Alkali-loving cobweb (Cortinarius alcalinophilus)
- Division: Basidiomycota (Basidiomycetes)
- Subdivision: Agaricomycotina (Agaricomycetes)
- Class: Agaricomycetes (Agaricomycetes)
- Subclass: Agaricomycetidae (Agaricomycetes)
- Order: Agaricales (Agaric or Lamellar)
- Family: Cortinariaceae (Spiderwebs)
- Genus: Cortinarius (Spiderweb)
- Type: Cortinarius alcalinophilus (Alkali-loving cobweb)
- A lightning rod (Fr.) Fr. see Moser 1838
- Cortinarius majusculus Bolder 1955
- The most brilliant curtain Reumaux 2003
- A shiny curtain Reumaux & Ramm 2003
- A strange curtain Bidaud & Eyssart. 2003
- Cortinarius xanthophylloides Reumaux 2004
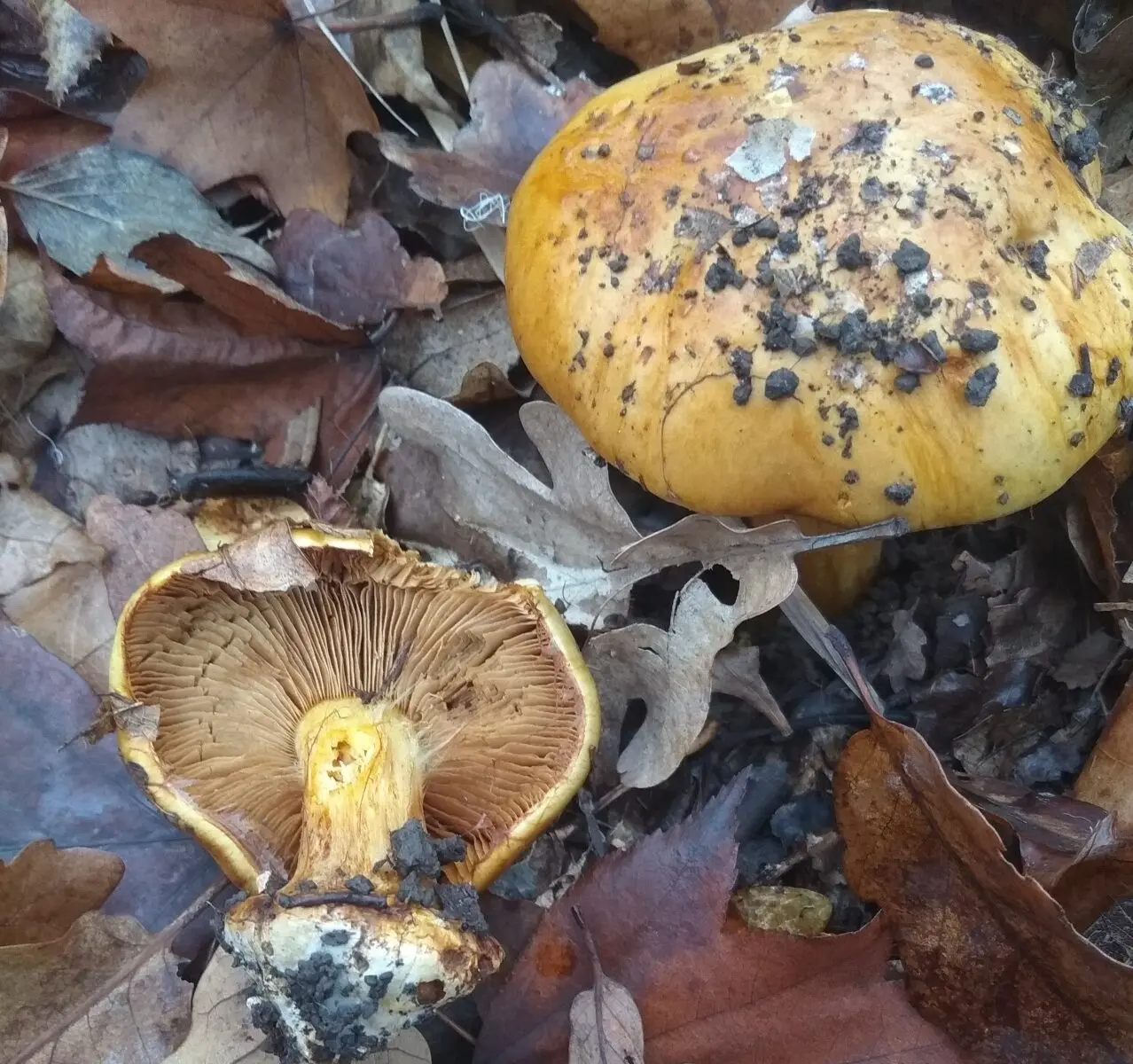

Current name: Cortinarius alcalinophilus Rob. Henry 1952
In accordance with the intrageneric classification of cobwebs after molecular phylogenetic studies, Cortinarius alcalinophilus is included in:
- Subgenus Phlegmatic
- Section Fawn
- Subsection More elegant
Etymology from cortīna (lat.) – veil. A veil caused by the characteristic remnants of a veil connecting the cap and stem. Alcalinus (lat.) – alkali, limestone, caustic and -φιλεω (Greek) – to love, to have a tendency.
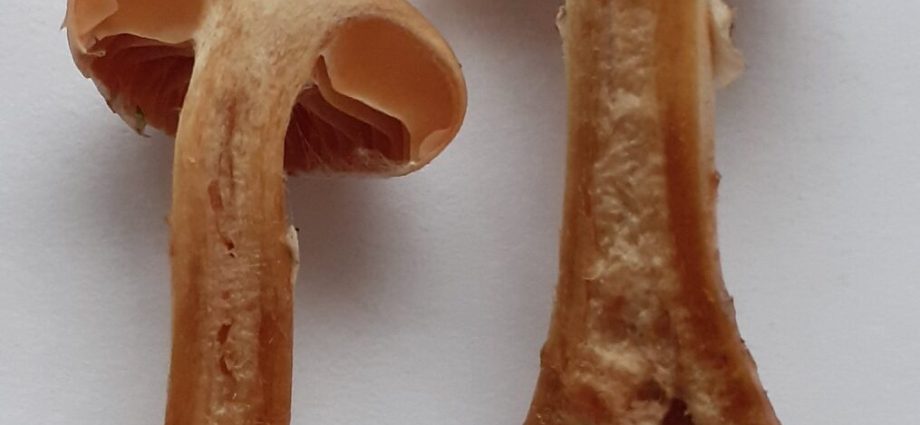
A medium-sized fruiting body is formed by a cap with a lamellar hymenophore and a stalk.
head dense, non-hygrofanous, 4-10 (14) cm in diameter, in young mushrooms it is hemispherical, convex with a tucked even edge, straightening as it grows to a flat, flat-depressed. The color is yellow, orange-yellow, ocher, in mature mushrooms it is yellow-brown, sometimes with a slight olive tint. The center of the cap is covered with light brown flat scales, while the edge is smooth and brighter, lighter.
The surface of the cap is indistinctly ingrown fibrous, sticky.
Private bedspread cobwebbed, copious, yellowish. From pale yellow to lemon.
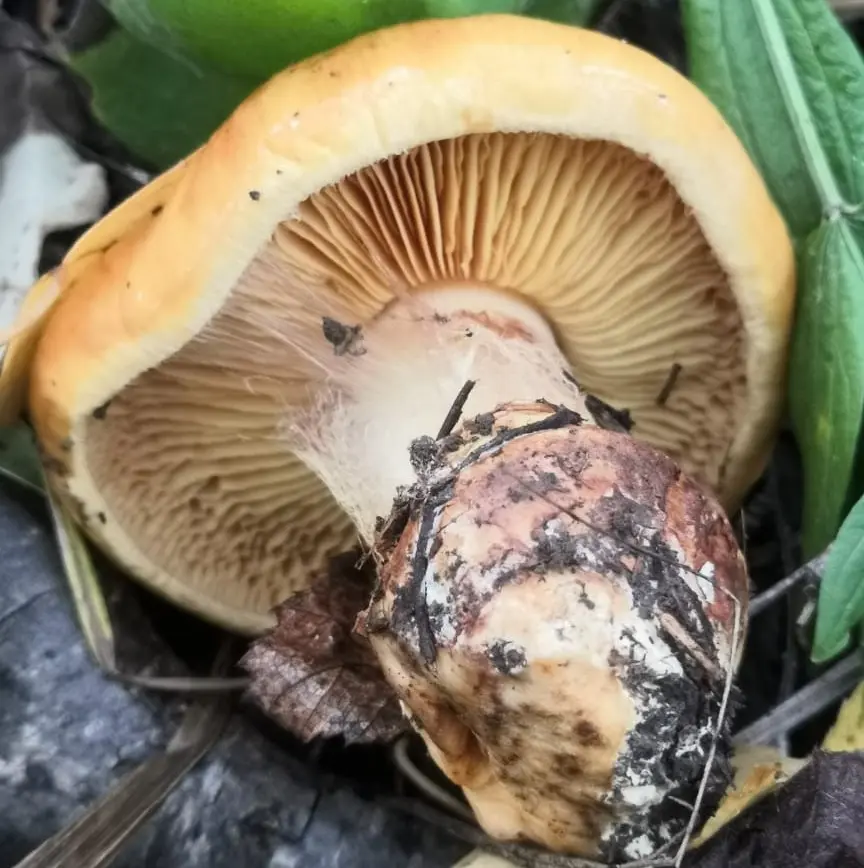

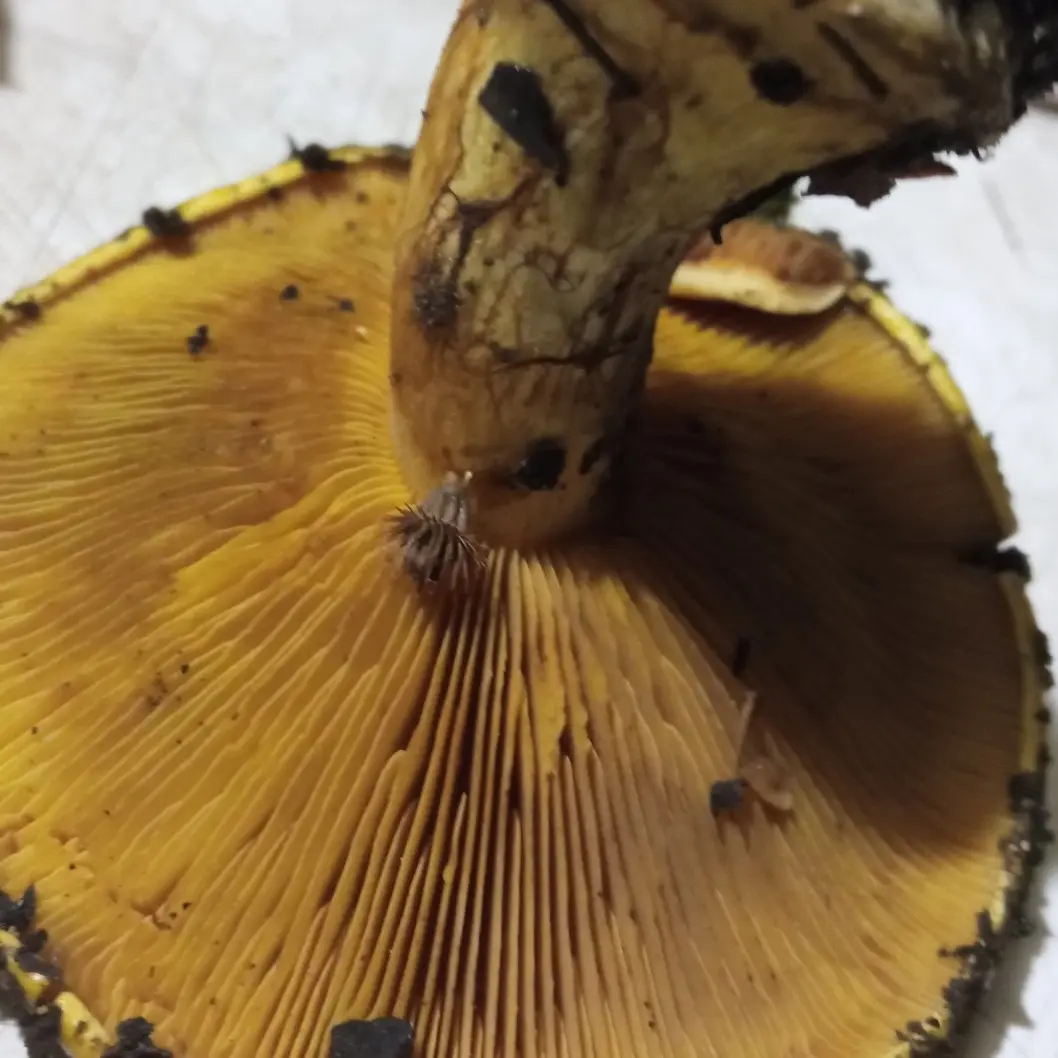
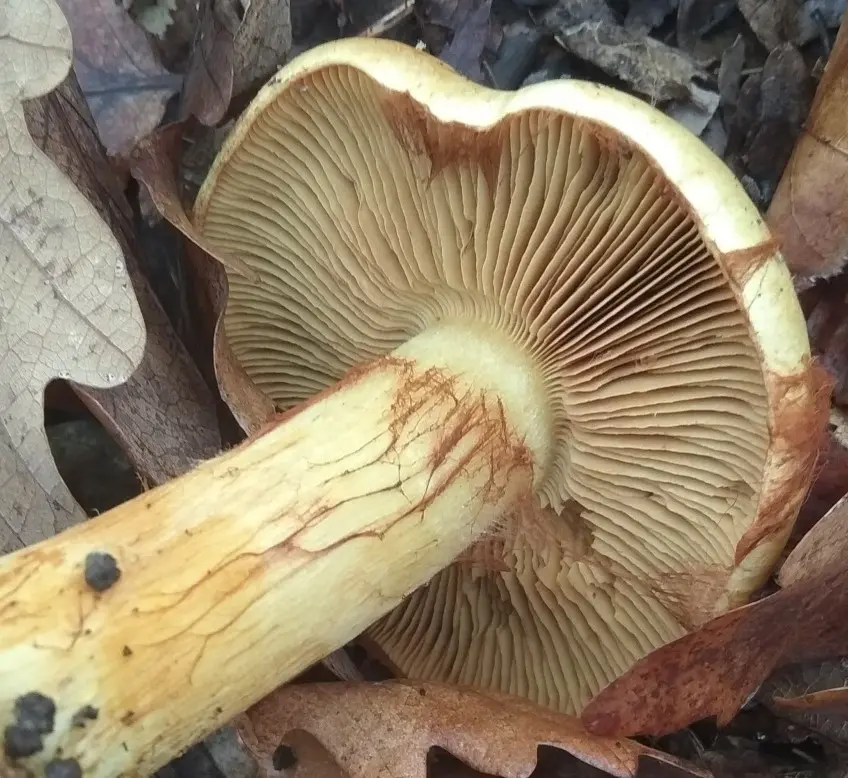
Hymenophore lamellar. The plates are narrow, rather frequent, adnate with a tooth with a notch, at first bright yellow. Darkens with age to yellow-brown, coffee-yellow.

Leg cylindrical dense, at the base with a sharply demarcated bulb, 4–10 x 1–2,5 (up to 3 in a tuber) cm, yellowish, light or yellow-buff, often with pale yellow mycelial filaments.

Pulp in the cap it is yellowish, brighter at the base of the stem (especially in the bulb), purple and lilac shades are absent, the color does not change, the smell and taste are inexpressive. Some sources indicate a sweetish and unpleasant taste.
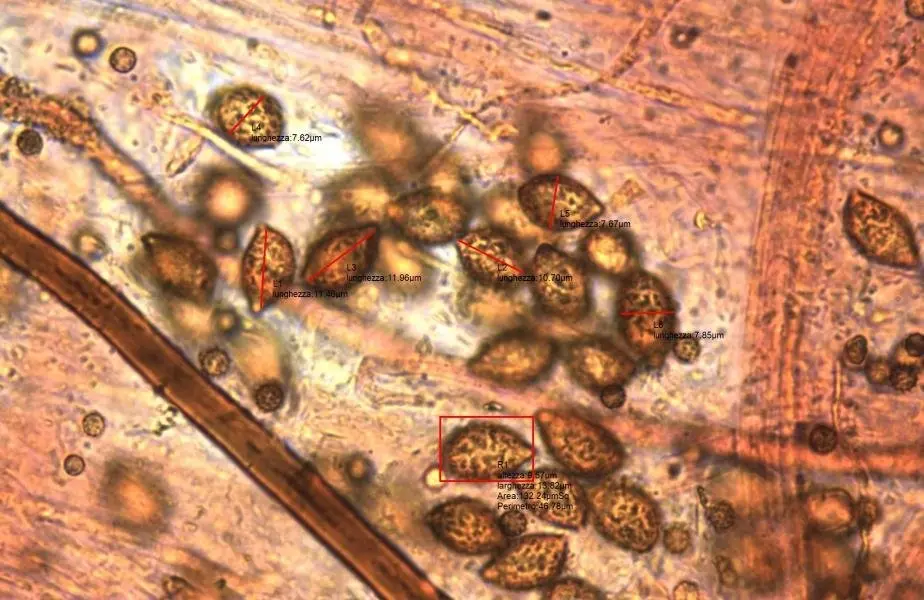
Споры almond-shaped or lemon-shaped large warty, mean values 11,2 × 7,7 µm
Chemical reactions. KOH on the surface of the cap gives a wine-red color, on the pulp – gray-pink, on the pulp of the base of the leg – red. Exicat (dried copy) does not give a red reaction.
Cortinarius alcalinophilus is a rare ectomycorrhizal fungus found in broad-leaved forests with oak, growing on soils with a high calcium content. It forms mycorrhiza, primarily with oak, but also with beech, hornbeam and hazel. Often grows in groups of several specimens of different ages. Distribution area – Western Europe, primarily France, Germany, Denmark and southern Sweden, much less common in eastern and southeastern Europe, Turkey, in Our Country – in the Stavropol Territory, the Caucasus region. In the Tula region, single finds were noted.
Finds are reported in southeastern Sweden in dry, open, treeless areas among sunflowers (helianthemum) adjacent to hazel forests.
From August to November, in more northern regions – to September.
Inedible.
As always in the genus Cortinarius, species identification is not an easy task, but Cortinarius alcalinophilus has several persistent macro-features, and the strict confinement to oak and high demands on the content of calcium in the soil, as well as characteristic chemical reactions to bases, make this task less difficult.
Паутинник пахучий has a similar reaction to KOH, but differs in a greenish color of the cap, white flesh and a characteristic smell similar to the smell of bird cherry flowers.
Black-green cobweb (Cortinarius atrovirens) has a dark olive-green to black-green cap, greenish-yellow flesh, tasteless with a slight pleasant smell, grows in coniferous forests, preferring spruce.
Eagle web (Cortinarius aquilanus) most similar. This species can be distinguished by its white flesh. In the eagle cobweb, the reaction to KOH at the cap is either neutral or light brown, at the stem it is yellow to orange-yellow, and at the bulb it is orange-brown.
Photo: from the questions in the “Qualifier”.