Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
An anal fissure is a narrow and shallow tear or ulceration in the mucosa of the anal canal (the short end of the digestive tract at the border of the rectum and anus). The fissure is caused by too much tension at the end of the anal canal during physical exertion or constipation. The ailment occurs in people of all ages, both men and women.
Anal fissure – definition
Anal fissure is caused by high tension in the end of the anal canal (due to exercise, persistent constipation and / or increased tension of the anal sphincters). It is characterized by the formation of a linear ulceration of the anal canal mucosa, usually located in the posterior or middle part of the anal canal. The ailment may also appear as a result of infections or mucosa ischemia in the area of the mucosa. An anal fissure can occur in people of all ages, both men and women. In the latter case, a high number of pregnancies and consultations increases the risk of the disease.
The causes of the formation of an anal fissure
Sales it is a tight, short (3-6 cm) and terminal section of the digestive tract surrounded by the muscles of the anal sphincter: internal and external. An anal fissure is the morning in the anal canal that occurs when the inner layer of the anus bursts. It usually occurs after the expulsion of hard stool (then there is a mechanical trauma and too much stretching of the anus and rupture of its inner layer).
Another reason for an anal fissure may be loose, diarrheal stools. Then, there is a chemical irritation by digestive juices, which enter the anal area too quickly and irritate the place that becomes susceptible to trauma, i.e. cracks on the inside. This creates a wound to the inner layer of the anus called an anal fissure. It runs longitudinally along the long axis of the anal canal and is located most often (in 85% of cases) from the top (from the back), less often (10%) from the bottom (from the vagina in women, from the scrotum in men), even more rarely in other the periphery of the anus. Sometimes there are more than one wounds (fissures).
Other factors that influence the formation of an anal fissure include:
- intestinal ulcers,
- Crohn’s disease,
- anal sex (common),
- infection of the anal glands,
- defecation in the form of hard and compact stool,
- long-term constipation
- long-term childbirth, during which a child is born with a large birth weight (then the doctor must use auxiliary organs),
Division of the anal fissure
An anal fissure may be;
- acute – then it has the form of a fresh damage to the anal canal mucosa,
- chronic – as a defect in the rectal mucosa that has not healed within six weeks of the onset of the symptoms.
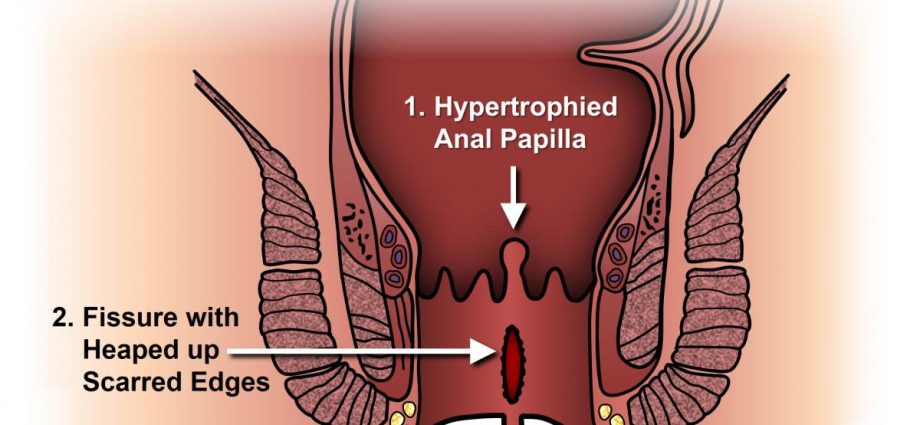
Where is an anal fissure?
1. Posterior midline of the anal canal – the most common.
2. Middle anterior line of the anal canal.
3. Posterior midline and anterior anal canal.
4. Lateral rectal quadrants (especially in patients with Crohn’s disease, cancer, leukemia or tuberculosis).
Symptoms of anal fissure
Symptoms of an anal fissure are similar to those of hemorrhoids or anal fistulas. The most characteristic are pain, bleeding and burning during defecation. Pain is most often felt as the stool passes through the anus and a few minutes after passing it, after which it usually resolves on its own. There are cases when the pain can stay with the patient for much longer, which hinders normal functioning. It can be or stinging, and it can be strong or unobtrusive. In addition, itching, burning or discomfort in the anus and perineum may be present.
Bleeding almost always occurs when you pass stools. Most often, blood is visible on the paper when wiped, on the toilet bowl, or as a stain on the stool. Sometimes the bleeding is bigger, lasting a little longer than the moment of defecation, and the marks are visible on the underwear. In addition, there may also be moist discharge around the edge of the anus. Another symptom of an anal fissure is the feeling of a lot of pressure on the stool.
Anal fissure – diagnosis of the disease
The clinical symptoms, which are revealed during the medical interview with the patient, play the main role and at the same time the basis for the diagnosis. In turn, for the final confirmation of suspicions, it is necessary to perform a proctological examination. This kind of study:
- in a fresh anal fissure reveals the presence of a linear rupture of the anal canal mucosa and pain,
- sentinel nodules are revealed in a chronic anal fissure; hard fibers of the muscle of the internal anal sphincter at the bottom of the fissure; defect of the mucosa in the form of a longitudinal ulcer with hard edges; an overgrown perianal nipple.
Some people may find it difficult to perform a proctological examination or an anoscopy because of the pain that comes with it. An anoscopy consists of examining the anus and the rectal fragment above it (8-15 cm). Another diagnostic test is signoidoscopy (especially in patients under 50, with no history of cancer). However, in other people with co-occurring rectal bleeding, a colonoscopy is recommended. It consists in examining the entire large intestine and all its parts: rectum, sigmoid colon, descending colon, transverse column, ascending colon and cecum – using a flexible speculum (up to 130 cm). During their performance, it is possible to take a sample from the diseased area, remove a lesion, e.g. a polyp.
Differentiation
It would be a mistake to treat an anal fissure that takes weeks, sometimes months, without ruling out previously a serious disease occurring higher in the intestines. This is especially true for people over 50 or for patients who have a family history of colorectal cancer. The statement that the patient certainly has an anal fissure and is bleeding from it does not exclude that he may have other diseases (e.g. he may bleed from colonic diverticula, polyps, hemorrhoids, intestinal cancer, due to inflammatory bowel diseases, vascular malformations of the large intestine). To exclude them, endoscopic examinations of the large intestine are needed, i.e. rectoscopy and colonoscopy.
Treatment of an anal fissure
Treatment of an anal fissure may be conservative (a diet rich in fiber, stool softeners, anti-inflammatory drugs and sphincter-relieving drugs). Surgical treatment is also used in justified cases (e.g. in relapses). The aim of the treatment is to reduce the tension of the internal anal sphincter, which improves the blood supply to the anoderm of the anal canal and heals defects in the mucosa.
In the case of an acute fissure and short-term symptoms, conservative treatment is usually sufficient, which lasts a few or several weeks and includes:
1. a proper diet that allows you to regularly defecate and pass soft stools,
2.appropriate hygiene of the anus,
3. use of an ointment with a medicine that relaxes the muscles of the anal sphincter. causing the anal sphincter to relax.
When an acute anal fissure fails to heal or is chronic, the next treatment step is to administer an injection in the form of botulinum toxin A (Botox) to the sphincter muscle. This method is aimed at loosening it, which lasts 2-4 months, giving a chance for the fissure to heal. Success is achieved after this procedure in 90% in cases of acute fissure and 60-70% in cases of chronic fissure treatment.
Another method is an operation involving intersection of the internal anal sphincter (a certain part of it), with the simultaneous cutting of the slit itself and stitching the resulting wound. The effectiveness of treatment is 90-95%.
Surgery it is very popular with the highest complication rate. Fecal incontinence or a lack of control over wind flow may occur in a few percent following anal fissure surgery. A few percent of complications with a 95% cure rate are few, but fecal incontinence is severe. Postoperative complications are more common in women whose effects overlap with undiagnosed perineal injuries during childbirth or pregnancy. The surgery is also associated with stress, pain and temporary exclusion from work.
It is important to undergo periodic examinations to monitor the progress of the treatment and possible change in the absence of such progress. The time of ineffective treatment added to the duration of the disease before it is started causes the crack to become “older” and the cure rate for each method decreases, and the time needed to heal is extended.
Anal fissure – complications
A complication of an anal fissure (more often in the case of a neglected or untreated fissure) may be even more serious diseases of the anus that threaten the function of the anal sphincter muscles:
- perianal fistula;
- perianal abscess.
Therefore, it is very important to see a specialist as early as possible and start treatment early, which is then simpler, more effective and allows you to avoid complications and complications. Postponing a visit to the doctor, procrastination, self-treatment, arbitrary use of medications, ointments, suppositories, in the absence of proper diagnosis and medical control, is dangerous to health and may lead to unnecessary suffering, and even disability, and endanger the patient’s health and life.
Text: SzB
The content of the medTvoiLokony website is intended to improve, not replace, the contact between the Website User and their doctor. The website is intended for informational and educational purposes only. Before following the specialist knowledge, in particular medical advice, contained on our Website, you must consult a doctor. The Administrator does not bear any consequences resulting from the use of information contained on the Website.
A proctologist in your area – make an appointment