- general description
- Types and causes of occurrence
- Symptoms
- Complications
- Prevention
- Treatment in mainstream medicine
- Healthy foods
- Folk remedies
- Dangerous and harmful products
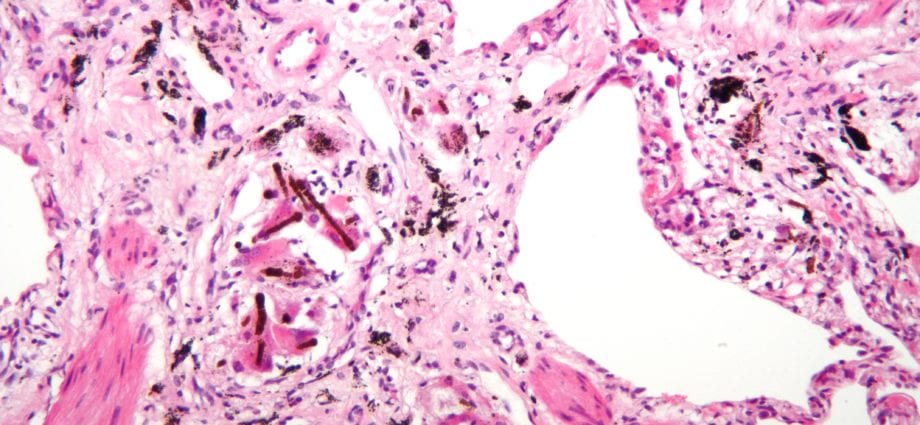
General description of the disease
Pneumoconiosis is a group of occupational pathologies in which, as a result of regular inhalation of air polluted with dust, inflammatory diseases of the lungs develop.
Most often, pneumoconiosis is diagnosed in workers in the asbestos, glass, steel industry, workshops for processing wheat into flour, elevators, miners. Workers in these professions are systematically exposed to dusty air and, depending on working conditions, from 30 to 55% of workers in “dusty professions” are ill with pneumoconiosis.
Pneumoconiosis is characterized by the irreversibility of the course, eventually leading to disability and shortening life expectancy.
Types and causes of occurrence
Depending on the etiology, the following types of pneumoconiosis are distinguished:
- silicosis – a type of pneumoconiosis, which causes silicon dioxide that enters the body through regular inhalation of silica dust;
- pneumoconiosiscaused by organic dust, these include all forms of dusty lung pathologies, the development of which is provoked by agricultural dust (flax and cotton, sugar cane), dust of synthetic substances;
- carboconiosis – develop due to the inhalation of dust, which includes carbon: graphite, soot, coke, coal;
- silicatoses – provoke dust minerals containing silica with minerals such as aluminum, calcium, iron and magnesium;
- pneumoconiosiscaused by inhalation of mixed dust without silica content – pneumoconiosis of welders or grinders;
- metalloconiosis caused by inhalation of dust from metals: tin, manganese, iron, steel, aluminum.
Solid dust particles have sharp corners, when they enter the lungs, they damage tissues, as a result of microtraumas, fibrosis develops.
According to the types of flow, pneumoconiosis is divided into:
- 1 slowly progressive pneumoconiosis – the pathology develops after 15-20 years of work in a production with an insignificant dust content. It is typical for most cases of pneumoconiosis. The chronic course can be in the form of simple pneumoconiosis with mild symptoms and mild changes in the tissues of the lungs or a complicated form of the disease with respiratory failure and disability;
- 2 rapidly progressive pneumoconiosis develop after 5 – 10 years of work in a production with a high content of silica dust;
- 3 late-onset pneumoconiosis – occur after the termination of contact with dust.
Symptoms
Regardless of the type and nature of the pathology, all pneumoconiosis is characterized by the following symptoms, which develop gradually:
- shortness of breath, which increases with physical exertion – one of the first symptoms of pneumoconiosis;
- a dry, unproductive cough is a common symptom;
- pain in the chest, interscapular and subscapular regions;
- wheezing;
- tightness in the chest;
- subfebrile temperature;
- decreased body weight;
- increased sweating;
- increased fatigue.
Complications
Pneumoconiosis is fraught with dangerous consequences. Their development depends on the state of the patient’s immune system and on the effectiveness of treatment. Most often, pneumoconiosis is complicated by the following pathologies:
- 1 emphysema of the lungs;
- 2 bronchial asthma;
- 3 tuberculosis;
- 4 cardiopulmonary insufficiency;
- 5 pneumonia;
- 6 sudden pneumothorax;
- 7 rheumatoid arthritis;
- 8 lungs’ cancer;
- 9 scleroderma.
Prevention of pneumoconiosis
To prevent the development of pneumoconiosis, you should:
- use respiratory masks;
- limit or completely quit smoking;
- be vaccinated against influenza and pneumococcal infection;
- be monitored by a phthisiatrician and regularly take x-rays;
- in hazardous production, carry out a set of measures aimed at improving working conditions;
- rational employment;
- increasing the body’s immune forces;
- avoiding contact with sick respiratory infections;
- preventive examination of personnel.
Treatment in mainstream medicine
Currently, there are no medicines and treatment methods that guarantee complete healing of the patient from pneumoconiosis. Therapy should be aimed at:
- 1 decrease in the manifestation of the main symptoms – cough, heaviness in the chest, shortness of breath;
- 2 improvement of the general condition of the patient;
- 3 prevention of complications;
- 4 minimizing side effects after medication.
In order for the therapy to be as effective as possible, contact with the agent that triggered the development of the pathology should be completely stopped. Of the physiotherapeutic procedures for pneumoconiosis, massage, salt-alkaline inhalations and physiotherapy exercises are shown. At least 2 times a year, such patients are recommended sanatorium treatment.
Useful foods for pneumoconiosis
During the treatment of pneumoconiosis, the patient should eat in fractional portions 6 times a day. To improve the protective functions of the body, it is necessary to give preference to protein foods and foods rich in vitamins. Food should be boiled, baked in the oven or steamed in order not to overload the patient’s stomach and intestines, the food should be mechanically and chemically gentle. The following foods should be included in the diet of a patient with pneumoconiosis:
- first courses based on vegetable broths;
- liquid milk porridge;
- boiled fish and lean meat;
- jelly, fruit drinks, compotes from berries or dried fruits, freshly squeezed fruit juices;
- fermented milk products to normalize the intestinal microflora: cottage cheese, kefir, fermented baked milk, sour cream, yogurt;
- honey;
- fresh vegetables and herbs;
- fresh fruits;
- to improve appetite moderately salty snacks: herring fillets, pickled vegetables, red and black caviar;
- chicken and quail eggs;
- dried fruits: figs, dried apricots, prunes, dates, raisins;
- walnuts and hazelnuts, cashews, peanuts;
- cod liver, fish oil.
Folk remedies for the treatment of pneumoconiosis
Traditional medicine has a high therapeutic efficiency in the treatment of pneumoconiosis, however, they cannot replace official therapy, they can only be an addition to the main treatment. To restore lung function, the following remedies are recommended:
- 1 heat 700-750 ml of good homemade buckwheat honey, add 100 g of chopped fresh birch buds there, strain. Take the resulting mixture in 1 tsp. before going to bed for 6-10 months. This remedy strengthens the immune system;
- 2 A decoction of dark raisins will help relieve coughing. For this, 300 g of chopped berries are steamed in ½ liter of boiling water, squeezed and filtered. Take 1 tbsp. l. 5 times a day;
- 3 You can relieve rough breathing with fig milk. To prepare it, you need 10 figs and 1 liter of milk. Combine the ingredients and simmer on a minimum heat for 5 minutes, drink during the day as tea;
- 4 you can get rid of a cough with a honey compress. Lubricate the back and chest area with honey, put a piece of cloth moistened with vodka on top (for children, dilute vodka with water in a 1: 1 ratio), cover with polyethylene on top;
- 5 Boil 1/3 cup of walnut kernels in 0,5 liters of red semi-sweet wine, cool, add 2 tbsp. honey. Take 1 tablespoon before bedtime;
- 6 50 g of unpeeled oat grains are simmered in 1 liter of milk for an hour, strain, cool, add 1 tablespoon of honey, drink 1 glass warm;
- 7 mix 100 g of fresh cottage cheese and 1 tbsp. honey, apply the prepared mass on the back and chest, excluding the area of the heart. Keep the compress for 30 minutes;
- 8 rub the chest and back with an ointment made from wax and pork fat in a ratio of 1: 4;
- 9 tea made from dried rose hips with honey;
- 10 when coughing, “mogul-mogul” helps well; for its preparation, grind the yolks of chicken eggs with sugar until the mixture triples.
Dangerous and harmful products for pneumoconiosis
During the treatment of pneumoconiosis, the following foods should be excluded from the diet:
- limit the consumption of table salt;
- alcoholic beverages;
- strong coffee and cocoa;
- fatty meat and butter;
- store semi-finished products;
- sweet soda;
- hot sauces and mayonnaise;
- snacks, chips and crackers;
- fried and smoked foods;
- meat and fatty fish broths;
- fruits with coarse fiber;
- chocolate;
- canned food and sausages;
- ice cream.
- Herbalist: golden recipes for traditional medicine / Comp. A. Markov. – M .: Eksmo; Forum, 2007 .– 928 p.
- Popov A.P. Herbal textbook. Treatment with medicinal herbs. – LLC “U-Factoria”. Yekaterinburg: 1999.— 560 p., Ill.
- Pneumoconioses, source
- Carbon pneumoconiosis in a synthetic graphite worker,
Use of any material without our prior written consent is prohibited.
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to apply any recipe, advice or diet, and also does not guarantee that the specified information will help or harm you personally. Be prudent and always consult an appropriate physician!
Attention!
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to use the information provided, and does not guarantee that it will not harm you personally. The materials cannot be used to prescribe treatment and make a diagnosis. Always consult your specialist doctor!