sometimes even one patient may experience the listed symptoms at the same time or periodically change. So, the following are common symptoms of psychosis:
- Misconceptions. False, irrational beliefs do not change even after the evidence given and are not shared by other people from the same cultural background.
- Hallucinations. A person can see, hear, feel, taste or smell something that is not really there. The most common hallucinations during psychosis are voices, which tend to suggest something negative.
- Disordered thinking. Thoughts and speech may become confused or slowed down. The person with psychosis may confuse words or use them in strange ways, form new ones, use mixed sentences, or change subject frequently. They may also have memory problems.
- Disordered behavior. A person with psychosis may become agitated, act childish, mumble or swear, or behave in other atypical, inappropriate ways. They may ignore their personal hygiene and household chores. In severe cases, they may stop responding to the world around them.[4].
Types of psychosis
The classification of psychoses is quite extensive. By origin and reasons for their appearance, they are divided into the following groups:
- Endogenous – caused by internal causes, diseases of the body;
- Somatogenous – based on a somatic disease;
- Psychogenic – arising as a result of mental processes that occur in the body;
- Organic – caused by a pathology of the brain;
- Intoxicating – develops as a result of exposure to various toxic factors (narcotic or alcoholic substances, medicines, industrial poisons) and others.
In addition, psychoses can also be classified according to the patient’s predominant symptomatology. depressive, manic, hypochondriacal and others, including also their combinations (for example, depressive manic).
Since psychosis can often be associated with other diseases or psychological conditions, the following diseases are classified as types of psychosis:
- 1 Schizophrenia – a mental disorder characterized by erratic thinking and behavior, which often includes delusions and hallucinations. Psychotic symptoms as well as significant social or occupational dysfunction persist for at least six months.
- 2 Schizophrenic disorder: Symptoms are similar to schizophrenia but persist for one to six months.
- 3 Schizoaffective disorder – combines the signs of both schizophrenia and affective disorder, with abnormal thinking processes and disorders of the emotional state.
- 4 Delusional disorder – includes strong, false beliefs (delusions). There are usually no hallucinations. In addition to the influence of delusions, a person’s psychosocial functioning can be markedly weakened, and behavior becomes clearly strange. However, in some circumstances, delusions are false enough to cause problems with daily life.
- 5 Psychoactive psychosis – manifests itself during the period of drug or alcohol use, may disappear after the cessation of the action of the substances. In some cases, psychosis persists after the initial substance-induced psychosis. This is often seen as an effect of stimulant drugs such as methamphetamine (“tic”).
- 6 Dementia – persistent dementia, loss of learned skills from knowledge as a result of physiological deterioration in the state of the brain, such as head trauma, AIDS, postencephalitis, Alzheimer’s disease or brain tumor.
- 7 Bipolar disorder – a mental health condition that affects mood. A person with bipolar disorder alternates between two very contrasting moods – depression, as well as intense excitement, elation – mania.
- 8 Severe depression – some people with depression also have symptoms of psychosis, which appear during periods of particularly high depression[3].
- 9 Postpartum psychosis – develops within six months after childbirth. This is usually part of a severe mood disorder, hormonal change.
- 10 Delirium – psychotic symptoms can be part of an acute confusional state that occurs as a result of another serious illness such as meningitis, sepsis, or after an epileptic seizure.
- 11 Brief psychotic episode – psychotic symptoms appear suddenly in response to a recognizable and very stressful life event. This is often the case with victims of violence. Symptoms can be severe but short-lived from one day to one month.
- 12 Psychosis due to general health – psychotic symptoms can occur as a result of brain tumors, epilepsy and other chronic diseases[5].
Complications of psychosis
Being in a state of psychosis for a long time significantly reduces the quality of human life. Due to obsessions, hallucinations, anxiety or depressive mood, thoughts of harming yourself or others, or even suicide may arise.
People with psychosis are also more likely to experience drug or alcohol abuse. Some use these substances as a way to treat or distract psychotic symptoms. However, substance abuse can worsen psychotic symptoms as well as trigger a range of other health problems.
Prevention of psychosis
Alas, psychosis is not always preventable. For example, schizophrenia is caused by a combination of biological, psychological and environmental factors that we cannot always act on. But in some cases, we can influence the development of psychosis: for example, to stop using drugs and alcohol, which provoke the development of the disease. Or to distribute the psychological load at home and at work so as not to experience high levels of stress, and to minimize the traumatic impact of the environment on our psyche. And in case of difficult situations or alarming symptoms, you can always turn to a psychologist who will help you deal with the reasons and cope with a difficult period in life, preventing it from developing into a very serious mental disorder.
It is also important to have the support of loved ones who can notice the warning signs, help you turn to a specialist for help.
Diagnosis of psychosis
Early diagnosis of the disease helps improve long-term outcomes and offers more treatment prospects. However, the problem lies in the difficulty of diagnosing psychosis at the initial stages of its development. The disease may progress slowly over several months or even years before the symptoms become noticeable.
Psychiatrists have developed recommendations for the health care system, according to which people should be examined in more detail for the presence of psychosis, in whom:
- deterioration in productivity at school or at work;
- manifestation of social isolation;
- the appearance of frustration, anxiety, the reasons for which they cannot explain.
There are no biological tests or tests to diagnose psychosis. Laboratory research can be carried out only in order to exclude other medical problems that could provoke the onset of symptoms that are characteristic of psychosis, as well as to exclude intoxication or poisoning with toxic substances.
Psychosis is primarily diagnosed by clinical research and history – the doctor examines the patient and asks about their symptoms, experiences, thoughts and daily activities. It also clarifies whether there are people with mental illness in the family.
Sometimes assigned electroencephalography – it records the electrical activity of the brain and helps to rule out delusions, head trauma or epilepsy as possible causes of psychotic symptoms[6].
Treatment of psychosis in mainstream medicine
Treatment of this disease in official medicine involves the following steps:
- Taking antipsychotic drugs – they help relieve the symptoms of psychosis, but they cannot cure or completely eliminate the underlying cause.
- Psychological therapy – individual work with a psychotherapist, elimination of the negative consequences of traumatic events. In the course of studies, it was determined that the inclusion of family members, relatives, friends of the patient to this therapy brought a good effect and reduced the need for inpatient treatment of patients.
- Social support – the embodiment and implementation of human social needs, such as education, employment, etc.
After an episode of psychosis has occurred, most people who feel better after taking medication should continue to take the medication as directed by their doctor for at least a year. About 50% of people need to take medication on a long-term basis to prevent symptoms from recurring.
If a person’s psychotic episodes are serious and can cause significant harm to them or those around them, the patient may be admitted to a psychiatric clinic for treatment.[6].
Healthy foods for psychosis
There are a number of foods that can cope with depression and improve mood. We provide a list of foods that help trigger the body’s production of the hormone of happiness – serotonin… It is made from an amino acid called tryptophan, which we get from food. In turn, the synthesis of tryptophan is facilitated by foods that contain vitamins B, C, as well as zinc and magnesium. They definitely need to be included in the diet.
- Eggs – contain vitamins A, D, E, tryptophan, proteins. It is best to eat them boiled.
- Fish – contains a large amount of vitamin D, tryptophan, fatty acids. Increases immunity, helps to improve mood.
- Red, orange vegetables and fruits – pumpkin, oranges, bell peppers, carrots, grapefruits, beets – all these foods help to recharge a good mood, and also contain bioflavonoids, which are very useful for proper blood circulation in the brain.
- Bananas are one of the most effective remedies for depression. Eat 1 banana a day, as they contain an alkaloid harman, which is based on mescaline, the so-called “drug of happiness.”
- Spices – cardamom, star anise, nutmeg are great for fighting stress. However, spices may have contraindications associated with other, physical characteristics of the body – you definitely need to familiarize yourself with them before using.
Traditional medicine for psychosis
- 1 Lemon balm broth is a tasty and useful remedy for combating psychosis. Pour a couple of teaspoons of dry lemon balm leaves with 500 ml of boiling water, let it brew in a sealed container for 2 hours, strain and drink this volume in 3 doses a day.
- 2 Valerian infusion – dry roots must be insisted in boiled water overnight, and then bring the mixture to a boil, cool, strain and take 3 tablespoon 1 times a day. By the way, you can also prepare a soothing bath from valerian root. For 10 liters of water, use 300 ml of strong root decoction. It is very easy to prepare it – 40 grams of crushed dry roots must be poured with a liter of water and cooked over low heat for 15 minutes. And then strain and pour into the bath.
- 3 Hop cones in traditional medicine are also considered an effective way to combat psychosis. To do this, 1 tbsp. cones need to be poured with a glass of boiling water, let it brew for about an hour, and then strain the broth and take it in 2 tbsp. 3 times a day.
- 4 Carrots or carrot juice are excellent remedies for depression. You need to consume 100-200 grams of this vegetable per day, or drink a glass of juice on a regular basis.
- 5 Ginseng root or dried leaves should be poured with hot water in a ratio of 1:10, infused for several hours, and then taken 1 tsp. in a day.
- 6 Another remedy that helps to cope with nervous disorders is peppermint infusion. You need to pour 1 tbsp. dried leaves with a glass of boiling water, boil for 5-7 minutes, let cool, strain and drink 0,5 cups twice a day – in the morning and in the evening.
- 7 Straw can be a tonic and tonic for depression. To do this, pour 3 tbsp. tablespoons of chopped straw 500 ml of boiling water, let it brew for 1-2 hours, and then drink this volume in small portions throughout the day[7].
Dangerous and harmful foods for psychosis
There are no strict dietary contraindications for people suffering from psychosis. However, it is advisable to give up drinks, foods that are strong pathogens for the nervous system. For instance:
- Coffee – increases the activity of the nervous system.
- Alcohol, drugs – negatively affect the work of the brain, provoke mental and motor excitement, intensify the symptoms of psychosis, and can provoke bouts of aggression.
- A large number of sweets, in particular chocolate, as sugar is another nervous system activator. The amount of its intake should be reduced, or even better, sweets or cakes in the diet should be replaced with more useful sweets – for example, dried fruits or jelly.
Use of any material without our prior written consent is prohibited.
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to apply any recipe, advice or diet, and also does not guarantee that the specified information will help or harm you personally. Be prudent and always consult an appropriate physician!
Attention!
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to use the information provided, and does not guarantee that it will not harm you personally. The materials cannot be used to prescribe treatment and make a diagnosis. Always consult your specialist doctor!