Contents
Enzymes are the “workhorses” of our body. If you look in the academic reference book, you can find out that the word enzymes, translated from Latin, means leaven. And it is thanks to such a leaven that a huge number of chemical processes take place in our body every second.
Each of these chemical processes has its own specialization. During one, proteins are digested, during the other – fats, and the third is responsible for the absorption of carbohydrates. In addition, enzymes are capable of converting one substance into another, which is more important for the body at the moment.
Enzyme rich foods:
General characteristics of enzymes
The discovery of enzymes happened in 1814, thanks to the conversion of starch into sugar. This transformation occurred as a result of the action of the amylase enzyme isolated from barley seedlings.
In 1836, an enzyme was discovered, later named pepsin. It is produced in our stomach on its own, and with the help of hydrochloric acid, it actively breaks down proteins. Pepsin is also actively used in cheese making. And in yeast transformation, alcoholic fermentation causes an enzyme called zymase.
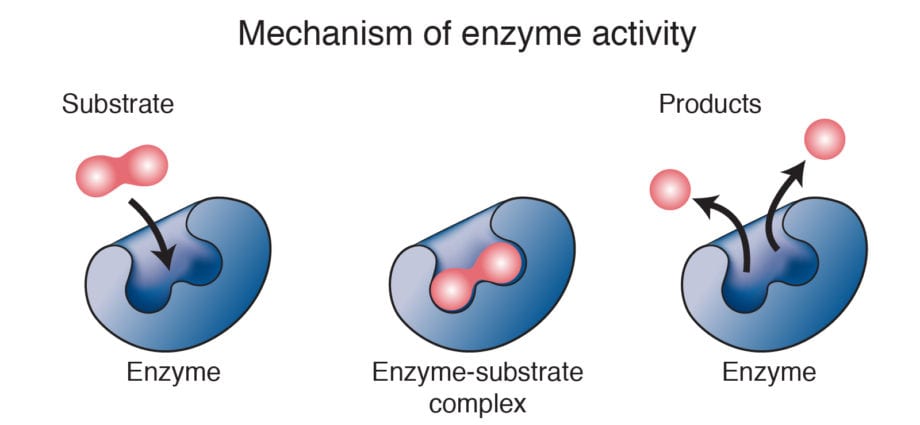
By their chemical structure, enzymes belong to the class of proteins. These are biocatalysts that convert substances in the body. For their purpose, enzymes are divided into 6 groups: lyases, hydrolases, oxidoreductases, transferases, isomerases and ligases.
In 1926, enzymes were first isolated from living cells and obtained in crystalline form. Thus, it became possible to use them as part of medicines to improve the body’s ability to digest food.
Today science knows a large number of all kinds of enzymes, some of which are produced by the pharmaceutical industry as medicines and dietary supplements.
Pancreatin extracted from the pancreas of cattle, bromelain (pineapple enzyme), papain obtained from the exotic fruit of papaya are in great demand today. And in fatty foods of plant origin, for example, in avocados, and in the pancreas of animals and humans, there is an enzyme called lipase, which is involved in the breakdown of fats.
Daily need for enzymes
It is difficult to calculate the total amount of enzymes required by the body for full functioning during the day, due to the large number of enzymes existing in our body in very different quantities.
If the gastric juice contains few proteolytic enzymes, then the amount of products containing the necessary enzymes should be increased. Pancreatin, for example, is prescribed in amounts ranging from 576 mg per day and ending, if necessary, with a 4-fold increase in the dosage of this drug.
The need for enzymes increases:
- with sluggish work of the gastrointestinal tract;
- with some diseases of the digestive system;
- excess weight;
- weak immunity;
- intoxications of the body;
- in old age, when their own enzymes are produced worse.
The need for enzymes decreases:
- in the case of an increased amount of proteolytic enzymes in gastric juice;
- individual intolerance to products and preparations containing enzymes.
Useful properties of enzymes and their effect on the body
Enzymes are involved in the digestion process, helping the body process food. They normalize metabolism, promoting weight loss. Strengthen immunity, remove toxins from the body.
Promote the renewal of body cells and accelerate the body’s self-purification process. Convert nutrients into energy. Accelerate wound healing.
In addition, food rich in enzymes increases the number of antibodies that successfully fight infections, thereby strengthening our immunity. The presence of digestive enzymes in food contributes to its processing and proper absorption of nutrients.
Interaction with essential elements
The main components of our body – proteins, fats, carbohydrates – closely interact with enzymes. Vitamins also contribute to the more active work of some enzymes.
For the activity of enzymes, an acid-base balance of the body, the presence of coenzymes (derivatives of vitamins) and cofactors are necessary. And also the absence of inhibitors – certain substances, metabolic products that suppress the activity of enzymes during chemical reactions.
Signs of a lack of enzymes in the body:
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- general weakness;
- malaise;
- joint pain;
- achilic gastritis;
- increased unhealthy appetite.
Signs of excess enzymes in the body:
- headache;
- irritability;
- allergies.
Factors affecting the content of enzymes in the body
Regular consumption of foods containing enzymes helps to replenish the lack of essential enzymes in the body. But for their full assimilation and vitality, it is necessary to ensure a certain acid-base balance, characteristic only of a healthy body.
In addition, in some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, certain types of enzymes are no longer produced by the body in sufficient quantities. In this case, dietary supplements and some medications come to the rescue.
Enzymes for beauty and health
Since enzymes are involved in the transformation of some compounds into others, more important, their functioning determines not only the health of our entire body, but also affects the appearance of the skin, hair, nails, and optimal body weight.
Therefore, using foods containing enzymes, you can not only establish general nutrition for the whole body, but also enhance your external beauty and attractiveness. No wonder they say that beauty is, first of all, excellent health of the whole organism!